Molecular marker of paddy rice flag leaf width controlling gene NAL1 and application thereof
A molecular marker and rice flag leaf technology, applied in the field of agricultural biotechnology engineering, can solve problems such as inability to establish, slow progress in functional research, and difficulty in revealing the molecular mechanism of leaves, so as to achieve the effect of improving efficiency and increasing the width of flag leaves
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
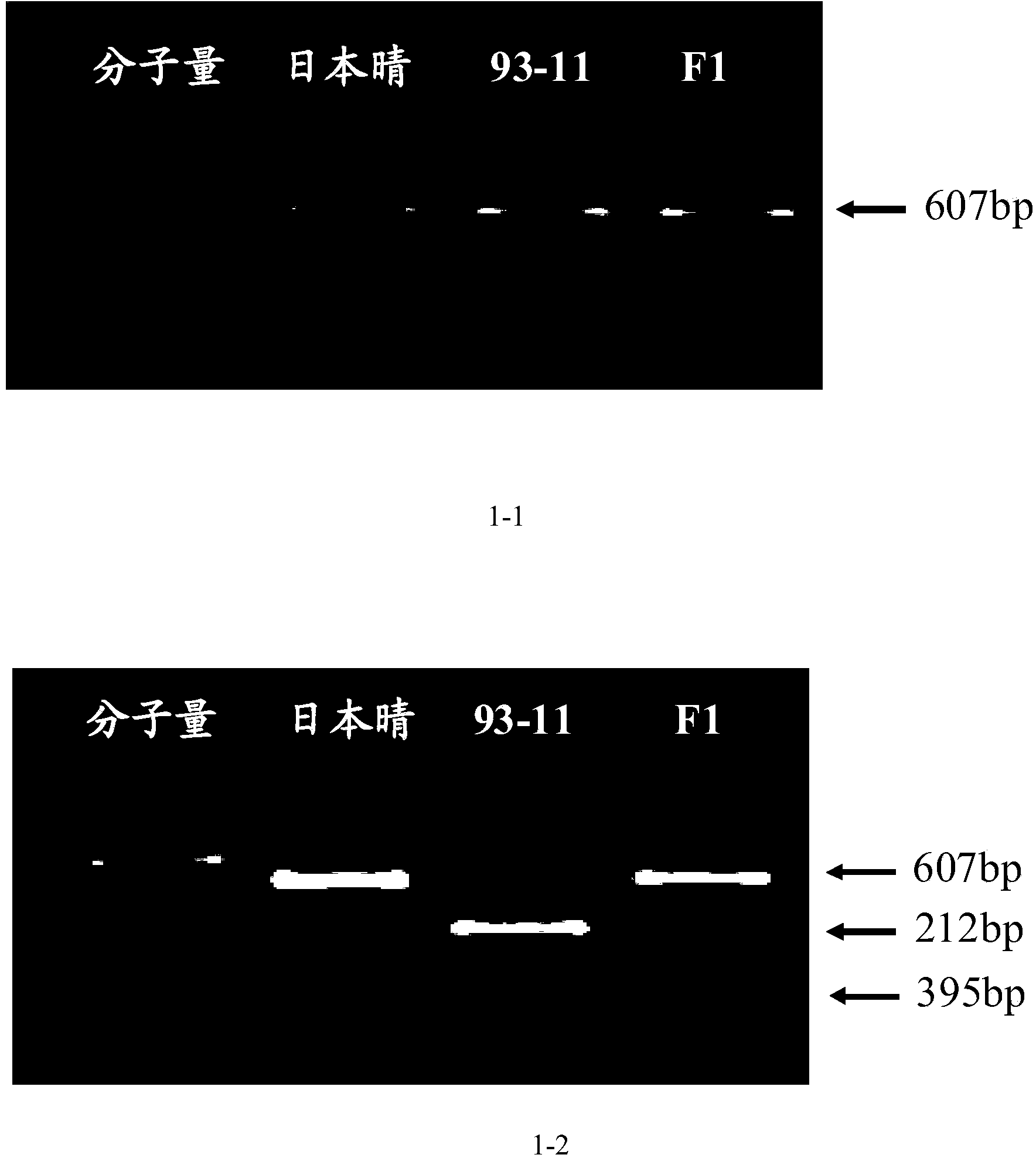
[0076] Example 1. Identification of polymorphisms in japonica Nipponbare and indica 93-11 using CAPS marker NAL1-Nar I
[0077] The specific method is: select the rice material Nipponbare and 93-11 from the germplasm resource bank of the China Rice Research Institute, hybridize with Nipponbare and 93-11 to obtain its F1, use the primer CAPS to mark NAL1-Nar I to amplify and use Nar I to identify its polymorphism ( figure 1 ).
[0078] 1. DNA extraction
[0079] 1) Prepare DNA extraction buffer:
[0080] Add 1 volume of DNA extraction solution (0.35M sorbitol; 0.1M Tris, pH8.2; 0.005M EDTA; the rest is water), 1 volume of nuclear lysis solution (0.2M Tris, pH7.5; 0.05M EDTA ; 2M NaCl; 0.055M CTAB; the rest is water) and 0.4 volume of 5% (mass concentration) sarkosyl solution (that is, the aqueous solution of sodium lauryl-N-methylglycinate); finally add sodium bisulfite to prepare DNA Extraction buffer; final concentration of sodium bisulfite in DNA extraction buffer is 0.0...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2. Using the CAPS molecular marker NAL1-Nar I to identify the sequence difference between the japonica rice Nipponbare containing the broad-leaf gene and the narrow-leaf gene 93-11
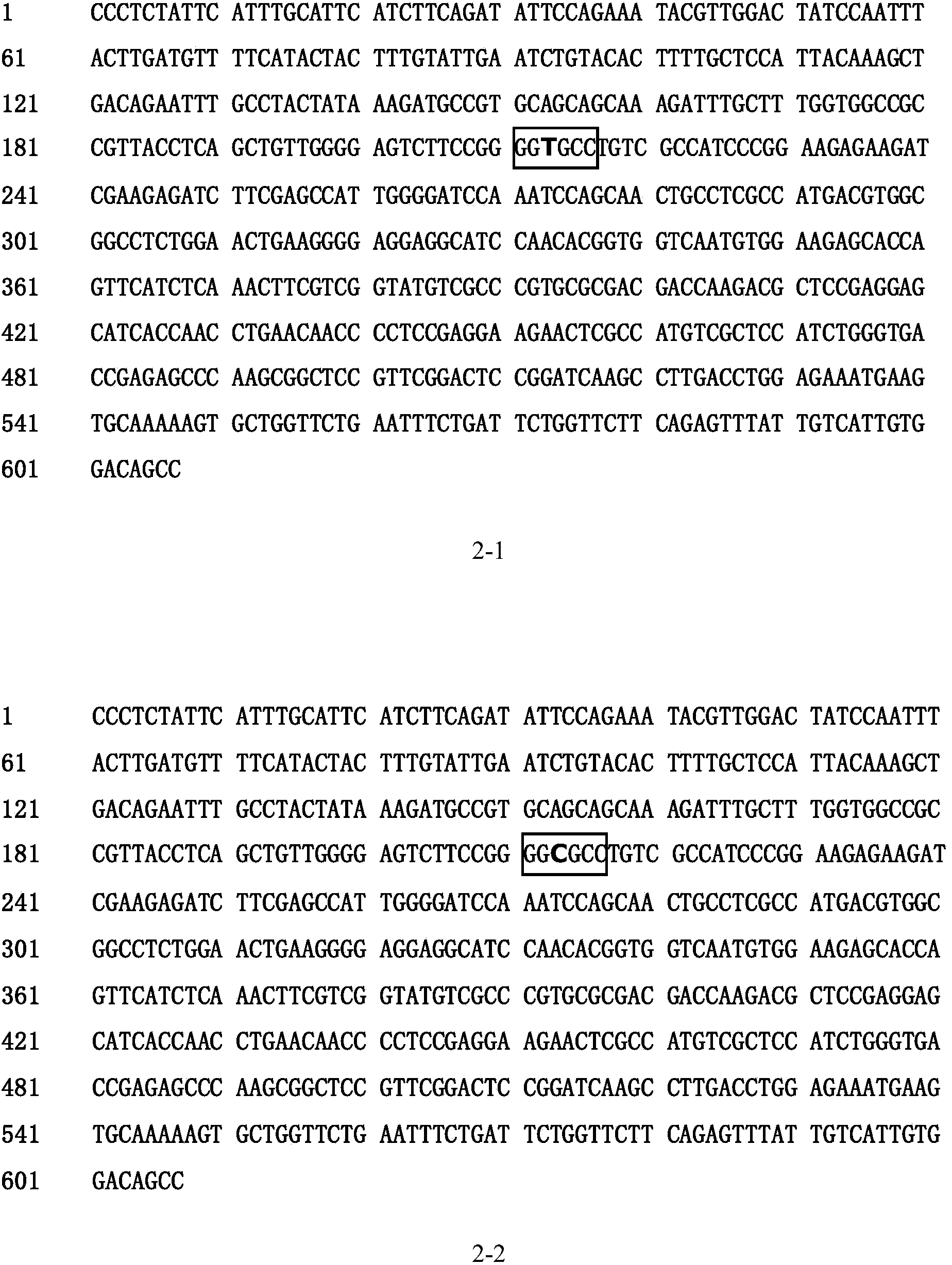
[0109] The specific method is: use the CAPS molecular marker NAL1-Nar I to perform PCR amplification on the genomic DNA of Nipponbare and 93-11, and entrust Shanghai Yingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Sequencing, comparing the differences in their sequences ( figure 2 ).
[0110] 1. DNA extraction
[0111] With embodiment 1.
[0112] 2. PCR amplification
[0113] With embodiment 1.
[0114] 3. Electrophoresis detection, recovery and sequencing
[0115] The electrophoresis detection and recovery are the same as in Example 1; the recovered PCR products are entrusted to Shanghai Yingjun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for sequencing, and the sequencing results are shown in diagram 2-1 and 2-2.
[0116] 4. Nar I digestion reaction and electrophoresis detection of digestion products
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Example 3, Utilizing CAPS molecular marker NAL1-Nar I to carry out assisted selection breeding of broad-leaved rice
[0122] The specific method is: the donor parent Nipponbare containing the broad-leaf gene is sequentially crossed, backcrossed and selfed with the indica rice variety 93-11, and the obtained offspring are combined with the assisted selection of the CAPS molecular marker NAL1-Nar I to select the segregation population with A single plant with the same type as the Japan Sunny Zone was used for breeding improvement of flag leaf width.
[0123] 1. DNA extraction
[0124] With embodiment 1.
[0125] 2. PCR amplification
[0126] With embodiment 1.
[0127] 3. Electrophoresis detection and recovery
[0128] With embodiment 1.
[0129] 4. Nar I digestion reaction and electrophoresis detection of digestion products
[0130] With embodiment 1.
[0131] 5. CAPS molecular marker NAL1-Nar I for assisted selection breeding of broad leaves
[0132] The japonic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com