Method for Optimizing Differential Cylindrical Image Motion LiDAR
A lidar and beam technology, applied in the field of optimizing differential beam image motion lidar, can solve problems such as the inability to detect the average tilt of the wavefront, and achieve the effect of improving data quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
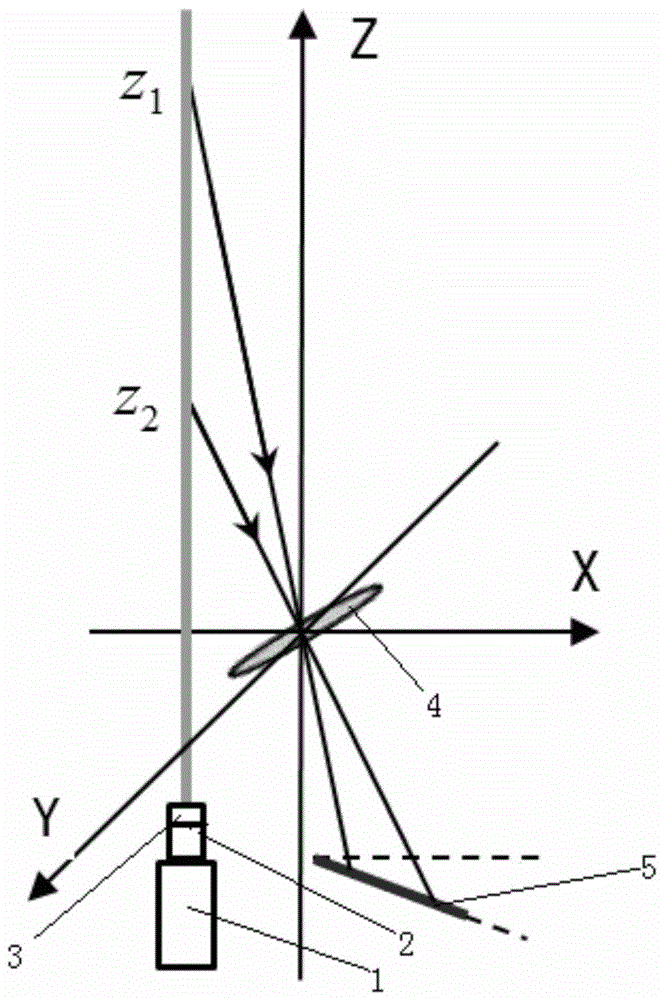
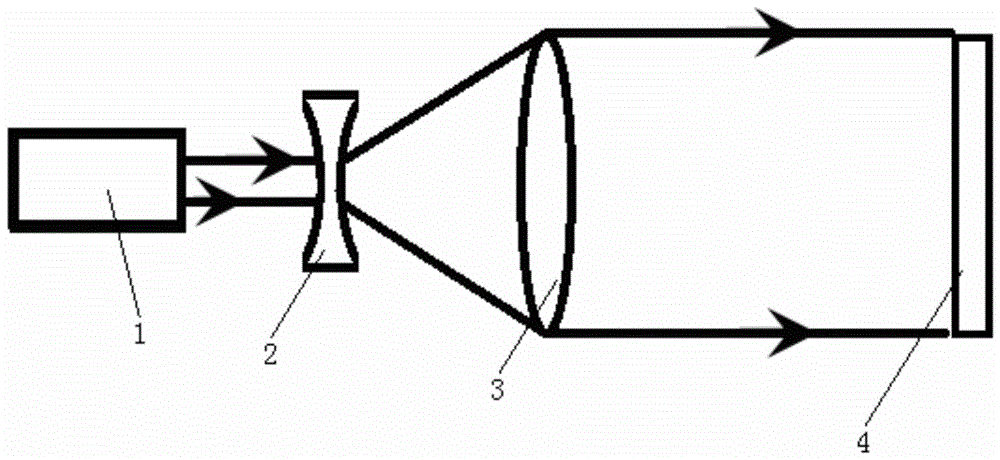
[0011] A method for optimizing differential beam image movement lidar, including a laser 1, a beam expander 2, a convex lens 3 and a receiving telescope 4, the laser light emitted by the laser 1 passes through the beam expander 2 and the convex lens 3 in sequence, and then is received by the receiving telescope 4 Receiving, the front side of the main mirror of the receiving telescope 4 is provided with a block 6, and four sub-apertures 7 are arranged on the block 6, the centers of the four sub-apertures 7 are four points of a square, and a pair of squares The diagonal line is parallel to the vertical plane of the system where the laser 1 emits and receives the telescope 4, and the other diagonal line is perpendicular to the vertical plane of the system. Two kinds of wedge angles are installed on the front side of the four sub-holes 7 diameters. The wedge angle directions of the four wedge mirrors are all perpendicular to the vertical plane of the system, and the angle between t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com