Carbon-based non-metallic oxygen reduction catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
A catalyst and non-metallic technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of difficult large-scale preparation, limited heteroatom content, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effect of strong controllability of material structure, controllable content of species, and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] This example is used to illustrate the preparation method of the N element-doped oxygen reduction catalyst provided by the present invention.
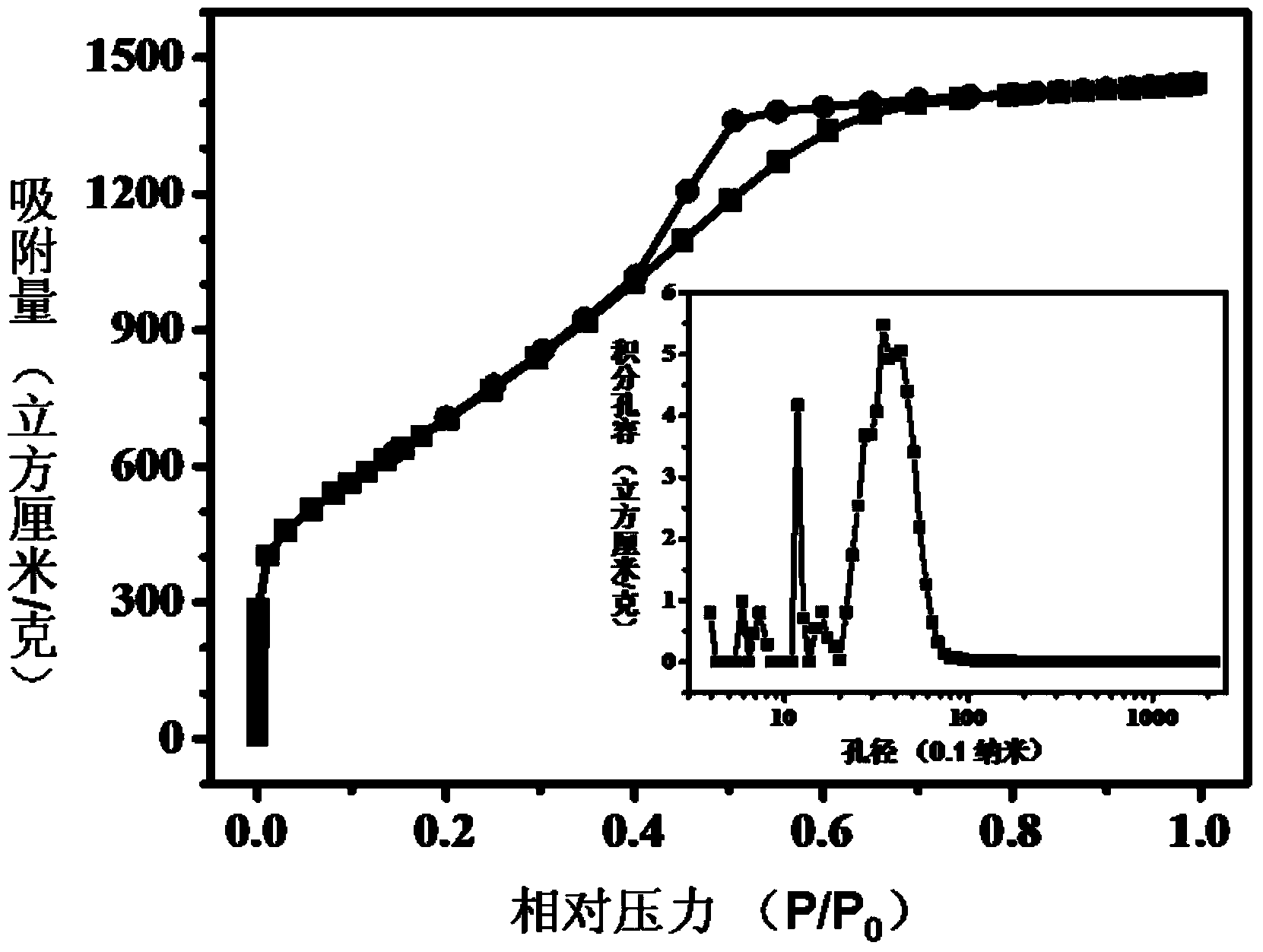
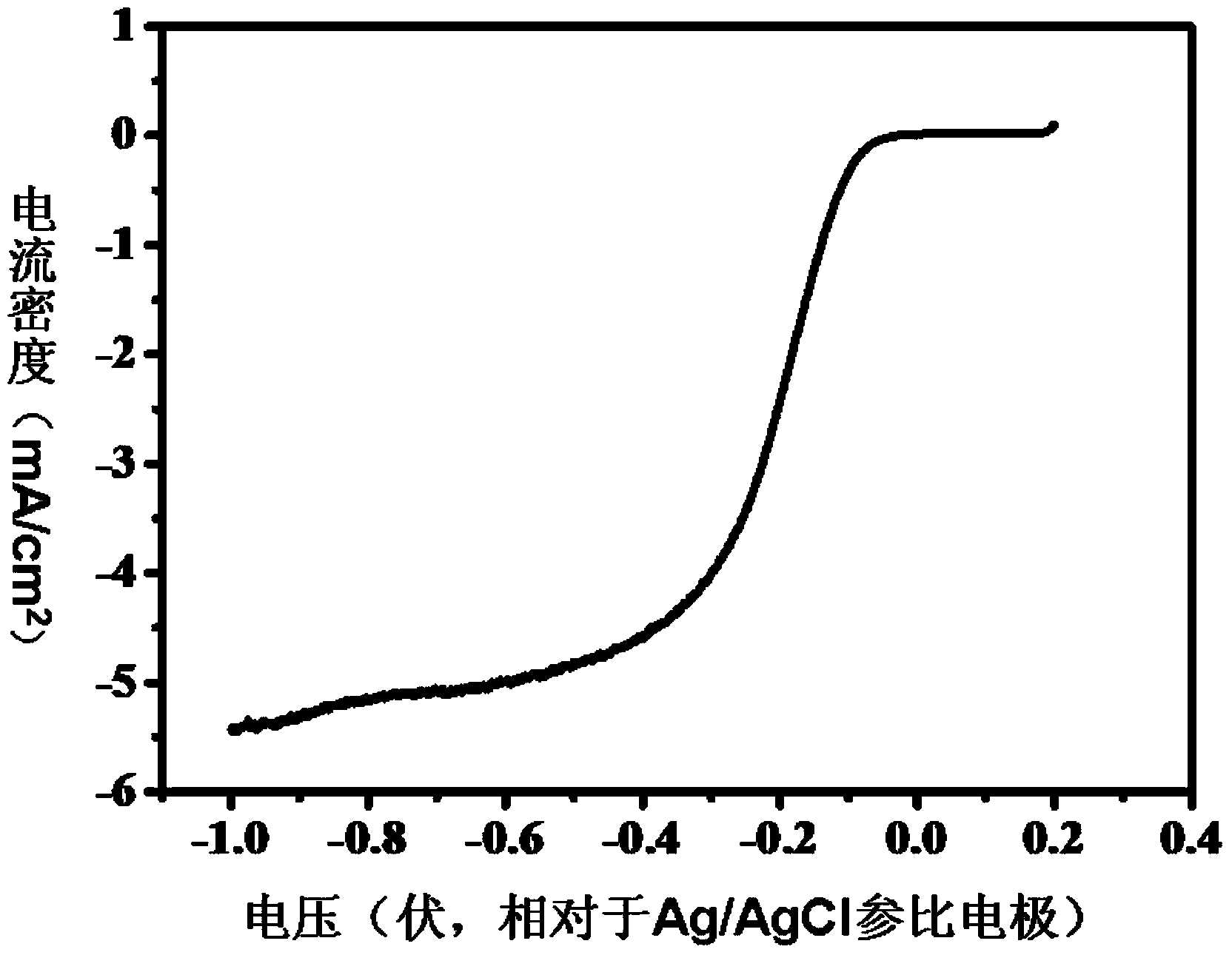
[0091] Mix 1g (7.81mmol) of terephthalonitrile (CAS No. 623-26-7) and 0.53g (3.9mmol) of anhydrous zinc chloride, and transfer them to a 10ml quartz tube, and replace the quartz with argon air in the tube, seal it and put it into a muffle furnace, react at 700°C for 0.5 hours, cool down to room temperature (25°C) naturally, open the glass tube, take out the polymerization product, and successively use 1mol / L Washed with hydrochloric acid and pure water, then placed in a vacuum oven and dried at 120°C for 10 hours to obtain an N-doped polymer product, which can be used as an oxygen reduction catalyst. Among them, the content of nitrogen in the catalyst is 10.3%, and the specific surface area is 1710m 2 / g, the pore size distribution range is: 0.5~4nm.
Embodiment 2
[0093] This example is used to illustrate the preparation method of the N element-doped oxygen reduction catalyst provided by the present invention.
[0094] Mix 1 g (7.81 mmol) of terephthalonitrile (CAS number: 623-26-7) and 10.64 g (78 mmol) of anhydrous zinc chloride, and transfer them to a 10ml quartz tube, and replace the quartz tube with argon After sealing it, put it into a muffle furnace, react at 700°C for 80 hours, cool it to room temperature (25°C) naturally, open the glass tube, take out the polymerized product, and successively wash it with 1mol / L hydrochloric acid , washed with pure water, and then placed in a vacuum drying oven and dried at 120 °C for 10 hours to obtain an N-doped polymer product, which can be used as an oxygen reduction catalyst. In the obtained oxygen reduction catalyst, the content of nitrogen element was 2.1%. The specific surface area is 2980m 2 / g, pore size distribution: 0.4~10nm.
Embodiment 3
[0096] This example is used to illustrate the preparation method of the N element-doped oxygen reduction catalyst provided by the present invention.
[0097] Mix 1g (7.81mmol) of terephthalonitrile (CAS No.: 623-26-7) and 1.06g (7.8mmol) of anhydrous zinc chloride, and transfer them to a 10ml glass tube, replace the glass with argon air in the tube, seal it and put it into a muffle furnace, react at 300°C for 5 hours, cool down to room temperature (25°C) naturally, open the glass tube, take out the polymerized product, and use 1mol / L of Washed with hydrochloric acid and pure water, then placed in a vacuum oven and dried at 120°C for 10 hours to obtain an N-doped polymer product, which can be used as an oxygen reduction catalyst. Among them, the content of nitrogen in the catalyst is 18.4%, and the specific surface area is 143m 2 / g, the pore size distribution range is: 0.4~2.8nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com