Switching control method and control circuit and switching power supply with control circuit
A switching power supply and switching control technology, applied in the field of electronics, can solve the problems of slow discharge speed and slow turn-off speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] figure 2 It is a schematic flowchart of a switching control method suitable for switching power supplies provided in this embodiment. see figure 2 As shown, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0066] Step 201: Generate a driving current signal according to the sampled voltage signal.
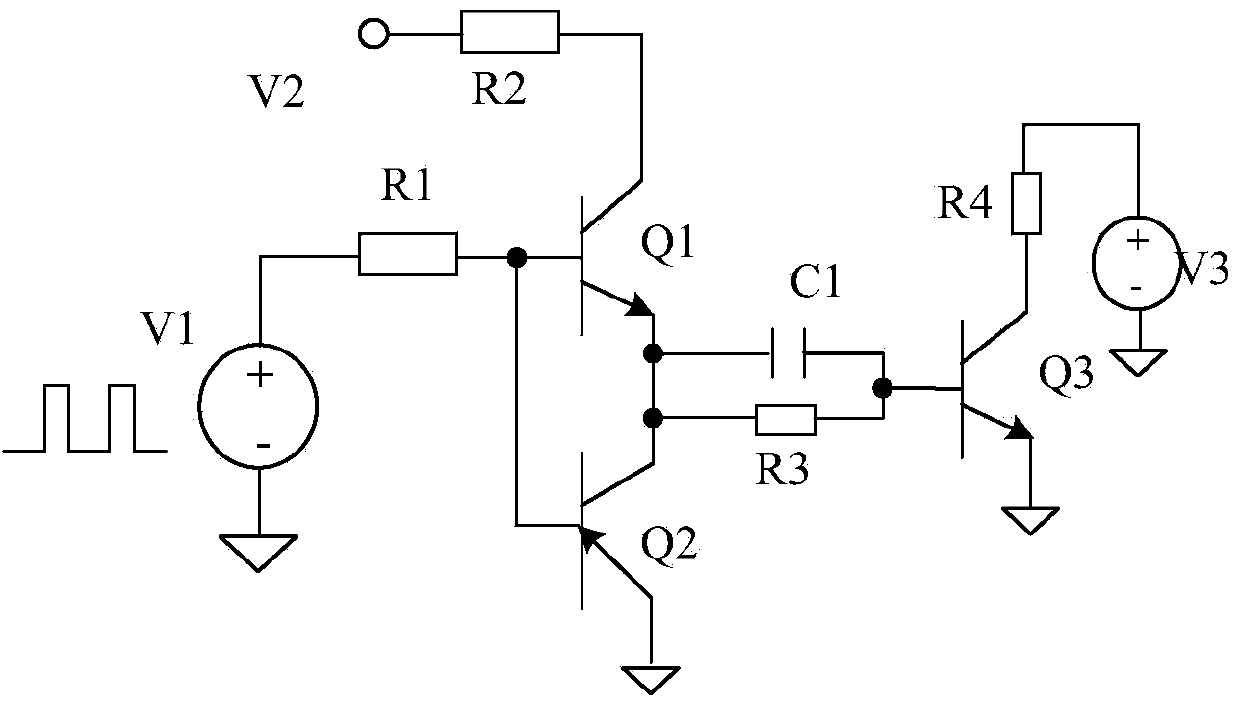
[0067] In this embodiment, the transistor Q1 is used as the power switch of the switching power supply, and the collector of the transistor Q1 is connected to the inductive element (such as the inductor L) in the switching power supply, so the collector current Ic flowing through the transistor Q1 is equal to the inductance in the switching power supply Current IL. The specific connection relationship can be, but not limited to, see Figure 10 shown.
[0068] As an illustration of this embodiment, the emitter voltage of the transistor Q1 can be sampled on the emitter of the transistor Q1 as the sampling voltage signal Vcs of this embodiment. For details, see Figure 6-8 show...
Embodiment 2
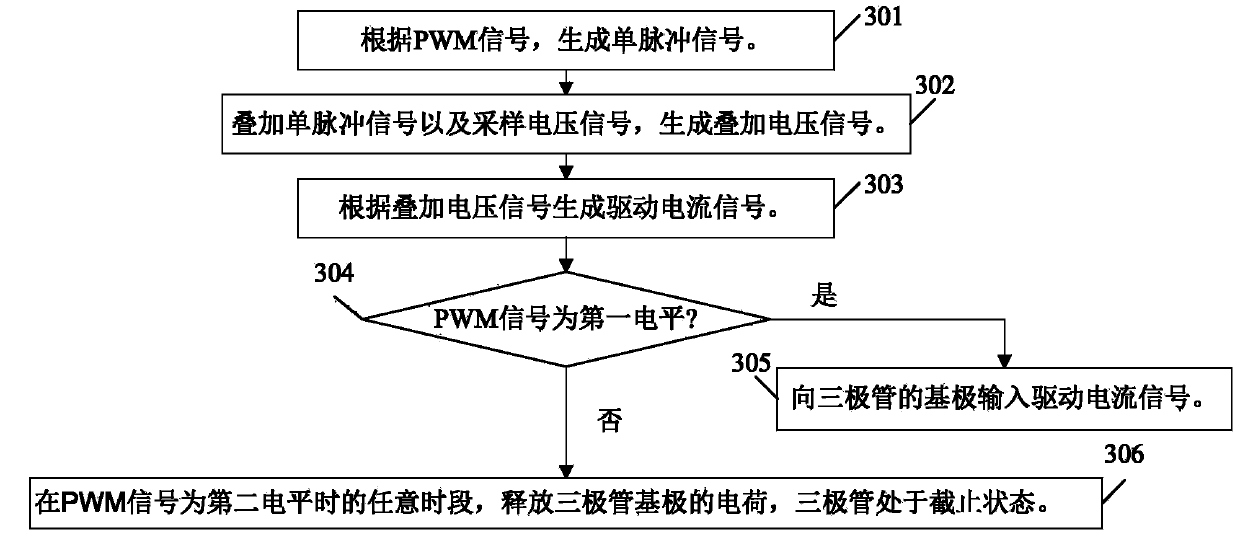
[0080] image 3 For the flow diagram of a switching control method suitable for switching power supplies provided in Embodiment 2, see image 3 As shown, the process of this embodiment mainly includes the following steps:
[0081] Step 301: Generate a single pulse signal according to the PWM signal.
[0082] As an illustration of this embodiment, specifically, a single pulse signal (denoted as Vm) may be generated according to the trigger of the first transition edge of the PWM signal, and the period of the single pulse signal Vm is consistent with the period of the PWM signal.
[0083] Wherein, the first transition edge of the PWM signal is: a transition edge transitioning from the second level to the first level.
[0084] for example Figure 9 As shown, when the second level is low and the first level is high, the first transition edge is the rising edge of the PWM signal.
[0085] When the second level is high level and the first level is low level, the first transition...
Embodiment 3
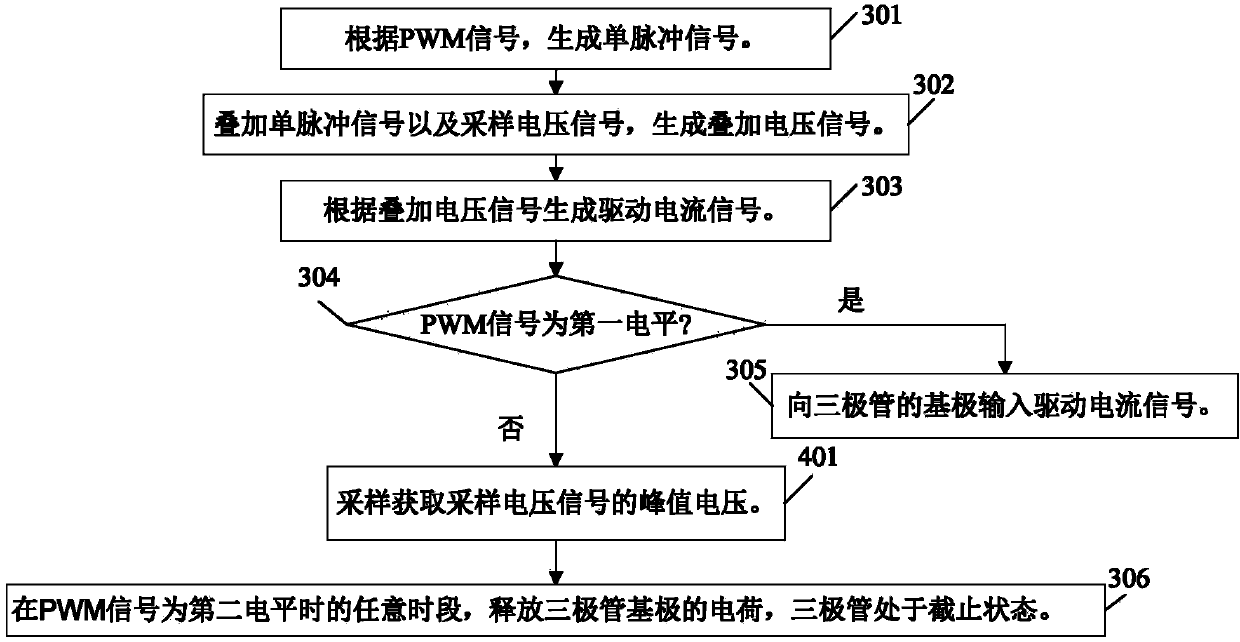
[0101] Figure 4 It is a schematic flowchart of a switching control method suitable for switching power supplies provided in this embodiment. see Figure 4 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and embodiment 2 mainly lies in:
[0102] Also further include before step 306:
[0103] Step 401: Sampling and acquiring the peak voltage of the sampling voltage signal.
[0104] When the PWM signal is at the first level, the emitter current Ie of the transistor Q1 is the superposition of the base current Ib of the transistor Q1 and the collector current Ic of the transistor Q1. The signal Vcs contains not only the information of the collector current Ic, but also the information of the base current Ib, which cannot accurately represent the information of the collector current Ic, that is, the information of the inductor current IL of the switching power supply.
[0105] And when the PWM signal is at the second level, the drive current signal Ib input to the base of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com