Field emission electron source and preparation method thereof
An electron source and field emission technology, applied in the field of field emission, can solve problems such as low emission efficiency and affecting imaging quality, and achieve the effects of simple preparation process, overcoming interface potential barrier, and controllable aspect ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
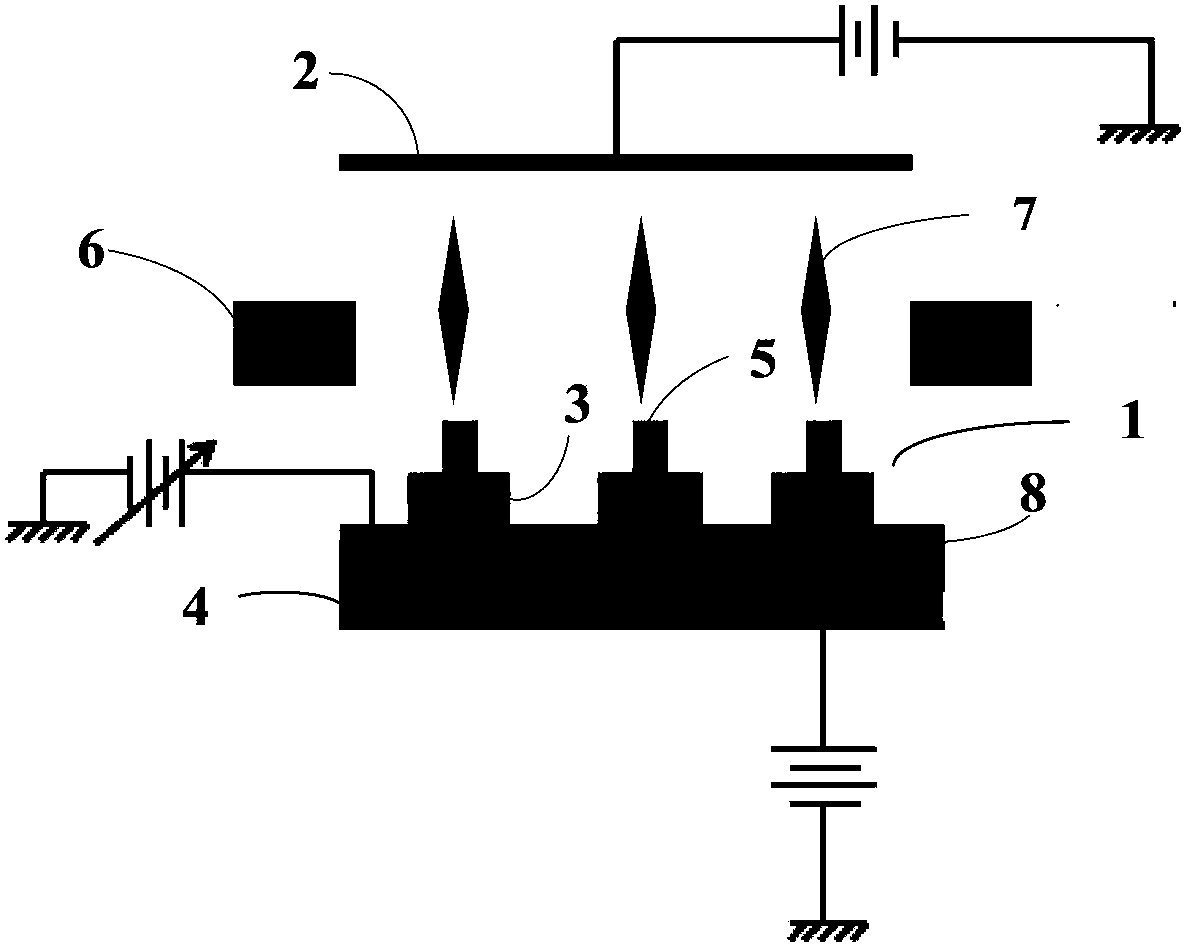
[0040] In order to solve the above technical problems, the present invention also provides a preparation method of a field emission electron source, Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram of the preparation process of the field emission electron source of the present invention. See Figure 9 , a method for preparing a field emission electron source, comprising the steps of:
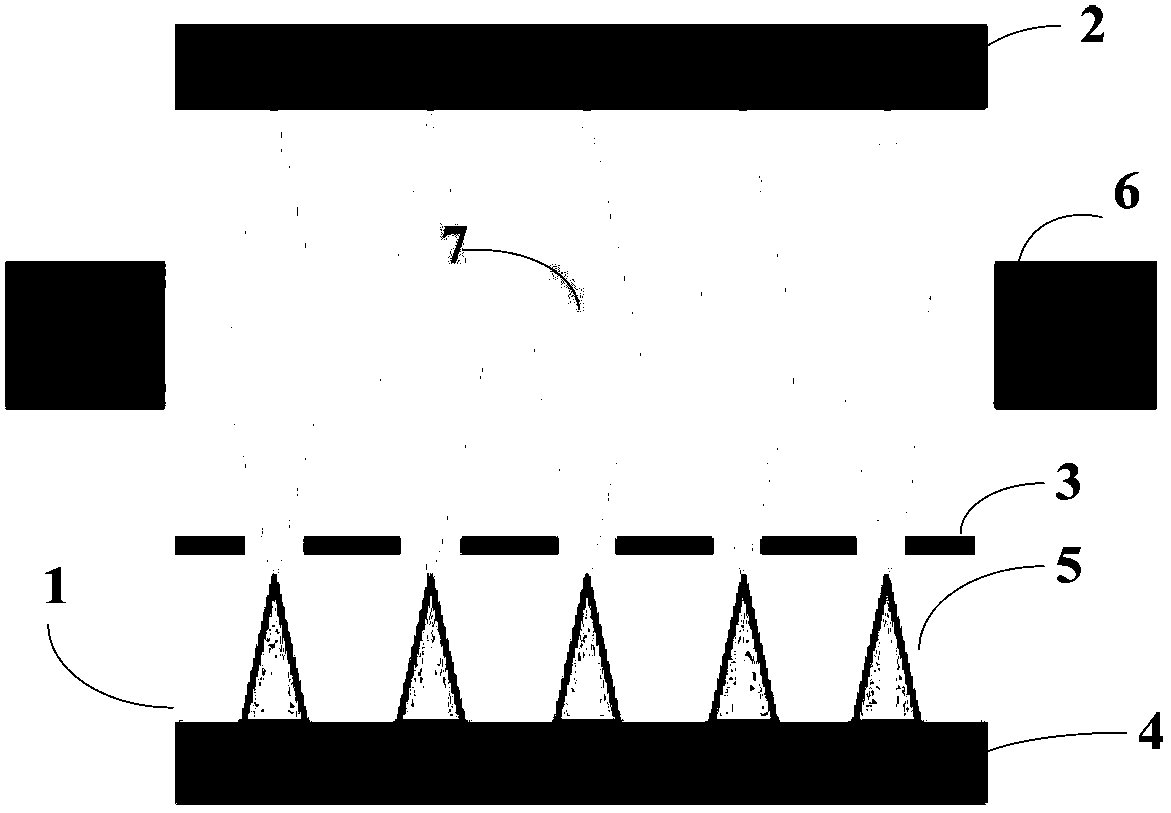
[0041] Executing step S10: etching the pretreated cathode substrate 4 to obtain a cathode 1 with an array of cathode emitters 5, the pretreatment method is: ultrasonically wash the cathode substrate 4 with deionized water and acetone for 1 to 3 Then dry at room temperature. The etching method may be photoetching, physical etching or chemical etching. In order to obtain nanometer or micron-scale array structure, chemical etching is preferred in the present invention.
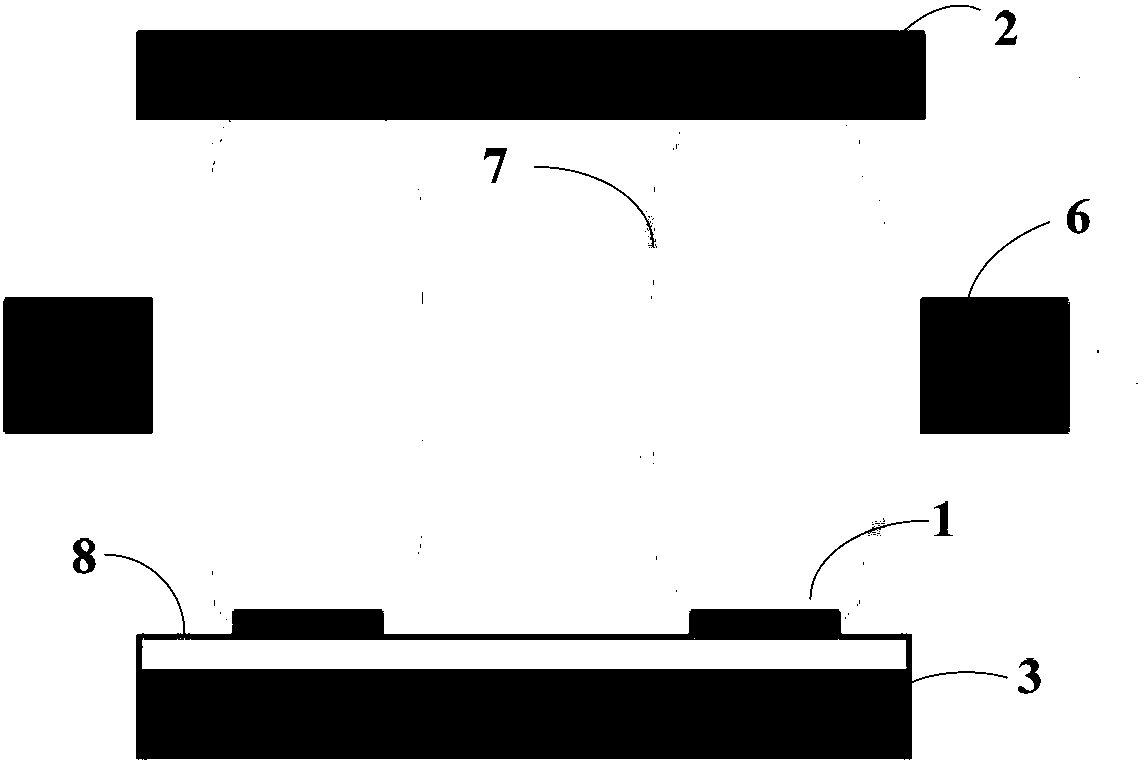
[0042] Executing step S20: depositing an insulating layer 8 on the surface of the cathode 1 having an array structure, for separating the c...
Embodiment 1
[0046] a) Take a heavily doped n-Si sheet as the cathode substrate, wash it ultrasonically for 1-3 times with deionized water and acetone respectively, and dry the obtained silicon sheet at room temperature for use.
[0047] b) Spin-coat photoresist on the surface of the silicon wafer, cover it with a mask plate, wash off the photoresist after one exposure to ultraviolet light, and obtain a surface patterned channel; use hydrogen fluoride (HF) to etch the Si wafer, and then protect it in an inert atmosphere The remaining photoresist was removed under high temperature to obtain a cathode Si sheet with an array structure, the height of the cathode base was 1 mm, and the height of the cathode emitter array was 100 μm.
[0048] c) Using chemical vapor deposition to deposit SiO on the cathode Si sheet with an array structure 2 insulating layer, the SiO 2 The height of the insulating layer is 80nm, continue to use the CVD method on the insulating layer SiO 2 Metal tungsten is depo...
Embodiment 2
[0051] a) Take a heavily doped n-Si wafer, wash it ultrasonically for 1-3 times with deionized water and acetone respectively, and dry the silicon wafer at room temperature for use.
[0052] b) Spin-coat photoresist on the surface of the silicon wafer, cover the mask plate with square gaps, wash off the photoresist after one exposure to ultraviolet light, and obtain a surface patterned channel; use HF to etch the Si wafer, and then under the protection of an inert atmosphere The remaining photoresist was removed at high temperature to obtain an etched Si sheet, the height of the cathode base was 2 mm, and the height of the cathode emitter array was 20 μm.
[0053] c) Spin-coat the photoresist on the etched Si wafer again, align the photolithographic template and the silicon wafer substrate on the positioning workbench, and wash off the photoresist after secondary ultraviolet exposure.
[0054] d) Depositing SiO on the surface of metal nanoarrays using ALD method 2 The insulat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com