Bridge head structure for controlling bump at bridge head
A technology of pavement structure and abutment, which is applied in the direction of bridges, bridge parts, bridge construction, etc. It can solve the problems that the bridge structure is easily damaged, damaged, and the bonding integrity of the pavement layer and the abutment is poor, so as to achieve a good prevention of settlement Effect, overcoming weak links, and eliminating the effect of jumping phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] In order to describe the present invention in more detail, the technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
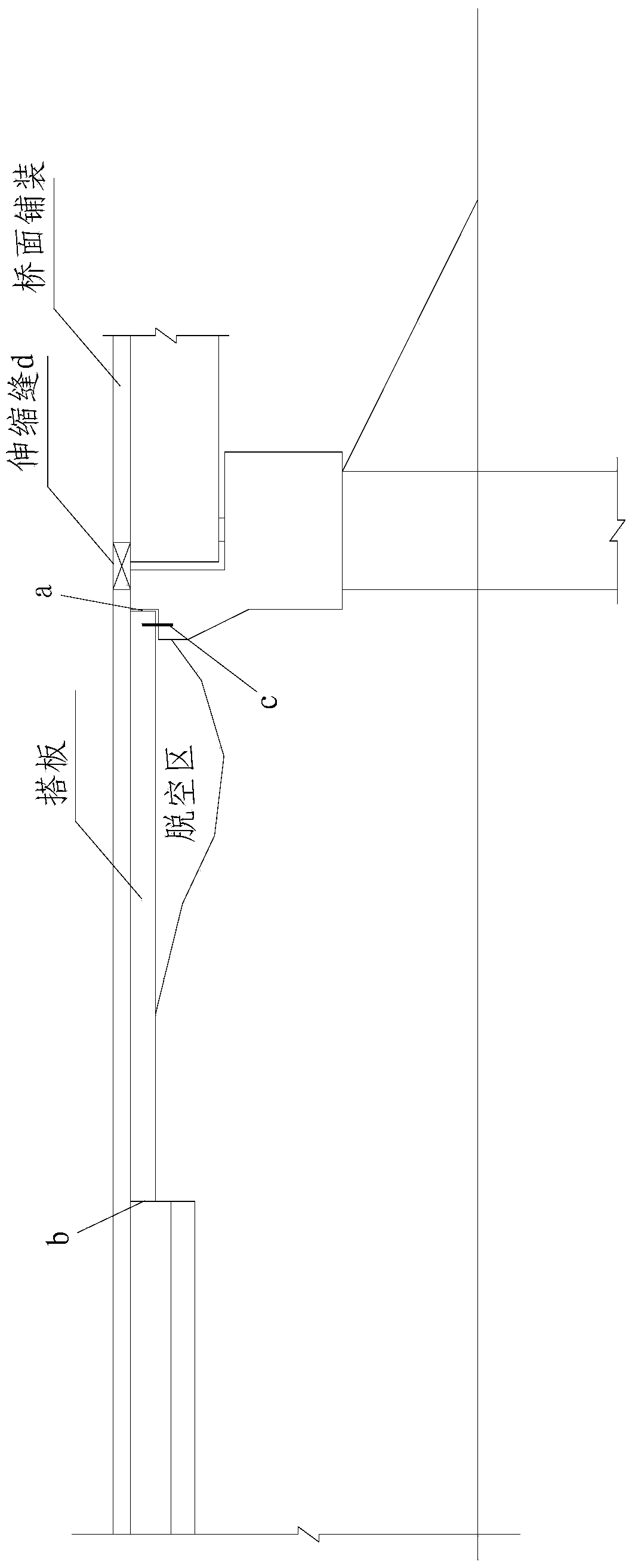
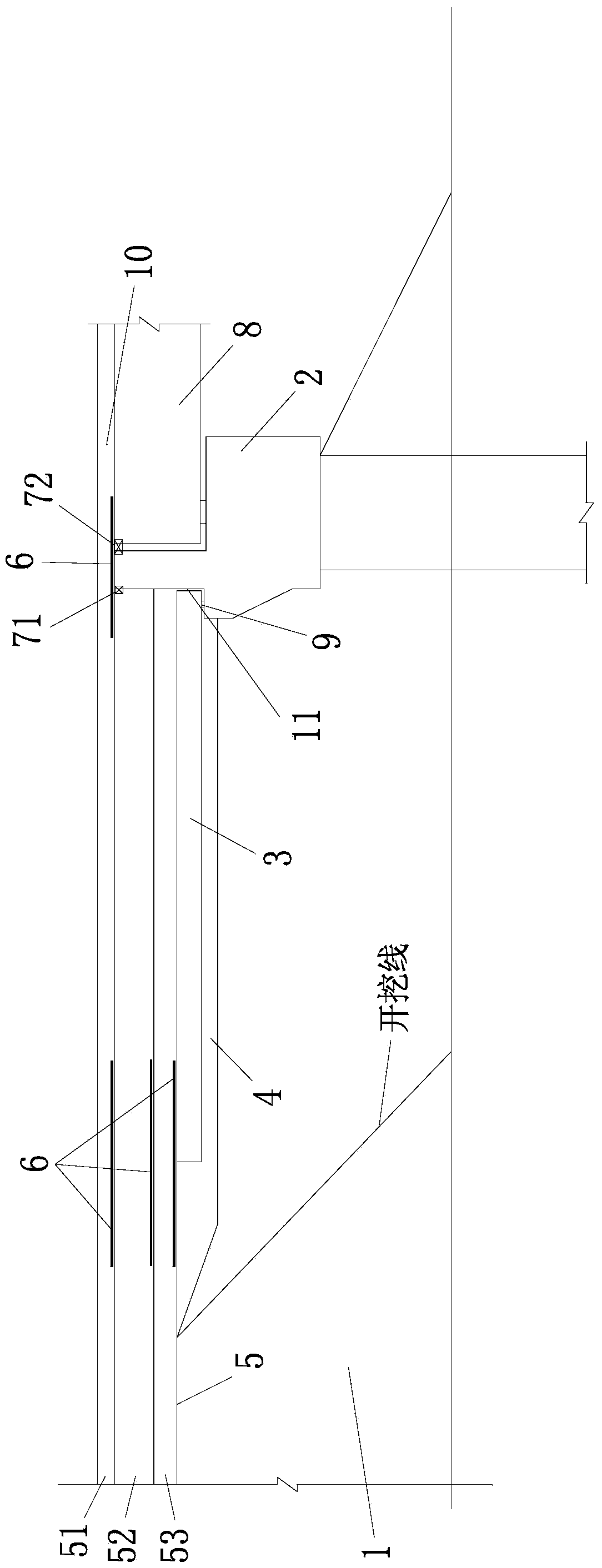
[0039] Such as figure 2 As shown, a bridge head structure used to treat bridge head bumping includes bridge abutment 2, beam slab 8, subgrade 1, pavement structure layer 5, bridge head slab 3, and bridge deck paving layer 10, and the pavement structure layer 5 is from below The upper part includes a base layer 53, a base layer 52 and a surface layer 51; the bridge head abutment 3 is set between the subgrade 1 and the base layer 53, and one end is laid on the corbel of the bridge abutment 2; a cushion layer 4 is provided under the bridge head abutment 3 There is a shrinkage joint 71 between the base layer 52 and the 2 abutment backs of the abutment, a water-stop expansion joint 72 is provided between the 2 abutment backs and the girder 8 and the surface layer 51 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com