Acinetobacter calcoaceticus capable of efficiently degrading lignin
A technology of lignin and calcium acetate, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganism-based methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of difficult biodegradation of lignin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Acinetobacter calcoaceticus LG-1 has been registered and preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC); the preservation date is March 12, 2014; the number is CCTCC M 2014079.
[0025] The screening, identification and application procedures of the strain are as follows:
[0026] 1. Screening of bacterial strains
[0027] A: The sewage area of the paper mill was sampled to obtain the sample sludge.
[0028] B: Prepare lignin inorganic salt culture solution and inorganic salt culture medium, and sterilize them in 100ml to 250ml Erlenmeyer flasks.
[0029] C: Configure 200g / L lignin mother liquor, sterilize it, and dialyze it with a sufficient amount of sterilized ddH2O (aseptic condition), and distribute it to a triangular flask containing 100mL inorganic salt medium to obtain Dialyze the lignin inorganic salt culture solution.
[0030] D: Prepare 0.9% (w / v) NaCl solution, sterilize it, add it to the sludge sample at a ratio of 1:100 (w / v), incubate ...
Embodiment 2
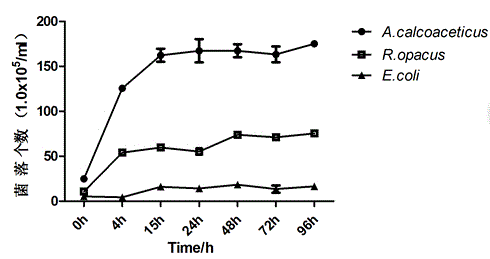
[0047] Embodiment 2: The degradation experiment of bacterial strain to lignin can also be verified by following experiments:
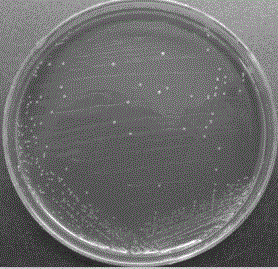
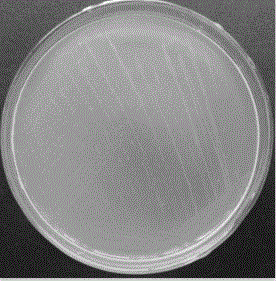
[0048] Streak the bacterial liquid obtained from culturing in LB medium on solid lignin inorganic salt medium and solid inorganic salt medium, and culture in a 37°C incubator for 12 hours to perform degradation verification.
[0049] The formula of described solid inorganic salt culture medium is: 1.55g K 2 HPO 4 , 0.85g NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 0, 2.0g (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.1g MgCl 2 6H20, 10mg EDTA, 2mg ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 0, 1mg CaCl 2 2H 2 0.5mg FeSO 4 ·7H 2 0,0.2 mg Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 0,0.2mg CuSO 4 ·5H 2 0,0.4mg CoCl 2 ·6H 2 0, and 1mg MnCI 2 2H 2 0, Agar 15g;
[0050] The formula of the solid lignin inorganic salt medium using lignin as the sole carbon source is the same as that of the solid lignin inorganic salt medium, with 5g Lignin added.
[0051] The formula of the LB medium is: NaCl 10g, YEAST EXTRACT 5g, TRYPTONE 10g
[0052] The ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com