A method and system for individual identification and paternity identification of unknown specimens
A technology of paternity identification and material inspection, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, etc. It can solve the problems that cannot meet the requirements of forensic DNA rapid inspection and on-site inspection ability, shorten the detection time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
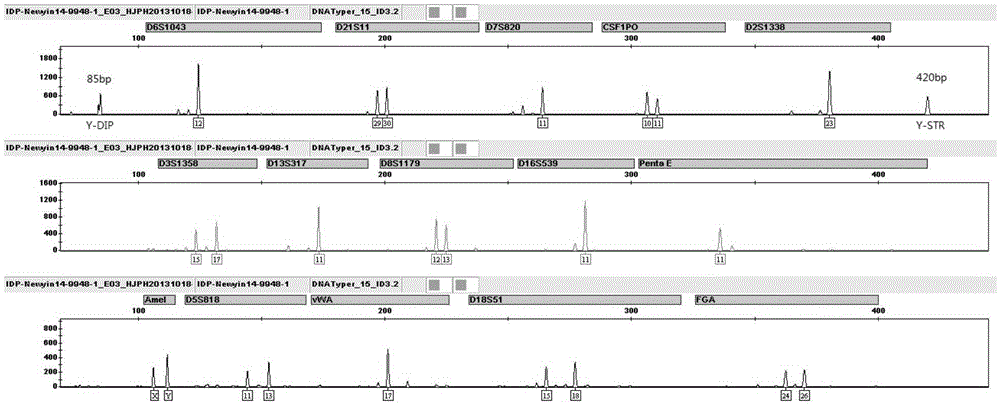
[0058] Example 1. Verification of the accuracy of the method and system for individual identification and paternity identification of unknown specimens of the present invention
[0059] In this example, the unknown specimens are 120 human fresh anticoagulated blood samples (60 males and 60 females). These specimens are samples collected by the applicant from Zhongguancun Community Hospital in Beijing, and their individual sources are known. , but in the implementation process of Example 1 of the present application, its individual source is assumed to be unknown, and the method and system of the present application are used to carry out individual identification and paternity identification, including:
[0060] 1) Utilize the DNA extraction system in the system of the present invention to extract the DNA of unknown specimens, 2) Utilize the composite detection system in the system of the present invention to obtain the DNA including 14 autosomal STR loci and 2 Y chromosome loci...
Embodiment 2
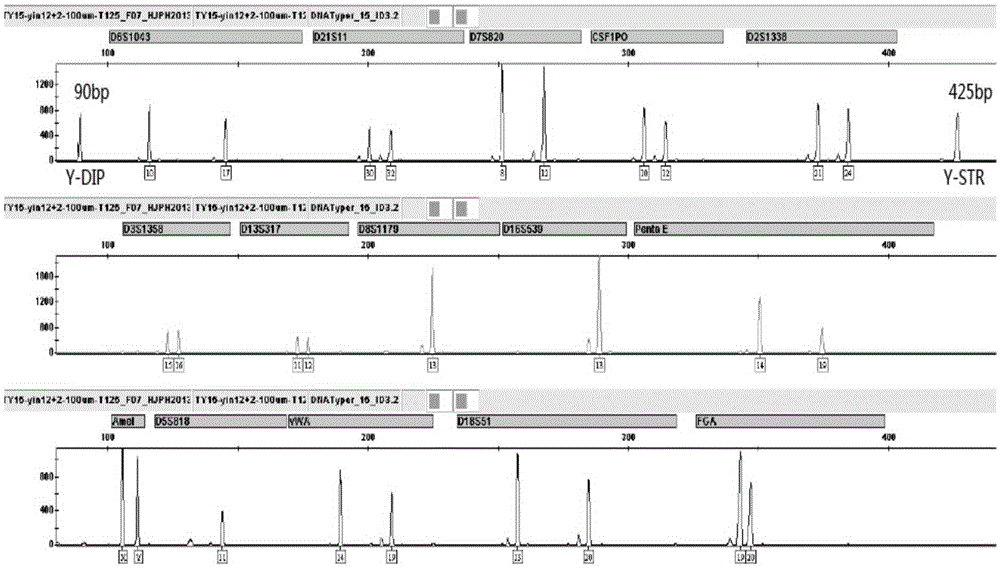
[0082] Example 2 Comparison of the system of the present invention for individual identification and paternity identification of unknown specimens with existing kits for individual identification
[0083] 120 parts of DNA samples in Example 1 were used to type 17 loci with the system of the present application (the typing process was the same as in Example 1, the difference being that the number of cycles of the amplification process was 28), while using the existing DNATyper15 TMThe kit (i.e. the conventional detection system) performs typing on the autosomal locus of the above samples (using the parameters of the kit itself), and the typing result is used as the positive control of the autosomal locus, Yfiler TM The kit performs typing on the Y chromosome locus (using the kit’s own parameters), and the typing result is used as a positive control for the Y chromosome locus, and a blank reagent is set as a negative control, and repeated 3 times in parallel.
[0084] The DNA t...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Embodiment 3 The sensitivity of the method and system result of the present invention
[0090] Get standard DNA sample 2ng, 1ng, 0.75ng, 0.5ng, 0.25ng, 0.125ng respectively, amplify and detect according to the method provided by the present invention, repeat 3 times in parallel, the result is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0091] The results are shown in Table 4. It can be seen that the optimal amount of DNA template in the method of the present invention is between 0.5 and 2 ng. For samples with a DNA concentration greater than 0.5 ng / μL, the detection rate can reach 100%, which is slightly lower than the detection line. It is lower than the detection level of the STR detection kit (0.125ng) commonly used in the field of forensic science, but the amplification time of about 1 hour is significantly shorter than these conventional kits, which usually require about 3 hours of amplification time.
[0092] Table 4 DNA test results of sensitivity verification
[0093]
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com