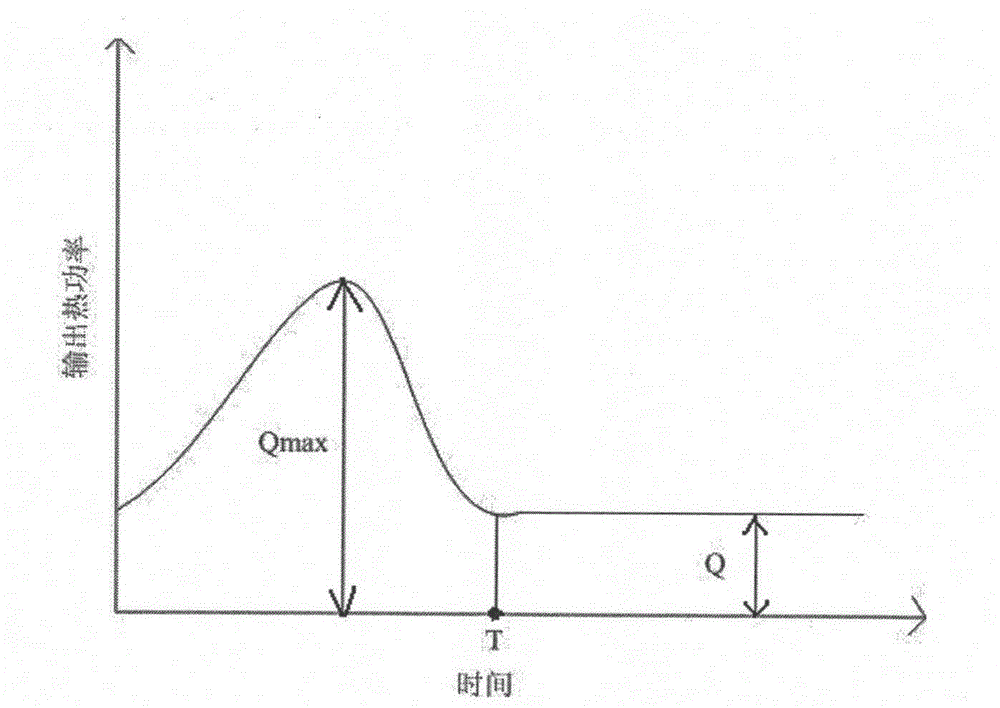
Temperature variation sensing and index calculating method of textiles
A test method and index calculation technology, applied in the direction of calculation, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unscientific and reasonable test methods and indexes of cold and warm feeling, loss of comparability, and difficulty in quantification, and achieve the scientific rigor of test methods, Control random errors and simple quantification of indicators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] 1. Sample information
[0075] Goose down quilt, process parameters: core material 90% goose down, core material weight 239.13g / m 2 ;ingredient: 100% cotton.
[0076] 2. Thermal power curve test of sample heat transfer
[0077]The instrument used is shown in the invention patent 201210587792.8, and 6 sets of heating elements are evenly distributed on the central test hot plate. The test method of thermal power curve is as follows:
[0078] (1) Sample balance: 2 samples to be tested and 1 identical preheated sample are suspended in a standard constant temperature and humidity room with a temperature of 20°C and a relative humidity of 65% for 24 hours to balance the temperature and humidity inside and outside the sample; The average index of the two samples is used as the characteristic index of the batch of samples; about 15 minutes before the test, put the balanced sample to be tested into a plastic bag and seal it, then move it into the test room, and the moving sam...
Embodiment 2
[0092] 1. Sample information
[0093] Duck down quilt, process parameters: core material 90% duck down, core material weight 58.7g / m 2 ;ingredient: 100% cotton.
[0094] 2. Thermal power curve test of sample heat transfer
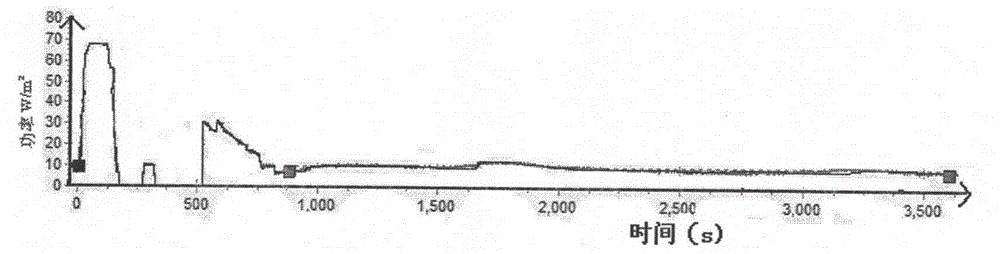
[0095] Apparatus and test method used are the same as embodiment 1, and the heat power curve that records a sample is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the thermal power curve of another sample is the same as Figure 4 similar.
[0096] 3. Calculation of coldness and warmth index
[0097] The calculation method of the coldness and warmth index is the same as that in Example 1, and each sample and its average coldness and warmth index are shown in Table 1.
[0098] 4. Test results of cold and warm feeling
[0099] The test indicators of the two samples to be tested are averaged to obtain the cold and warm characteristic indicators of the eiderdown quilt after equilibrium treatment at a temperature of 20°C and a relative humidity of 65%, as shown in the la...
Embodiment 3
[0103] 1. Sample information
[0104] Old quilts, process parameters: core material 100% cotton, core material weight 600g / m 2 ;ingredient: 100% cotton.
[0105] 2. Thermal power curve test of sample heat transfer
[0106] Apparatus or test method used are the same as embodiment 1, and the heat power curve that records a sample is as follows Figure 7 As shown, the thermal power curve of another sample to be tested is the same as Figure 7 similar.
[0107] 3. Calculation of coldness and warmth index
[0108] The calculation method of the coldness and warmth index is the same as that in Example 1, and each sample and its average coldness and warmth index are shown in Table 2.
[0109] 4. Test results of cold and warm feeling
[0110] Average the test indexes of the two samples to obtain the cold and warm characteristic index of the old cotton quilt after balanced treatment at a temperature of 20°C and a relative humidity of 65%, as shown in the last row of Table 2.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com