Rock abrasiveness determination method
A measurement method and abrasive technology, applied in the direction of testing wear resistance, etc., can solve the problems of discrepancy, little guidance on the selection and use of drill bits, and no drilling depth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
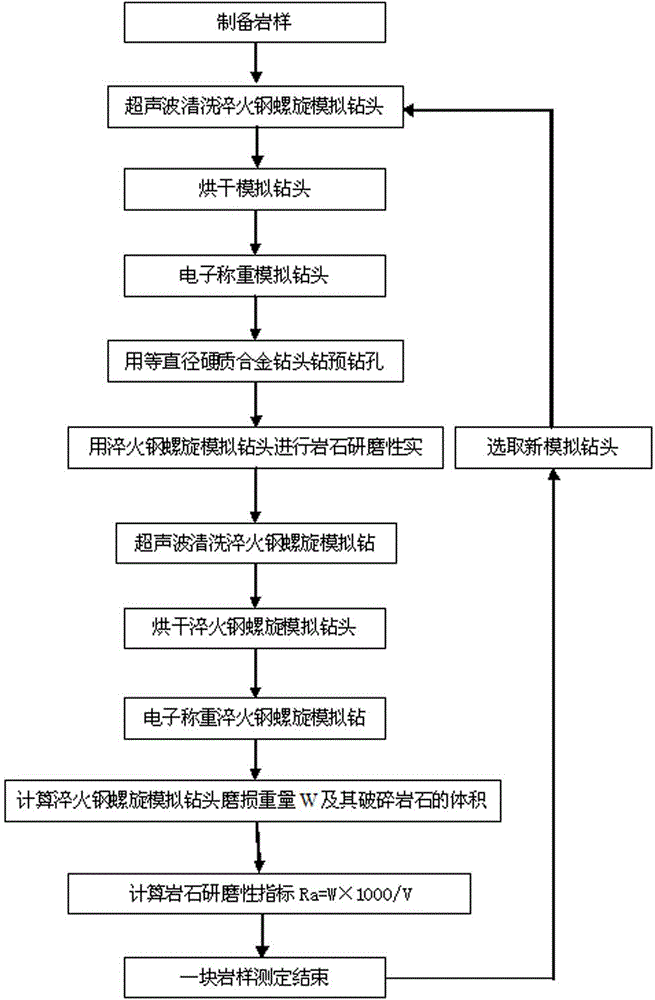
[0025] A rock abrasiveness determination method, comprising the following steps:
[0026] (1) Preparation of standard rock samples;
[0027] (2) Cleaning, drying and weighing of the hardened steel helical simulation drill bit before the experiment;
[0028] (3) Drill pre-drilled holes;
[0029] (4) Determination of rock abrasiveness;
[0030] (5) Cleaning, drying and weighing after the test of the hardened steel helical simulation drill bit;
[0031] (6) Calculation of rock abrasiveness index.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 is a further refinement of Embodiment 1. Among them: the rock sample described in step (1) needs to be parallel to the upper and lower ends, the diameter is greater than the cylindrical shape of the hardened steel helical simulation drill bit, and the height is 150-200mm; A cemented carbide drill bit with the same diameter as the simulated micro drill bit drills a hole with a depth of 10-20mm; the rock abrasiveness measurement parameters described in step (4) are the rotational speed 200 r / min, the drill pressure 500N, and record the drilled depth during the experiment; Before and after the simulated drill bit experiment described in steps (2 and 5), it needs to be cleaned and dried with an ultrasonic cleaner, and weighed with an electronic balance; the abrasiveness index R of the rock described in step (6) a It is the ratio of the wear weight W (mg) of the quenched steel helical simulated micro-drill bit to the wear volume V (mm3) of the broken rock before...
Embodiment 3
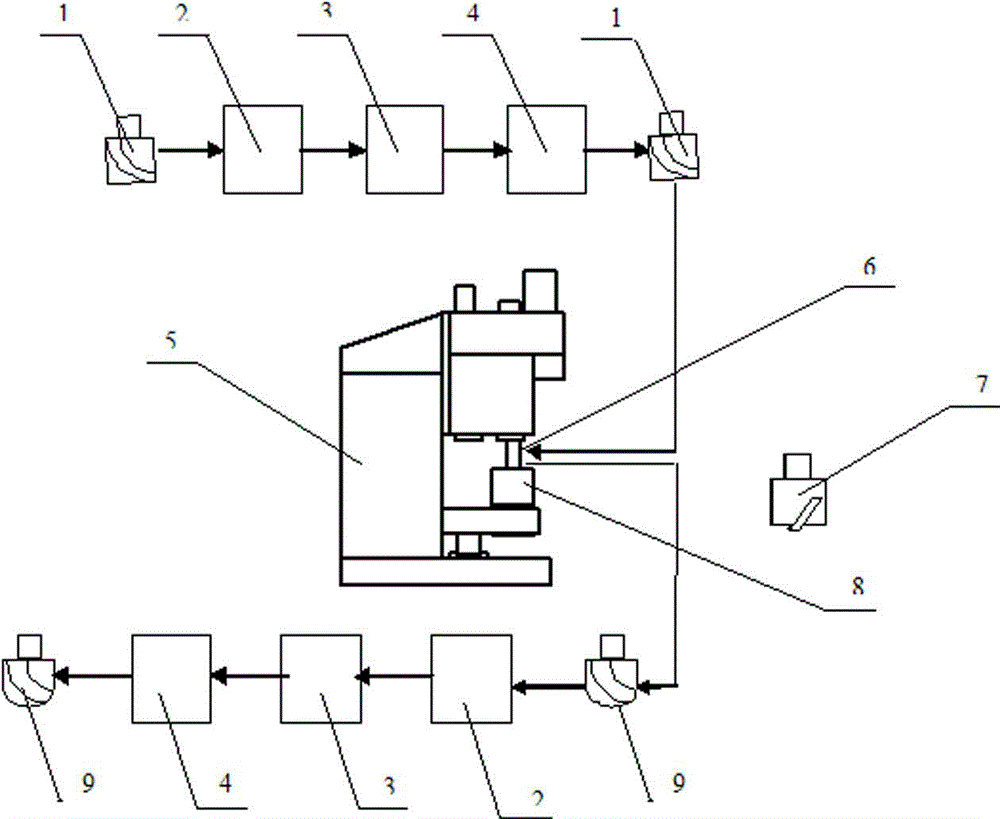
[0035] Refer to attached figure 1 and figure 2 , including the following steps:
[0036] (1) Preparation of standard rock sample 8;
[0037] (2) Wash, dry and weigh the quenched steel helical simulation drill bit 1 before the experiment;
[0038] (3) Install the cemented carbide drill bit 7 of equal diameter on the drill rod 6 to drill a 20mm pre-drilled hole;
[0039] (4) Remove the drill bit 7, and install the weighed quenched steel helical simulation drill bit 1 on the drill pipe 6 for rock abrasiveness experiments. After the experiment, record the drilling depth;
[0040] (5) Remove the hardened steel helical simulation drill bit 1 for cleaning, drying and weighing;
[0041] (6) Calculate the wear weight W of the hardened steel helical simulation drill bit 1 and the volume V of the broken rock sample 8 to obtain the abrasiveness Ra of the rock.
[0042] Further, described rock abrasiveness measuring method, in order to better simulate the actual drilling conditions, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com