Body cavity probe apparatus
A technology for detecting devices and body cavities, applied to endoscopes, diagnostic recording/measurement, catheters, etc., can solve the problems of large radiation damage, inability to generate real-time image-guided images, and structures that do not record the direction of real-time image detection , to achieve the effect of reducing radiation damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
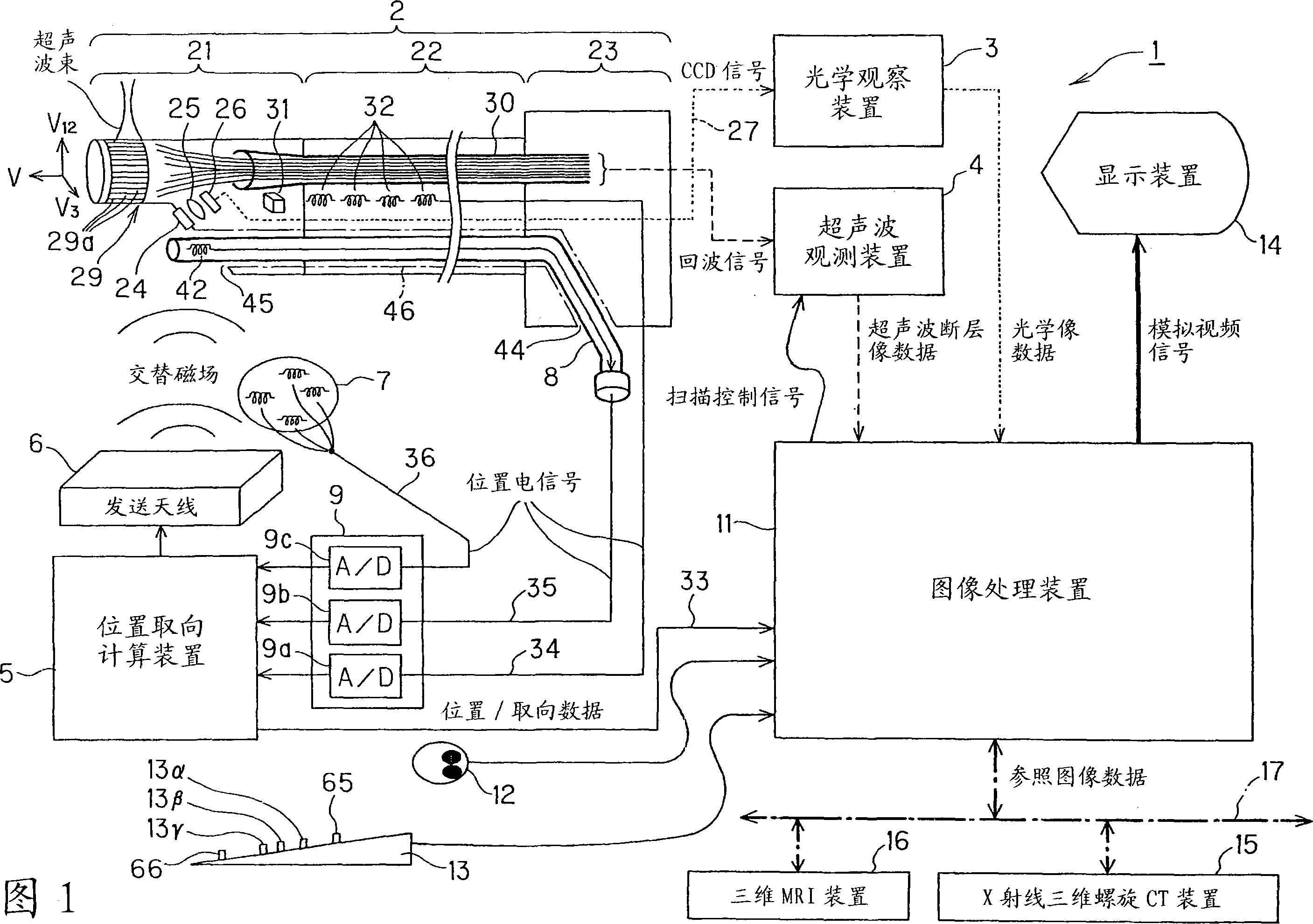
[0052] Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 21 . First, the configuration of the intra-body cavity detection device 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
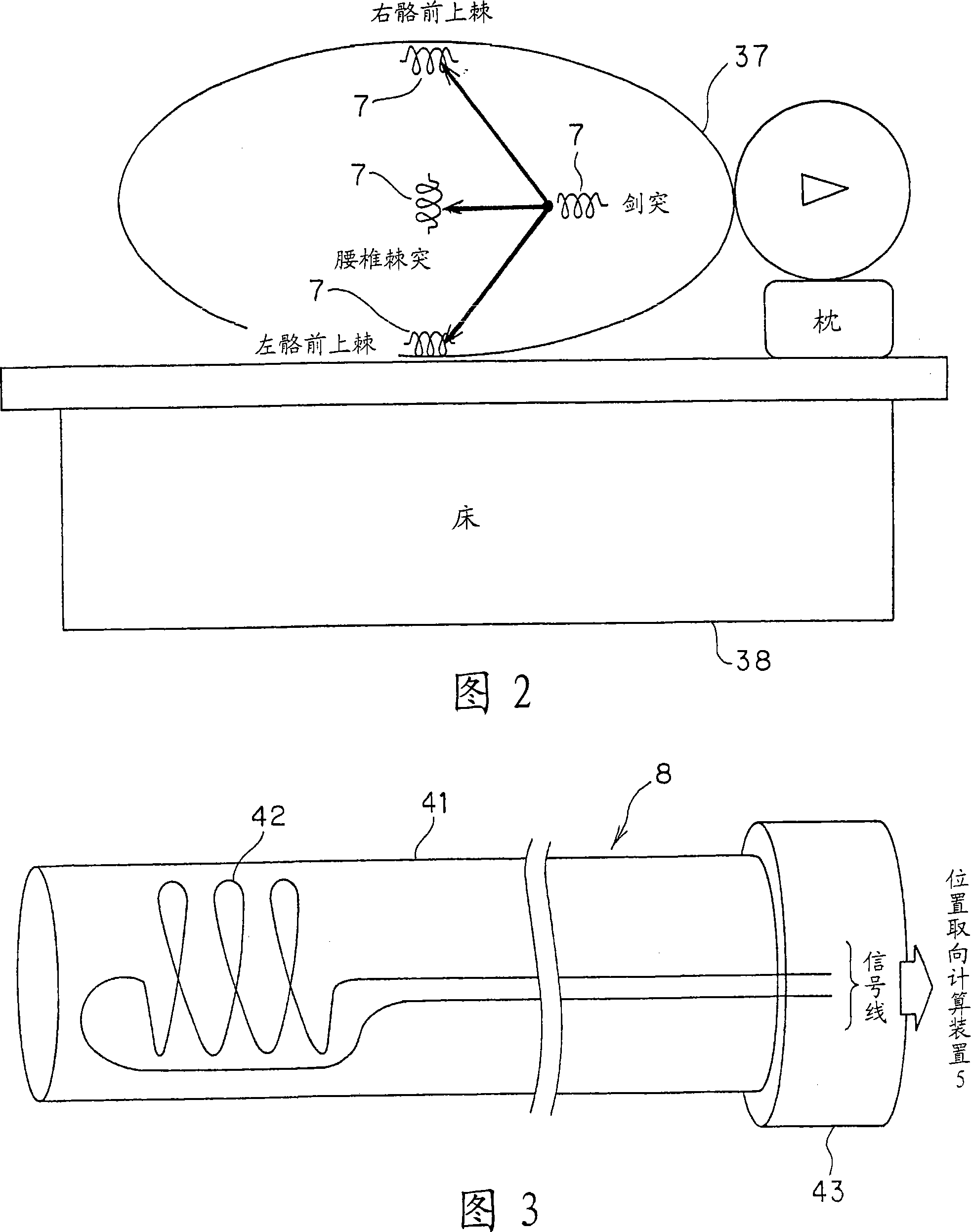
[0053] As shown in Figure 1, the body cavity detection device 1 of Embodiment 1 includes: an electronic radial scanning ultrasonic endoscope 2 as a body cavity detector, an optical observation device 3, an ultrasonic observation device 4, a position and orientation calculation device 5, Transmitting antenna 6, body surface detection coil 7, body cavity contact detector 8, A / D unit 9, image processing device 11, mouse 12, keyboard 13, and display device 14 are connected by signal lines.
[0054] An X-ray three-dimensional helical CT device (X-ray 3dimentional computer tomography system) 15, a three-dimensional MRI device (3 dimentionalmagnetic resonance imaging system) 16, and fast networks such as optical communication and ADSL connect...
Embodiment 2
[0335] Next, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. The structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1. However, only the function of the three-dimensional guide image generation circuit B is different from that of the first embodiment.
[0336] Next, the action of this embodiment will be described.
[0337] As described above, this embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 only in the function of the three-dimensional guide image generating circuit B.
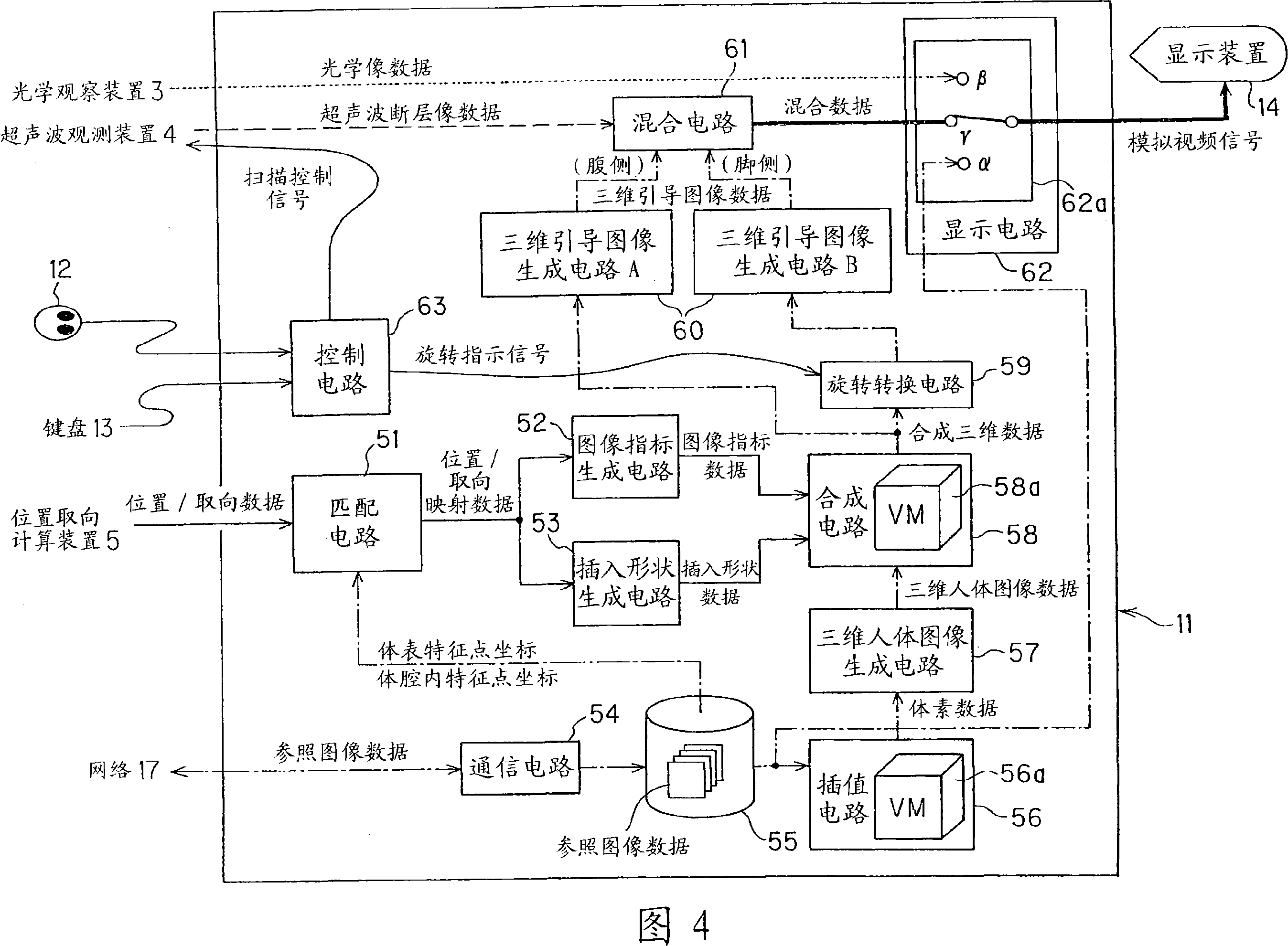
[0338] In Embodiment 1, as shown in FIG. 15 , the three-dimensional guide image generating circuit B generates three-dimensional guide image data viewed from the direction of the subject's feet, and outputs the data to the mixing circuit 61 .
[0339] In addition, along with the movement of the radial scanning plane accompanying the manual manipulation of the flexible part 22 and the rigid part 21 by the doctor, the ultrasonic tomographic image marker Mu, the distal end direction marker Md, the...
Embodiment 3
[0351] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described.
[0352] The structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 2. Only the function of the three-dimensional guide image generating circuit B in this embodiment is different from that in Embodiment 2.
[0353] Next, the action of this embodiment will be described.
[0354] As described above, the present embodiment differs from the second embodiment only in the function of the three-dimensional guide image generating circuit B.
[0355] In Embodiment 2, as shown in FIG. 22, the three-dimensional guide image generation circuit B makes the ultrasonic tomographic marker Mu in the image index data translucent, so that the six o'clock direction marker Mt and the direction of the tip of the image index data can be seen through. The mark Md, and the insertion shape mark Ms and the coil position mark Mc of the insertion shape data, for other organs, make the ultrasonic tomographic image mark Mu opaque...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com