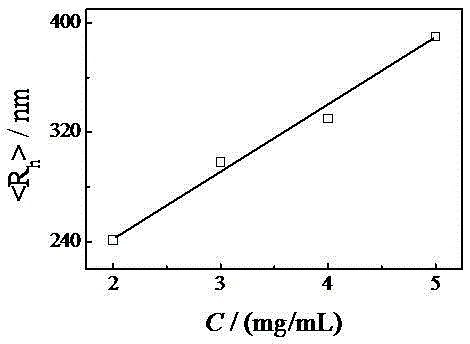A detection method and application of cellulose acetate tow
A technology of cellulose acetate tow and cellulose acetate, applied in the field of detection, can solve the problems of easy blockage, inability to obtain, limited data, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding blockage and improving production capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] S1. Dissolve the cellulose acetate tow in acetone, ultracentrifuge to remove the titanium dioxide added in the synthesis process of the cellulose acetate tow, take the upper layer of filtrate, and filter it with a membrane to remove dust and other impurities in the solution;
[0040] S2. The filtrate obtained after filtering the S1 membrane is detected by light scattering method to obtain the hydrodynamic radius R h , Mean square radius of rotation R g Structure factor R g / R h ;
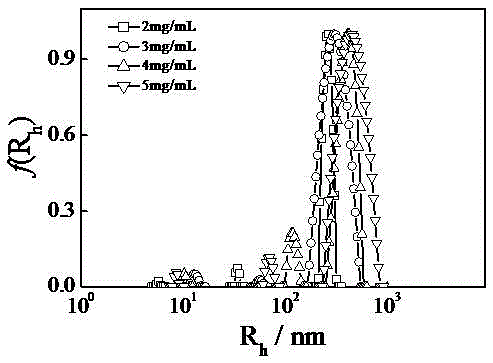
[0041] figure 2 Is the hydrodynamic radius distribution diagram of acetate tow at different concentrations f ( R h ), it can be seen that as the concentration of the acetate tow solution increases, the micelle aggregates further increase.
[0042] S3. Through the hydrodynamic radius R h The size and hydrodynamic radius distribution map f ( R h ), it can be judged that the tows are single-stranded, micelles or micellar aggregates in the acetone solution.
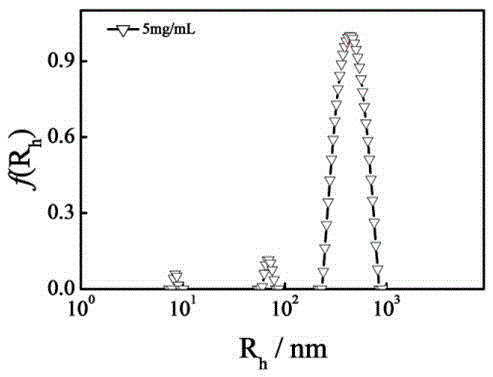
[0043] image 3 Is the hydrodynamic radius o...
Embodiment 2
[0048] S1. Dissolve the cellulose acetate tow in acetone, ultracentrifuge, take the filtrate, filter it with a membrane, and detect its clogging value; make the clogging value 15 g / cm²;
[0049] S2. The filtrate obtained after filtering the S1 membrane is detected by light scattering method to obtain the hydrodynamic radius, the mean square rotation radius, and the structure factor;
[0050] S3. Through the size of the hydrodynamic radius distribution and the hydrodynamic radius distribution diagram; determine the distribution state of the tow in the acetone solution: that is, the size of single strands, micelles or micellar aggregates; after testing, the acetate filament The hydrodynamic radius of the beam in solution R h Is 100 to 200 microns.
[0051] According to the judgment result, it is considered that the clogging value of the acetate fiber tow is too low, which is prone to clogging, and its concentration needs to be reduced.
[0052] S4. Reduce the concentration of cellulose ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] S1. Dissolve the cellulose acetate tow in acetone, ultracentrifuge, take the filtrate, filter it with a membrane, and detect its clogging value; make the clogging value 15 g / cm²;
[0057] S2. The filtrate obtained after filtering the S1 membrane is detected by light scattering method to obtain the hydrodynamic radius, the mean square rotation radius, and the structure factor;
[0058] S3. Through the size of the hydrodynamic radius distribution and the hydrodynamic radius distribution diagram; determine the distribution state of the tow in the acetone solution: that is, the size of single strands, micelles or micellar aggregates; after testing, the acetate filament The hydrodynamic radius of the beam in solution R h Is 100 to 200 microns.
[0059] According to the judgment result, it is considered that the clogging value of the acetate fiber tow is too low, which is prone to clogging, and its concentration needs to be reduced.
[0060] S4. Reduce the concentration of cellulose ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com