A kind of method for preparing rice starch acetate catalyzed by immobilized heteropolyacid
A technology of immobilizing heteropoly acid and starch acetate, which is applied in the field of starch deep processing, can solve the problems of high environmental hazards, low economic benefits, equipment damage, etc., and achieve low equipment damage, high esterification efficiency, and high esterification degree Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
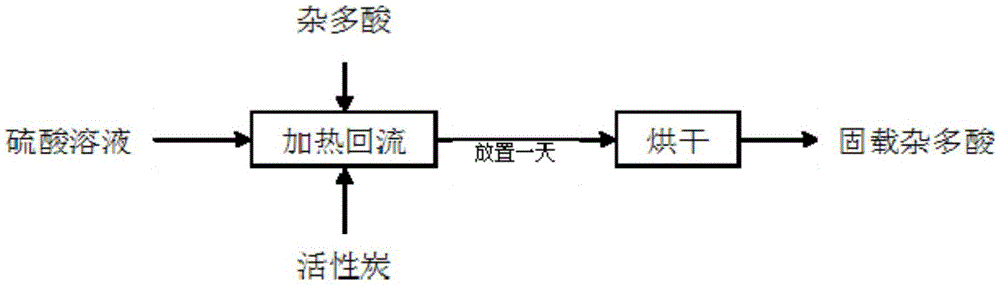
[0023] Use activated carbon with Keggin structure as a carrier, take 9 parts of activated carbon, mix 3 parts of phosphotungstic acid with 60 parts of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, heat the activated carbon with it and reflux for 12 hours, place it for one day, and bake it at 140°C dry to obtain the desired solid-supported catalyst.
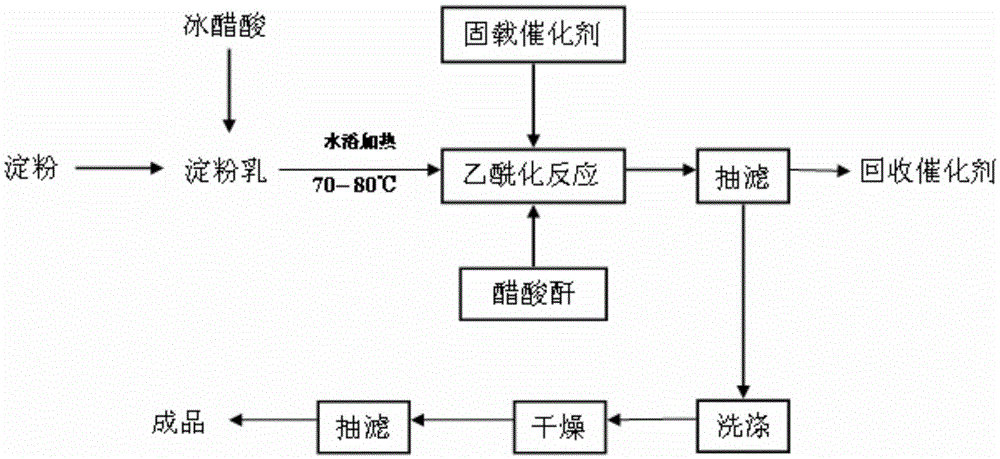
[0024] Weigh 10 parts of rice starch, add 25 parts of glacial acetic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 minutes to make it evenly mixed, add 3 parts of solid-loaded heteropolyacid and 25 parts of acetic anhydride in a constant temperature water bath at 75°C, and react for 2 hours , suction filtration, the filtrate was poured into 1L distilled water, a large amount of starch was separated out, washed, extracted, vacuum-dried at 40°C, ground and sieved to obtain rice starch acetate with a degree of substitution of 2.51.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Use activated carbon with a Keggin structure as a carrier, take 11 parts of activated carbon, mix 4 parts of phosphomolybdic acid with 50 parts of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.5mol / L, and heat the activated carbon with it for 12 hours and then place it for one day at 140°C drying to obtain the desired solid-supported catalyst.
[0027] Weigh 10 parts of rice starch, add 27 parts of glacial acetic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 minutes to make it evenly mixed, and add 4 parts of solid-loaded heteropoly acid and 30 parts of acetic anhydride in an environment of constant temperature water bath at 80°C, and react for 2.5 hours , suction filtration, the filtrate was poured into 1L distilled water, a large amount of starch was separated out, washed, extracted, vacuum-dried at 40°C, ground and sieved to obtain rice starch acetate with a degree of substitution of 2.65.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Use activated carbon with a Keggin structure as a carrier, take 12 parts of activated carbon, mix 5 parts of phosphovanadic acid with 60 parts of sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, heat the activated carbon with it for 12 hours, place it for one day, and bake it at 140°C dry to obtain the desired solid-supported catalyst.
[0030] Weigh 10 parts of rice starch, add 20 parts of glacial acetic acid, stir at room temperature for 3 minutes to make it evenly mixed, and add 3 parts of recovered solid-loaded heteropolyacid and 25 parts of acetic anhydride in an environment of constant temperature water bath at 70°C, and react After 2 hours, filter with suction, pour the filtrate into 1L of distilled water, precipitate a large amount of starch, wash, extract, vacuum-dry at 40°C, grind and sieve to obtain rice starch acetate with a substitution degree of 2.50.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com