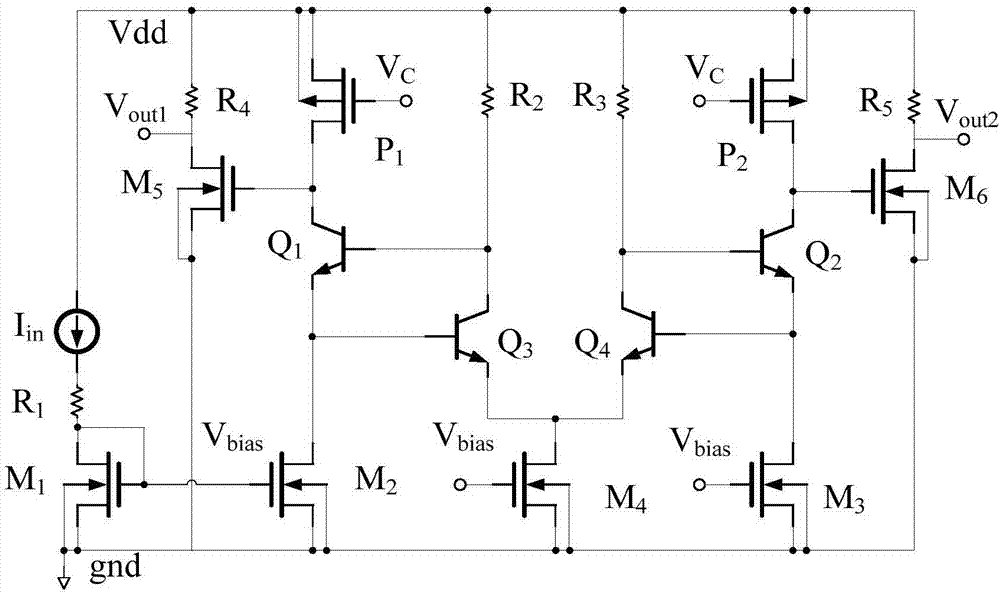
A High Gain Low Noise Differential Transimpedance Amplifier
A transimpedance amplifier and low-noise technology, applied in the field of high-gain, low-noise differential transimpedance amplifiers, can solve problems such as small bandwidth, high noise, and insufficient gain, and achieve fewer tubes, reduced power consumption, and reduced chip area Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and advantages to be solved by the present invention clearer, the following will describe in detail with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
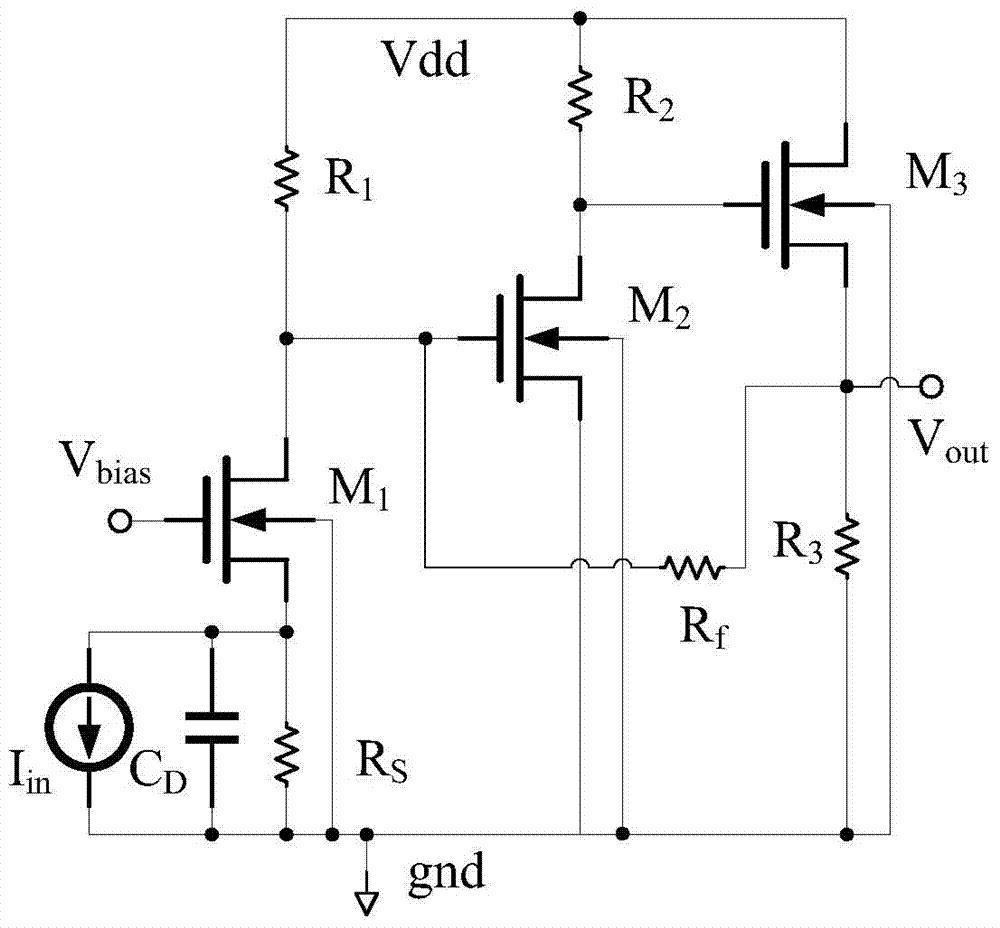
[0045] Such as figure 2 Shown is the circuit diagram of the RGC (Regulated-Cascade, adjusted cascode) transimpedance amplifier.
[0046] exist figure 2 Among them, Vdd is the power supply voltage, gnd is the ground terminal, I in is the input current signal, C D is the photodetector parasitic capacitance, V out is the output voltage signal;
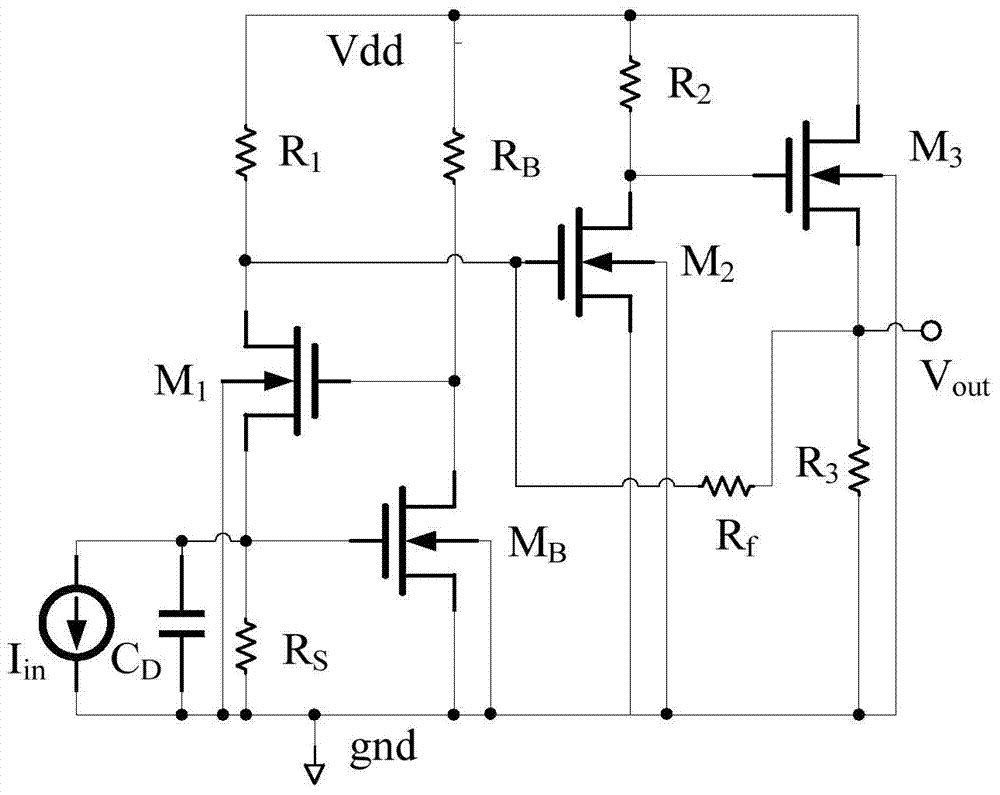
[0047] and figure 1 Compared with the current-mode form transimpedance amplifier structure shown, figure 2 The RGC transimpedance amplifier shown adds the NMOS transistor M B and resistor R B A common source amplifier is used as a negative feedback path, and the NMOS transistor M 1 Provide bias voltage; if M 1 The drain-source current increases, the resistor R S The voltage drop increases, that is, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com