Grape herbicide composition and using method thereof
A technology of herbicides and compositions, applied in the field of grape herbicide compositions, can solve the problems of phytotoxicity that sometimes occurs, fails to get a good answer, and cannot completely solve the problems of weed damage, and achieves a significant composite effect, The effect of reducing the labor intensity of pesticide application and facilitating promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0049] Example 1: Gramineae weed control experiment, time April 10, 2010.
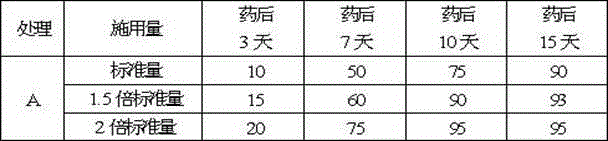
[0050] Because grapes are broad-leaved plants, we began to use herbicide A for weeding experiments in view of the prominent characteristics of grass weeds in grape planting bases. Select a place where weeds grow vigorously and with high density as the test plot, and each test plot has an area of 1 square meter. The dosage standard used is: 6.5 grams / 667 square meters, and set the lowest amount (ie standard amount), middle amount (1.5 times the standard amount), and the highest amount (2 times the standard amount) three plans, spraying includes all grapes plant.
[0051] A Grape weed control effect (dead weeds / total weeds%) is as follows:
[0052]
[0053] The test shows that: A has a good herbicidal effect, and symptoms of phytotoxicity begin to appear within 5 days of application, and the new leaves turn green and purple to yellow within 7 to 10 days, and the leaves other than the new lea...
example 2
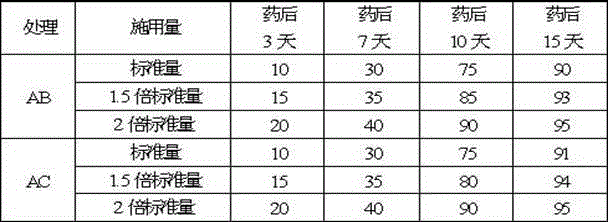
[0054] Example 2: Comprehensive use of herbicides to control grass weeds, from 2011 to 2014.
[0055] On the basis of the herbicide test in 2010, do a good job in the chemical weeding work in the grape production base. Every year in spring and autumn, we use herbicide A to control grass weeds according to the growth of weeds. For the grass with 5 true leaves, the dosage is the standard amount per mu of the above-mentioned experimental design, that is, 6.5 grams of active ingredient A is used per mu. If the weeds are large, the dosage is 1.5 times the standard dosage per mu. Add 5 grams of agricultural arm organic silicon synergist per barrel, mix and use now, use a backpack sprayer to spray evenly, the weed control has achieved the expected effect, the grapes are highly selective, and the growth condition is good.
example 3
[0056] Example 3: In 2013, a phytotoxicity test was carried out using herbicides for controlling broad-leaved grasses and sedge weeds.
[0057] There are a lot of broad-leaved weeds growing on the ground of the viticulture experiment, especially a variety of malignant weeds such as spinosa and three-edge grass. Grapes are also broad-leaved plants. If you use herbicides to control broad-leaved weeds, there are certain risks. In one case, the grapes may cause death or serious injury due to phytotoxicity, and in the other case, the grapes show drug resistance. This makes the herbicide less toxic. Both cases fit the broadleaf herbicide profile.
[0058] In order to verify the resistance of grapes to herbicides and reduce losses and blindness, the target crops selected from the existing herbicides are suitable for grass crops and broad-leaved crops, and have higher resistance to crops with higher glucose content. Herbicides are tested. Experiment with single potted grapes to r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com