Method and preparation for preventing mycoplasma hyorhinis from infecting cells
A technology of Mycoplasma hyorrhinosus and cells, which is applied in the directions of medical preparations, antibodies, and antibacterial drugs containing active ingredients, can solve the problems of lack of specificity in preventing Mycoplasma hyorrhinosus infecting cells, and the molecular mechanism of Mycoplasma hyorrhinosus infecting cells is not clear. The effect of preventing the infection of cells by Mycoplasma hyorhinosa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
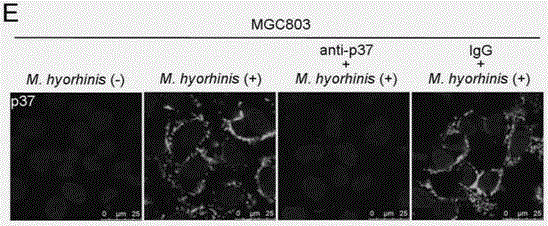
[0060] Example 1, Mycoplasma hyorhinois infection of mammalian cells depends on its surface membrane protein p37
[0061] In this example, it was confirmed by common cell ELISA experiments reported in literature that both Mycoplasma hyorhinosus and p37 protein can bind to cells respectively.
[0062] Cell ELISA experiments first inoculated gastric cancer cells MGC803 and AGS (these cells were from the tumor cell bank of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences) in 96-well plates and cultured them for 48 hours, and then added 1ⅹ10 3 CCU, 1ⅹ10 4 CCU, 1ⅹ10 5 CCU / mL of M. hyorhini to infect cells. After the infection lasted for 24 hours, wash with PBS three times, fix with 0.4% glutaraldehyde at room temperature for 10 minutes, and block with 5% milk powder / PBST at room temperature for 2 hours, and then add anti-Mycoplasma hyorhini antibody, enzyme-labeled secondary antibody and substrate solution in sequence, Finally, measure OD with ELISA READER 492nm . Higher readings indic...
Embodiment 2
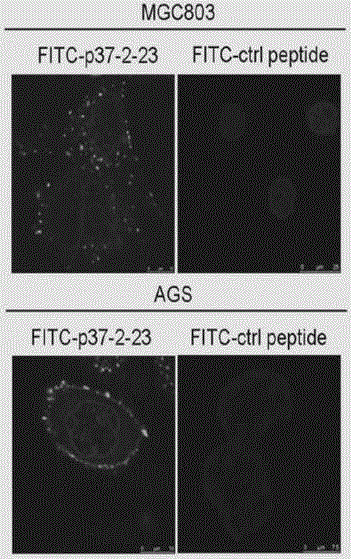
[0072] Example 2, N-terminal polypeptide of p37 blocks mycoplasma infected cells
[0073] The amino-terminal sequence of p37 (the 2nd to 23rd amino acid sequence of the p37 protein sequence, denoted as p37-2-23: LKKLKNFILFSSIFSPIAFAIS, SEQ ID No.1) is unique to Mycoplasma hyorhina, while in other types of Mycoplasma Does not exist (Dudler R, Schmidhauser C, Parish RW, et al. A mycoplasma high-affinity transport system and the in vitro invasiveness of mouse sarcoma cells. (1988) The EMBO Journal 7, 3963-3970).
[0074] In order to explore the role played by the amino terminal of p37 in mediating the infection of cells by Mycoplasma hyorhina, in this example, GST fusion protein was used to detect its binding to cells by ELISA. It was found that the amino-terminal polypeptide fusion protein (GST-p37-2-23) expressed by prokaryotic recombinant expression could bind to gastric cancer cell lines in a time- and concentration-gradient dependent manner, while the p37 protein lacking the...
Embodiment 3
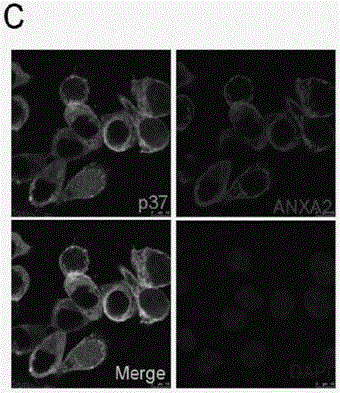
[0079] Example 3, p37 protein and host ANXA2 protein interact through the amino terminal respectively
[0080] In order to find host cell surface receptor molecules that interact with p37, this example first enriches the p37-interacting proteins in the cell lysate by GST pull-down technology, and then finds them out by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie brilliant blue staining. difference band ( Figure 3A Indicated by the arrow in the middle), the band was identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and the polypeptide fragment was found to be the Annexin A2 sequence ( Figure 3A ), indicating that the interacting protein of p37 is Annexin A2 (hereinafter referred to as ANXA2).
[0081] In order to verify that there is an interaction between p37 and Annexin A2, in this example, p37 and ANXA2 antibodies (the antibody was purchased from Novus Biotechnology) were also used to pass the conventional two-way co-immunoprecipitation experiment, and the results showed that immunoprecipitation wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com