Heat dissipation structure of electric device and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for electrical devices and heat dissipation structures, which is applied in the manufacture of electrical equipment components, circuit devices, printed circuits, etc., and can solve problems such as poor heat dissipation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach )
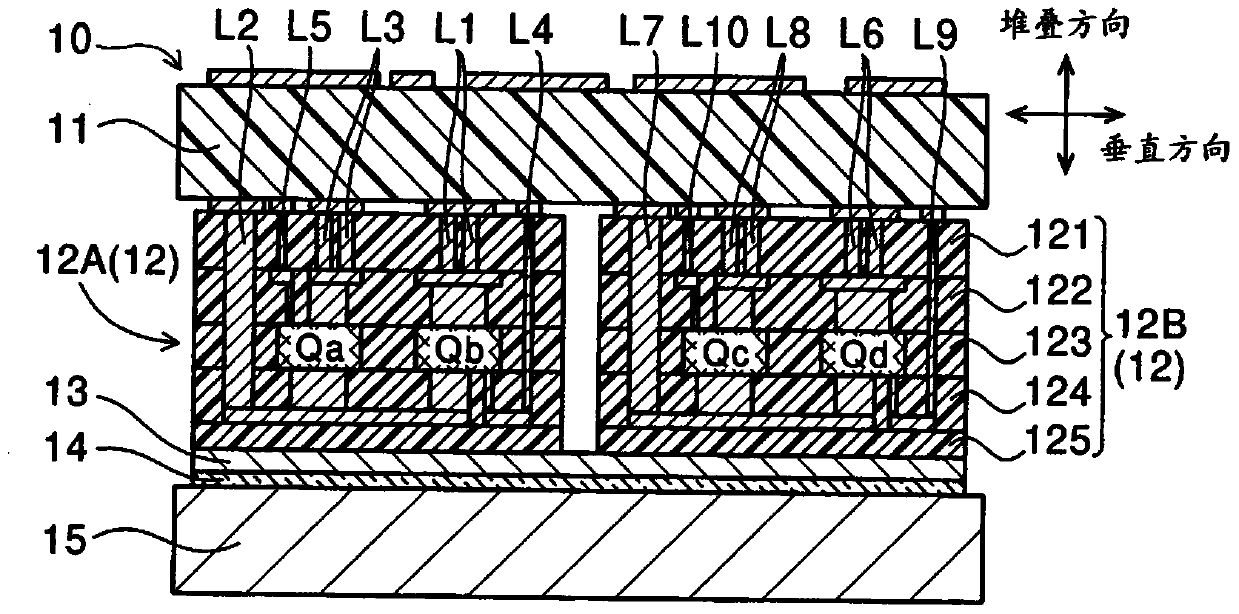
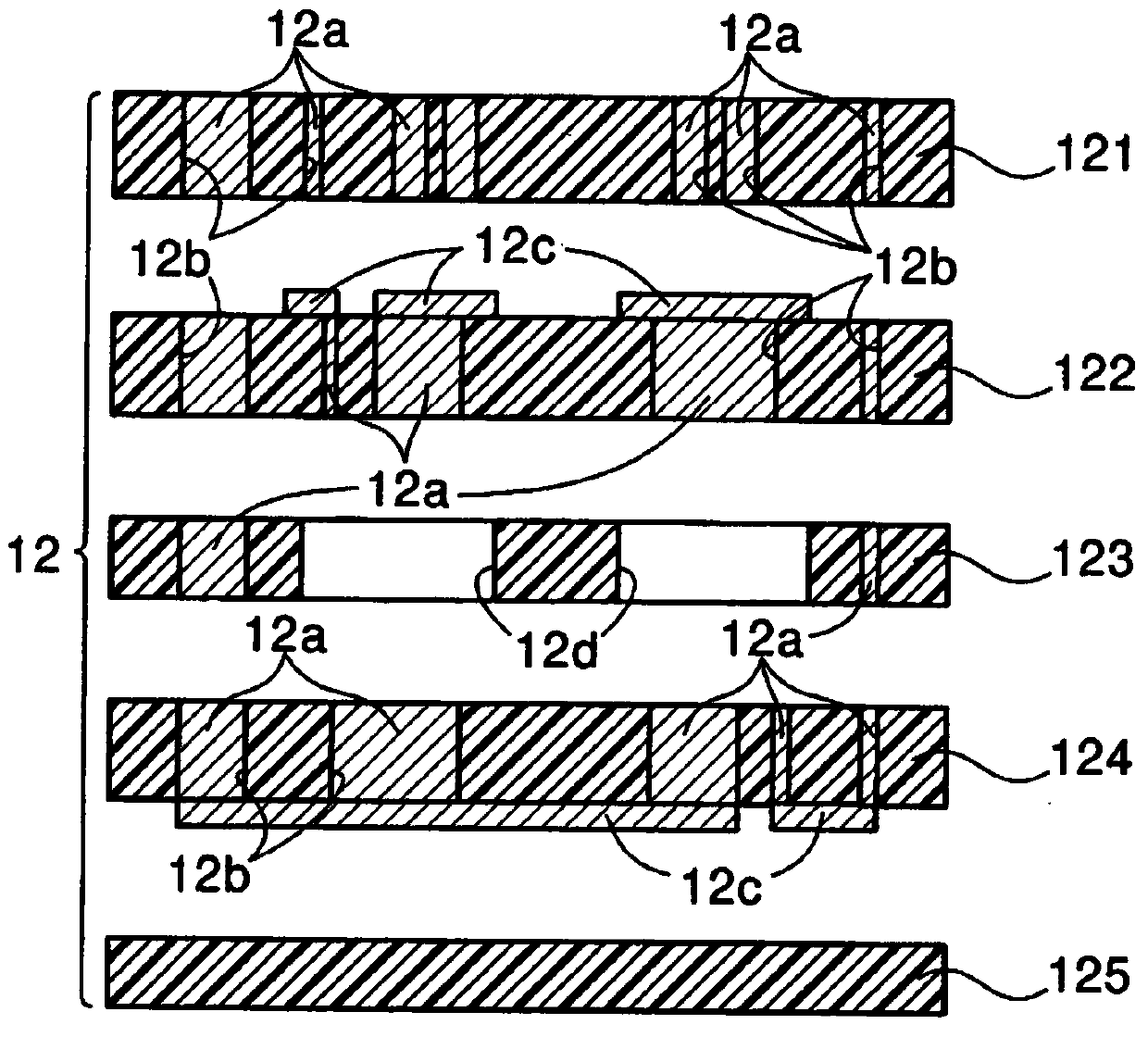
[0036] The heat dissipation structure according to the first embodiment includes a plurality of multilayer substrates between the circuit board and the heat dissipation body. will refer to Figures 1 to 8 This structure will be described. figure 1 The heat dissipation structure 10 shown in includes a circuit board 11 , a plurality of multilayer substrates 12 , a low thermal resistance element 13 , a heat conduction element 14 and a heat sink 15 . In the present embodiment, the plurality of multilayer substrates 12 includes a first multilayer substrate 12A and a second multilayer substrate 12B.
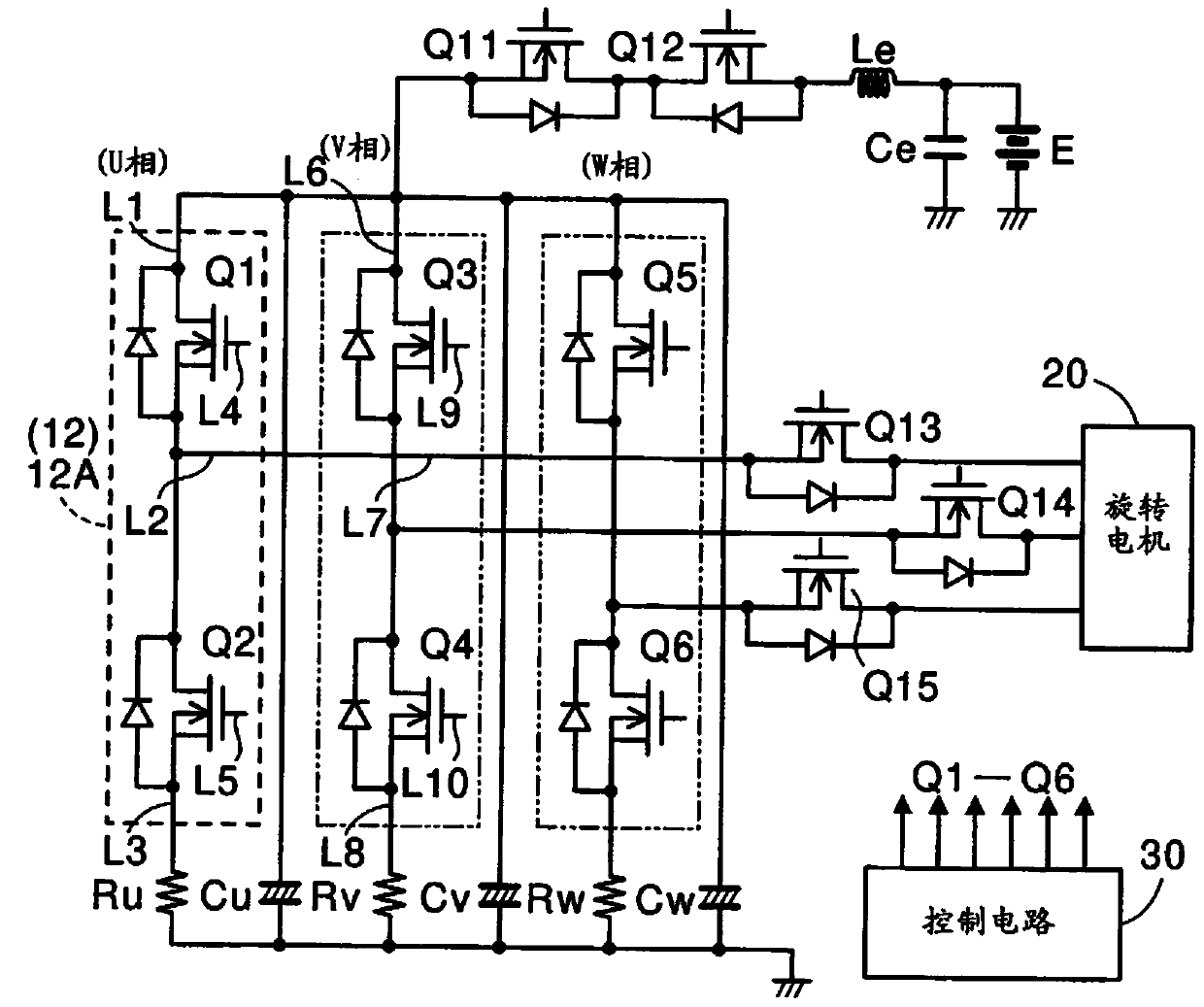
[0037] The circuit board 11 is a board on which electrical components are mounted and a conductor pattern is formed. In the present embodiment, the circuit board 11 is provided to control the rotating electric machine 20 having three phases such as U phase, V phase and W phase. Specifically, the circuit board 11 includes: a control circuit 30; resistors Rv, Ru, Rw; capacitors Cu, Cv...
no. 2 approach )
[0070] In a second embodiment, a heat dissipation structure has a multilayer substrate and electrical components located between a circuit board and a heat dissipation body. will refer to Figures 10 to 13 This structure will be described.
[0071] Figure 10 The heat dissipation structure 10 shown in the figure includes a circuit board 11 , a multilayer substrate 12 , a low thermal resistance element 13 , a heat conducting member 14 , a radiator 15 and an electrical element 16 . In this embodiment, structure 10 includes a multilayer substrate 12 and an electrical component 16 .
[0072] The multilayer substrate 12 corresponds to the substrates 12A, 12B in the first embodiment. Alternatively, the substrate 12 according to the second embodiment corresponds to the multilayer substrate according to other embodiments. The electrical elements 16 may be semiconductor devices such as switching elements, diodes, semiconductor current collectors, and integrated circuits (ICs), and / ...
no. 3 approach )
[0083] In a third embodiment, the heat dissipation structure includes a plurality of electrical components located between the circuit board and the heat dissipation body. will refer to Figures 14 to 16 This structure will be described.
[0084] Figure 14 The heat dissipation structure 10 shown in includes a circuit board 11 , a low thermal resistance element 13 , a heat conducting member 14 , a heat sink 15 , and a plurality of electrical components 16 . In the present embodiment, the plurality of electrical components 16 include a first electrical component 16A and a second electrical component 16B.
[0085] The electrical elements 16A, 16B correspond to the electrical element 16 and / or other electrical devices according to the second embodiment. The electrical elements 16A, 16B may be semiconductor devices such as switching elements, diodes, semiconductor current collectors, and integrated circuits (ICs), and / or resistors, capacitors, coils, reactors, and the like. El...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com