Surface conduction electron emission source structure and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for conduction electrons and electron emission, which is applied in the manufacture of thermionic cathodes, cathode ray tubes/electron beam tubes, circuits, etc. Low efficiency and other problems, to achieve the effect of low equipment requirements, improved field emission electron efficiency, and easy scattering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
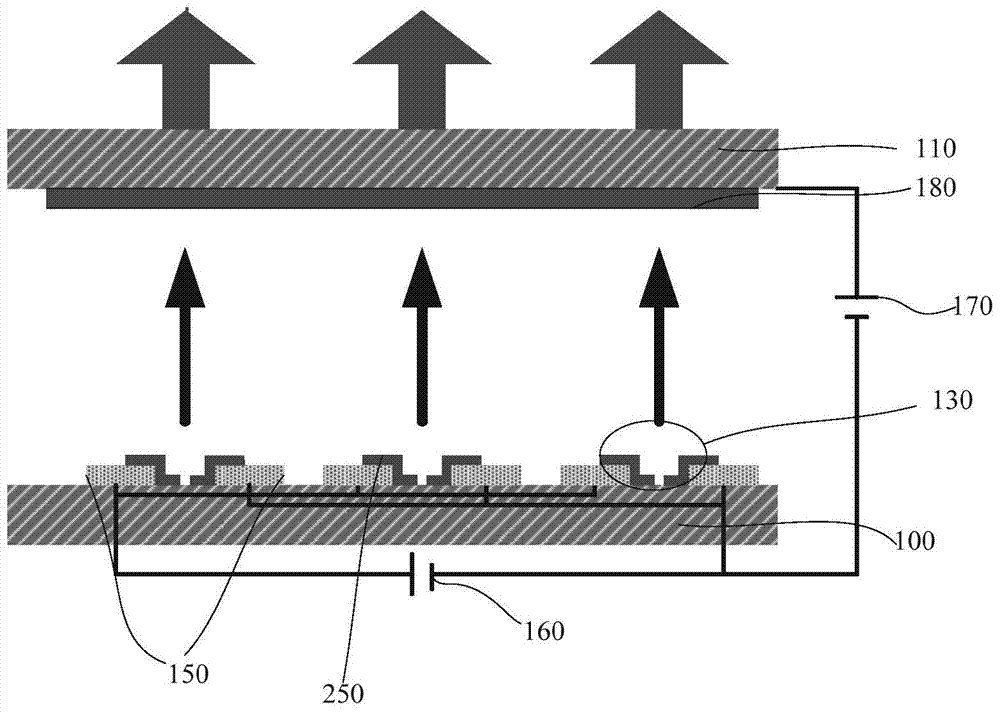
[0049] see Pic 4-1 and Figure 4-2 , a surface conduction electron emission source structure with a raised center, including two device electrodes 150, a protruding dielectric 310 and an electron emission film 250 located in the middle of the electrode gap.
[0050] The process of making this structure is:
[0051] 1) Using magnetron sputtering or other methods to sputter several groups of metal electrodes 150 on the substrate 100 to form an electrode array, the thickness of the electrodes is 100-200 nm, and there is a gap of 8-20 μm between the electrodes;
[0052] 2) Sputter a layer of protruding dielectric 310 between the device electrodes 150 with a width of 2-5 μm, a length equivalent to that of the surface conduction electron emission film 250, and a thickness of 100-150 nm between the device electrodes 150 by means of magnetron sputtering;
[0053] 3) sputtering a surface conduction electron emission film 250 between the device electrodes 150 by means of magnetron sp...
Embodiment 2
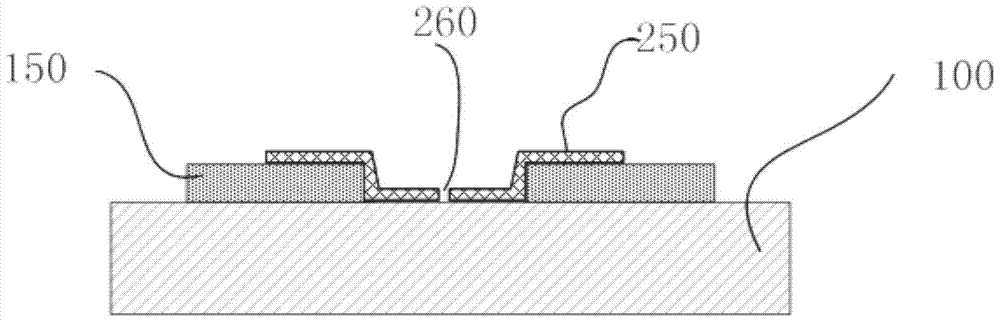
[0056] see Figure 5-1 and Figure 5-2 , a surface conduction electron emission source structure with one side raised, the structure includes two device electrodes 150, one side is connected to the electrodes, a dielectric filling layer 300 and an electron emission film 250 filling part of the gap between the electrodes.
[0057] The process of making this structure is:
[0058] 1) Using magnetron sputtering or other methods to sputter several groups of metal electrodes 150 on the substrate 100 to form an electrode array, the thickness of the electrodes is 100-200 nm, and there is a gap of 8-20 μm between the electrodes;
[0059] 2) Use magnetron sputtering or other methods to sputter a dielectric filling layer 300 with a thickness equivalent to the thickness of the electrodes between the device electrodes 150, fill the dielectric filling layer 300 with a width of 4-8 μm, one side of which is connected to one end of the electrode, and the other side in the electrode gap.
...
Embodiment 3
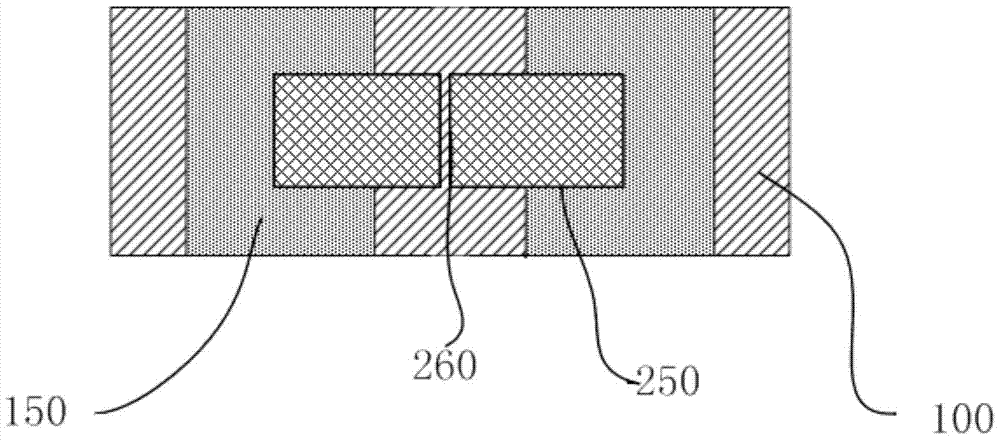
[0063] see Figure 6-1 and Figure 6-2 , a surface conduction electron emission source structure with a filled middle pad, including two device electrodes 150 , a dielectric filling layer 300 , a protruding dielectric 310 and an electron emission film 250 .
[0064] During fabrication, the dielectric filling layer 300 is fabricated first, and then the protruding dielectric 310 is fabricated. The specific fabrication steps are as follows:
[0065] 1) Using magnetron sputtering or other methods to sputter several groups of metal electrodes 150 on the substrate 100 to form an electrode array, the thickness of the electrodes is 100-200 nm, and there is a gap of 8-20 μm between the electrodes;
[0066] 2) Sputtering a dielectric filling layer 300 with a thickness equivalent to the electrode thickness between the device electrodes 150 to fill the electrode gap by magnetron sputtering or other methods;
[0067] 3) sputtering a layer of protruding dielectric 310 between the device e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com