Wireless multi-hop self-organizing network time synchronization system base on parallel transmission
A time synchronization system and wireless multi-hop technology, applied in synchronization devices, wireless communication, network topology, etc., can solve the problems of long time synchronization convergence time, large time delay, and data transmission packet conflicts in the entire network
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
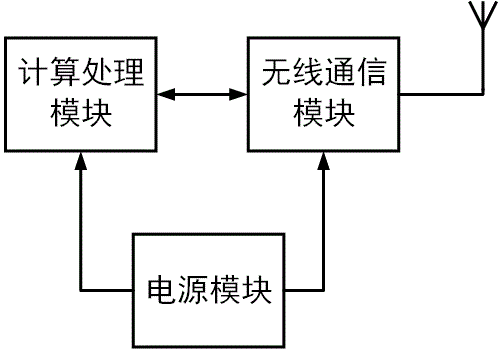
[0093] see Figure 7 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a time synchronization system based on parallel transmission applied to a wireless multi-hop ad hoc network. The network node adopts the IEEE 802.15.4 communication standard. Specifically, the network node can adopt the widely used TMOTE SKY node, which includes four parts: sensor module, computing module, wireless communication module and power supply module. The sensor module has nothing to do with this time synchronization system and can be ignored. The calculation module adopts TI's MSP430F149 low-power single-chip microcomputer, and an external 4MHz crystal oscillator O 1 . The wireless communication module adopts the CC2420 module of TI company, and the external 16MHz crystal oscillator O 2 . The computing module and wireless communication module can also be integrated in a unified chip, using a single crystal oscillator, such as TI's new low-power microcontroller CC430, thereby reducing the nod...
Embodiment 2
[0109] In this embodiment, the nodes in the network are in a static or quasi-static state, and the network topology remains basically unchanged, such as Image 6 shown.
[0110] This embodiment is mainly applied to occasions where the nodes will not move after being fixedly deployed, such as atmospheric environment monitoring, agricultural and forestry monitoring, and the like.
[0111] On the basis of ensuring coverage, by reducing the number of nodes in parallel transmission, the probability of beacon packet collision is reduced and energy consumption is reduced.
[0112] Given a network topology map, first use the BFS algorithm to traverse the network topology map, calculate the shortest number of hops from each node to the sink node, and classify the points with the same shortest number of hops as a set at the same level, such as Φ 1 , Φ 2 ,…,Φ M . set Φ i Represents the set of nodes that are i hops away from the sink node.
[0113] from Φ 1 Start selecting the mini...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 also have a variant, that is, the node adopts another linear recursive method to estimate the clock frequency deviation and the variance of the clock frequency deviation. At this time, the node may not perform step S51, that is, the phase deviation correction is not performed, and the rest Same as Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
[0125] When the i-th beacon packet is received, the measurement time of the local clock is c i , then the estimated value p of the clock phase deviation after linear recursion is used 校 , the clock frequency deviation estimate f 校 , the variance of the clock frequency deviation estimate var(f 校 )for:
[0126] c ‾ = 1 w Σ i = 1 w c i - - - ( 5 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com