Electrolytic cell for low-energy extraction of rare-earth metals
A rare earth metal, electrolytic cell technology, applied in the electrolysis process, electrolytic components and other directions, can solve the problems of increased energy consumption, the inability to collect anode gas well, and the temperature of the electrolytic cell, to reduce the amount of precipitation, reduce temperature, and reduce energy. consumption effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
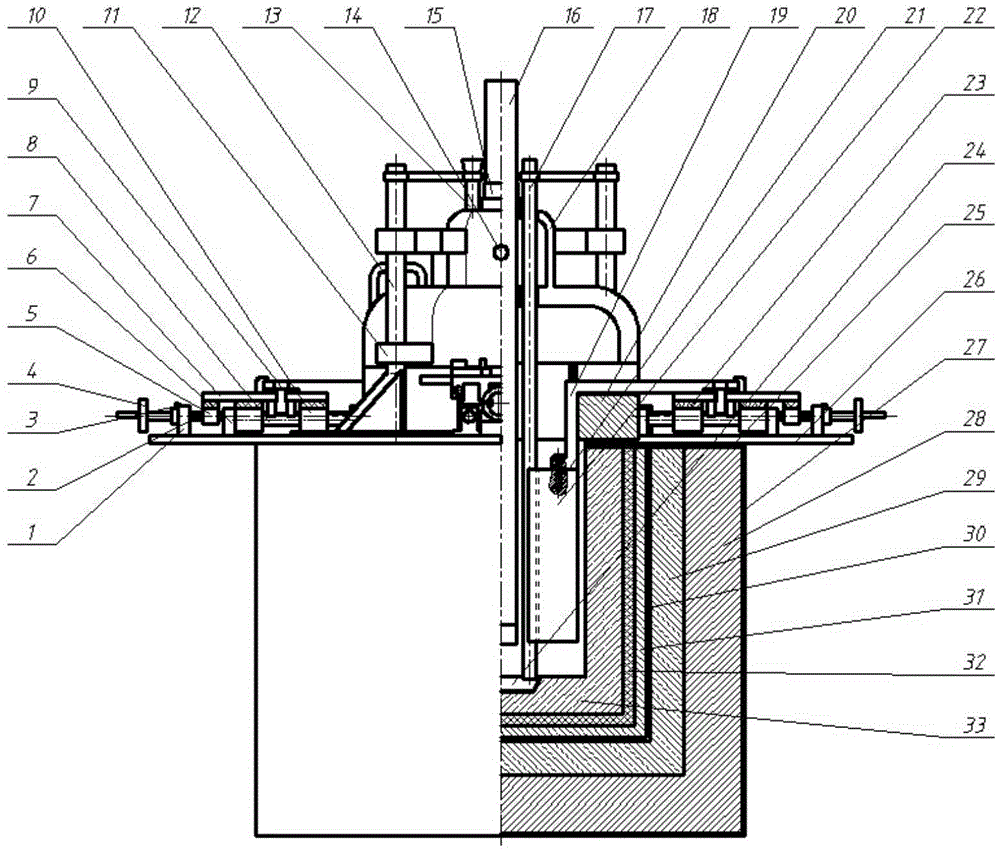
[0035] In the 4000A rare earth electrolyzer, the cylindrical graphite crucible carries the electrolyte, and the outside of the graphite crucible is a refractory and heat-insulating material, and the upper part of the electrolyzer is a cover with heat preservation and gas collection. The graphite anode is 4 equal-arc rings, and the cathode adopts an overall cylindrical shape. The distance between the cathode and anode is 5 cm, and the current densities of the cathode and anode are 3.1 A / cm 2 and 1.11A / cm 2 . During the electrolysis process, every time the graphite anode consumes 3mm, it starts to move the graphite anode to the center of the electrolytic cell by 3mm. This movement can be moved manually or automatically, thus keeping the distance between the electrodes unchanged. The electrolysis temperature was maintained at 1055°C, and the voltage of the electrolytic cell was equal to 7.2V. Rare earth metals are extracted from the electrolytic cell by differential pressure a...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In the 6000A rare earth electrolytic cell, the electrolyte is carried by a cylindrical graphite crucible, and the graphite crucible is made of refractory and thermal insulation materials, and the upper part of the electrolytic cell is a cover with thermal insulation and gas collection. The graphite anode is 4 equal-arc rings, and the cathode has a cylindrical structure as a whole. The distance between the cathode and anode is 6 cm, and the current densities of the cathode and anode are 3.6 A / cm 2 and 1.3A / cm 2 . During the electrolysis process, every time the graphite anode consumes 3mm, the graphite anode moves 3mm to the center of the electrolytic cell, thus keeping the distance between the electrodes unchanged. The molybdenum crucible with slope structure accepts rare earth metals. The electrolysis temperature was maintained at 1050°C, and the voltage of the electrolytic cell was equal to 7.6V. During the process of extracting metal and replacing the anode, the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com