Primer-free gene synthesis method
A gene synthesis and gene technology, applied in the field of library-based primer-free gene synthesis, can solve the problems of high synthesis cost, high error rate, and reduced error rate, and achieve the effects of high splicing accuracy, low synthesis cost, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1 constructs pNew carrier plasmid
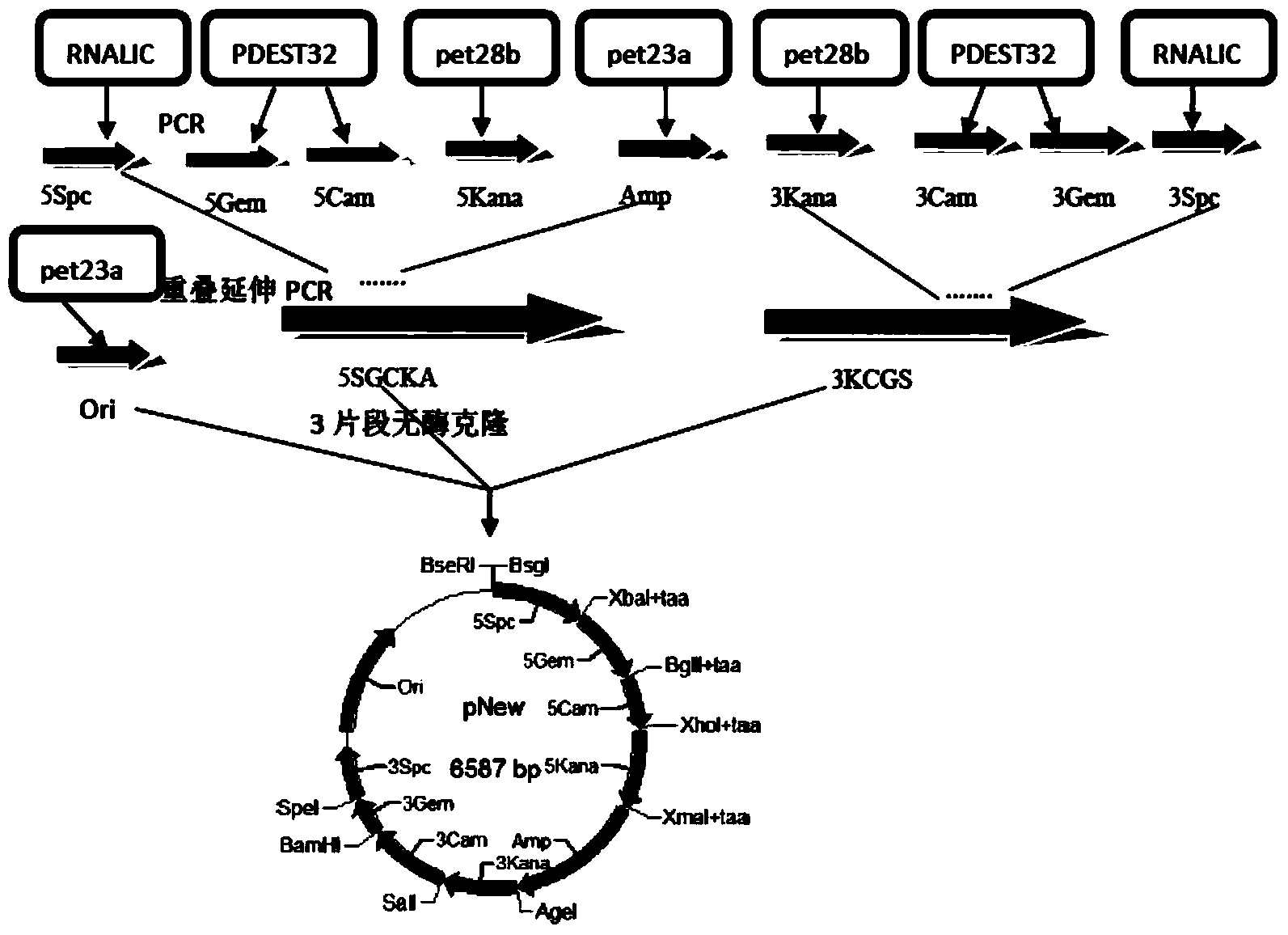
[0049] 1. Construct the linear vector backbone pNew
[0050] Using the commercialized vector pet23a plasmid as a template and ori-PF / ori-PR as primers (see Table 1 for the sequence), the linear vector backbone pNew (1.9kb) was obtained by PCR amplification (its nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO. 21), the recognition site of restriction endonuclease BseRI was introduced by primer ori-PR in the PCR process.
[0051] 2. Construction of large fragment 5SGCK
[0052] Design primer 5Spc-PF / 5Spc-PR (sequence is shown in Table 1), take RNALIC plasmid as template, obtain 5Spc fragment (656bp) (its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.22) by PCR amplification, amplify The 5' and 3' ends of the good 5Spc fragments were respectively equipped with restriction enzyme sites BsgI and XbaI; design primers 5Gem-PF / 5Gem-PR (see Table 1 for the sequence), and use the pDEST32 plasmid as a template to amplify by PCR The 5Gem fragment (535...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Synthesis of embodiment 2 target gene
[0061] 1. Construction of plasmid library
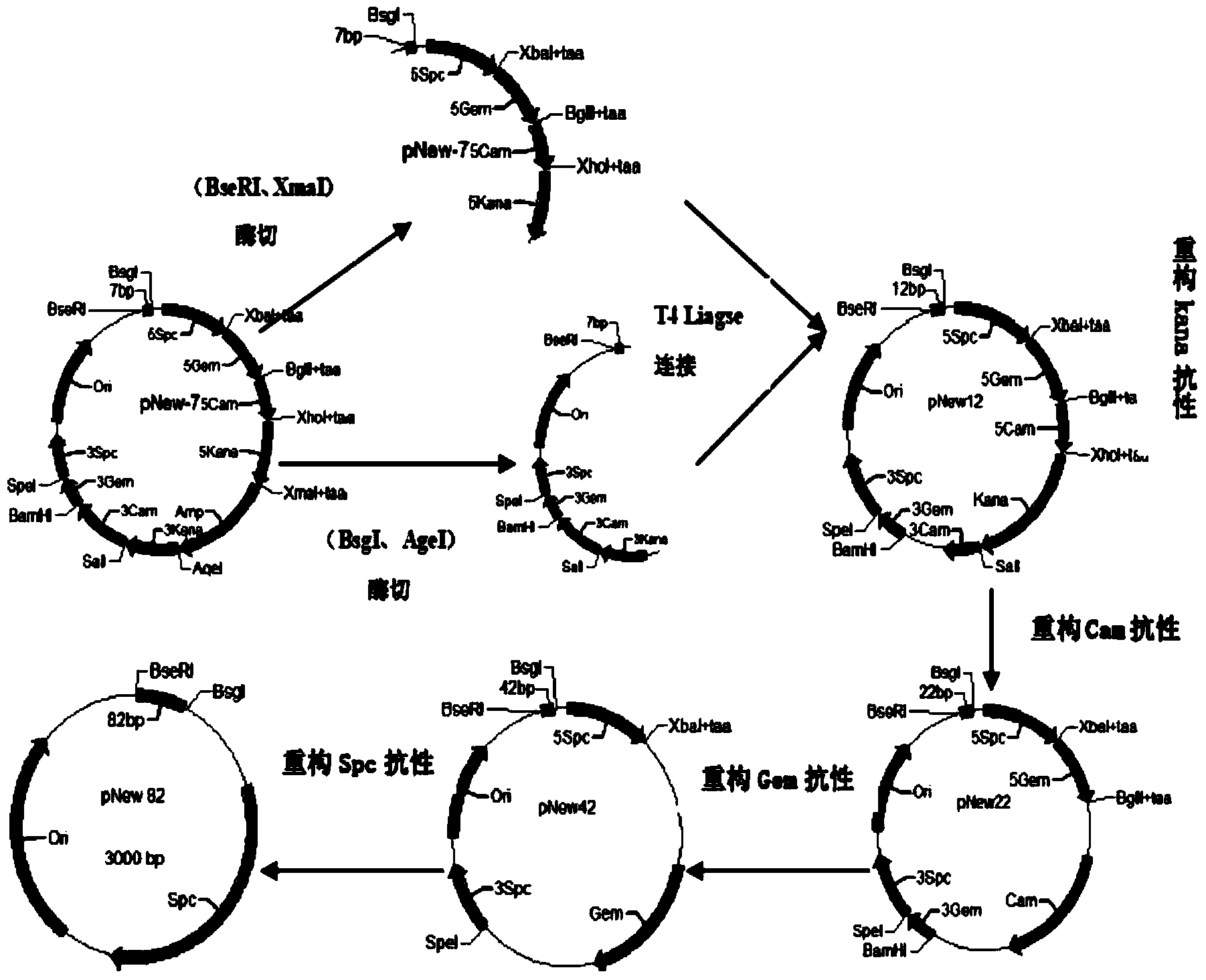
[0062] The pNew vector constructed in Example 1 was constructed by conventional construction methods of PCR, reverse amplification vector, and enzyme-free cloning 4 7 (16384) kinds of plasmid libraries, each plasmid in the plasmid library randomly contains any permutation and combination sequence of 7 base pairs.
[0063] 2. Analysis and grouping of target genes
[0064] Select the target gene X to be synthesized, divide the pre-synthesized target gene DNA sequence according to 82bp of each fragment, and name each fragment G1, G2, G3, G4, G5..., between each fragment There are 3 base repeats.
[0065] 3. Library plasmid search
[0066] According to the one-to-one correspondence between the sequences of small fragments such as G1 and G2 and the corresponding numbers of the plasmids, find the corresponding plasmids in the established 7bp plasmid library, and each 82bp fragment requires...
experiment example 1
[0074] The gene synthesis of experimental example 1 avidin (avidin)
[0075] A gene fragment of avidin derived from chicken (G. gallus) was synthesized by using the gene synthesis method of the present invention.
[0076] The synthesis process of avidin includes the following steps:
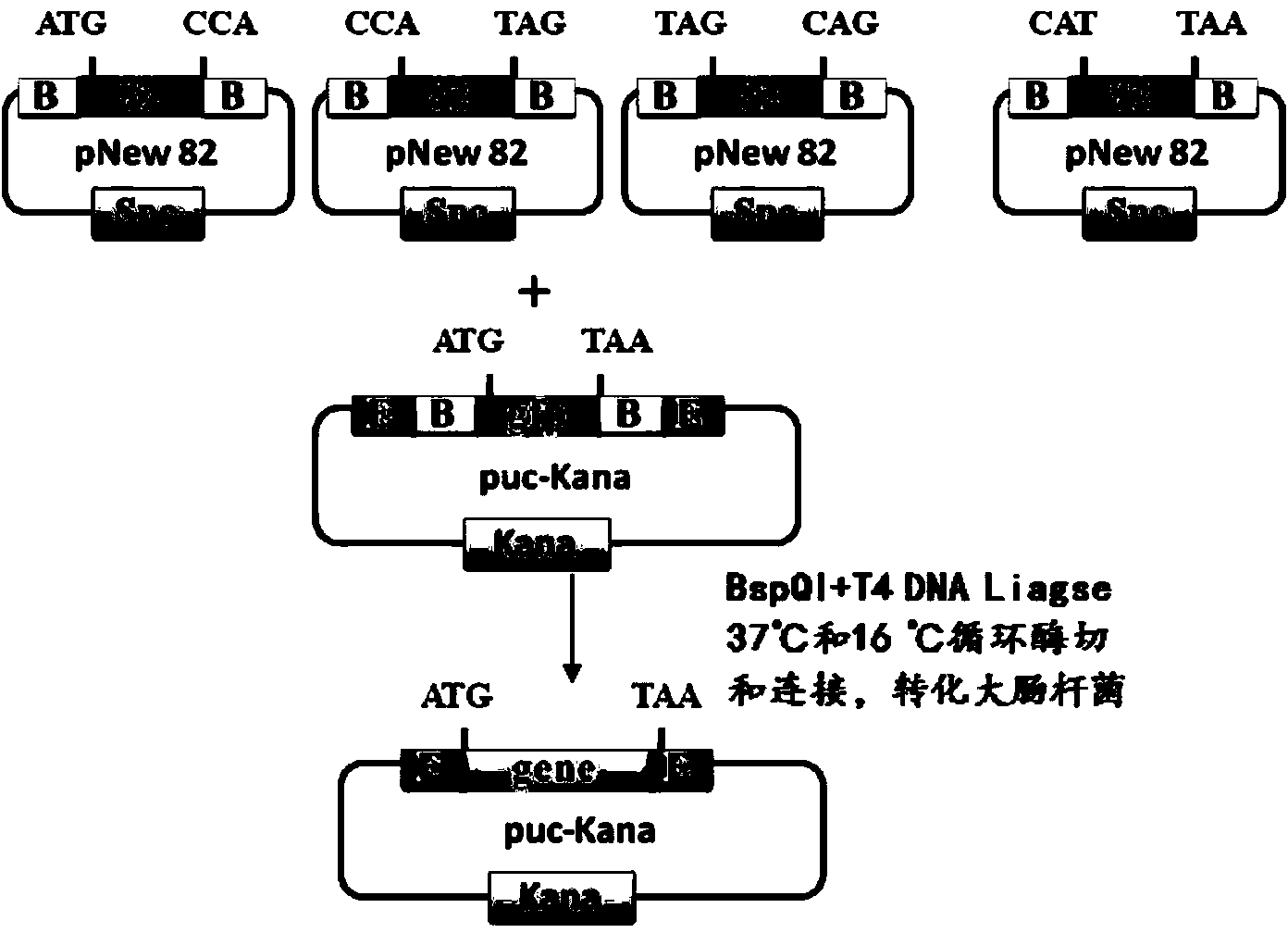
[0077] (1) The commercially available puc-19 plasmid and pGSilG-Lic plasmid (purchased from Invitrogen) were used to construct the puc-Kana plasmid vector by conventional methods such as PCR, nested PCR, and enzyme-free cloning.
[0078] (2) Divide the base sequence (438bp) of the target gene avidin into 6 segments, and each segment is named AV1, AV2, ... AV6, each of the first 5 segments is 82bp, and the sixth segment is 42bp. Then, find out the corresponding plasmids in the constructed 16384 7bp plasmid libraries, each 82bp fragment needs 16 plasmids, and each 42bp fragment needs 8 plasmids.
[0079] (3) The 16 plasmids found in each group are grouped in pairs and named A1\B1, A2\B2...A8\B8. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com