A Finite Arbitrary Frequency Difference Reflection Control Method for Microwave Signals
A control method, microwave signal technology, applied in the direction of amplitude to angle modulation and conversion, which can solve the problems of limited simulation range, continuous cable and cable, discontinuous frequency difference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In the present invention, the input signal is coupled out one way, and after wave detection, it is collected by DAC, and then after data processing, power detection is performed. If the power is large, a corresponding voltage is inserted through DAC, and attenuated by a voltage-controlled attenuator. , then remain unchanged, and finally adjusted to match the suitable power range of the IQ modulator, and used as the local oscillator signal input of the IQ modulator. The required frequency difference digital signal is generated by FPGA or an equivalent digital circuit. After digital-to-analog conversion by DAC, it is divided into sin signal and cos signal. After multiplication in the IQ modulator, a single sideband signal and carrier and image frequency signals are suppressed to a certain extent. The signal output by the IQ modulator passes through a multi-stage power attenuator and an amplitude stabilization loop, and is output after being adjusted to the power required ...
Embodiment 2
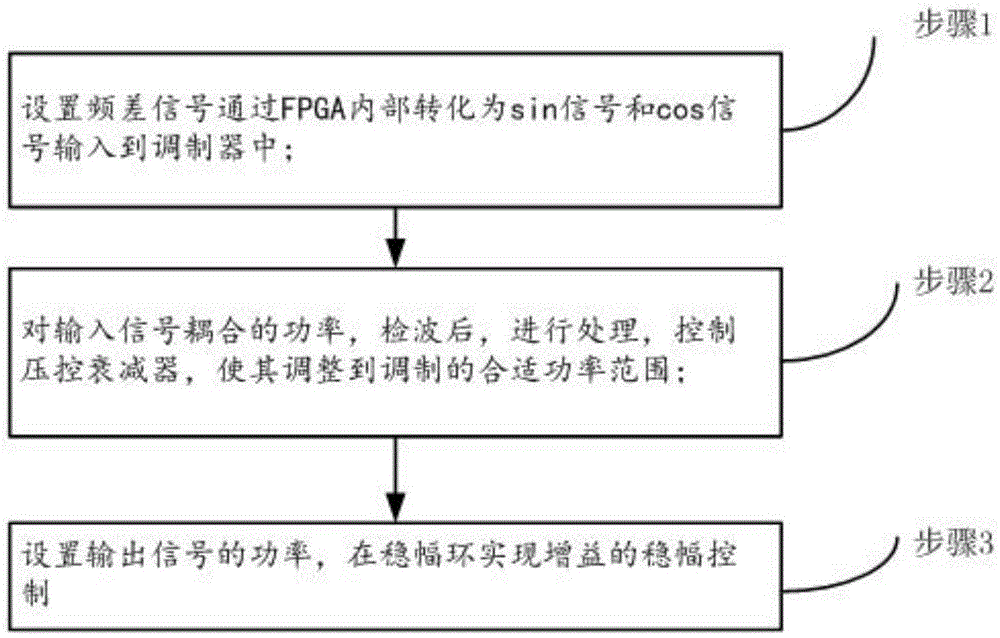
[0039] On the basis of above-mentioned embodiment, further as figure 1 As shown, a limited arbitrary frequency difference reflection control method for microwave signals is provided, which includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1, set the frequency difference signal to be converted into a sin signal and a cos signal through the FPGA and input to the IQ modulator;
[0041] Step 2, after detecting the coupled power of the input signal, process it, and control the voltage-controlled attenuator to adjust it to a suitable power range for modulation;
[0042] In step 3, the power of the output signal is set, and the amplitude stabilization control of the gain is realized in the amplitude stabilization loop.
[0043]Step A1 is also performed after the step 1: the amplitude, phase and delay setting of the two-way signals of the IQ modulator are calibrated by adjusting the digital value through the FPGA.
[0044] In the step 1, the sin signal and the cos signal are multiplied in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com