Visual navigation method based on SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) algorithm
A visual navigation and algorithm technology, applied in the field of visual navigation based on the SIFT algorithm, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory computer real-time processing speed, difficulty in applying small and medium-sized robots, and large errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
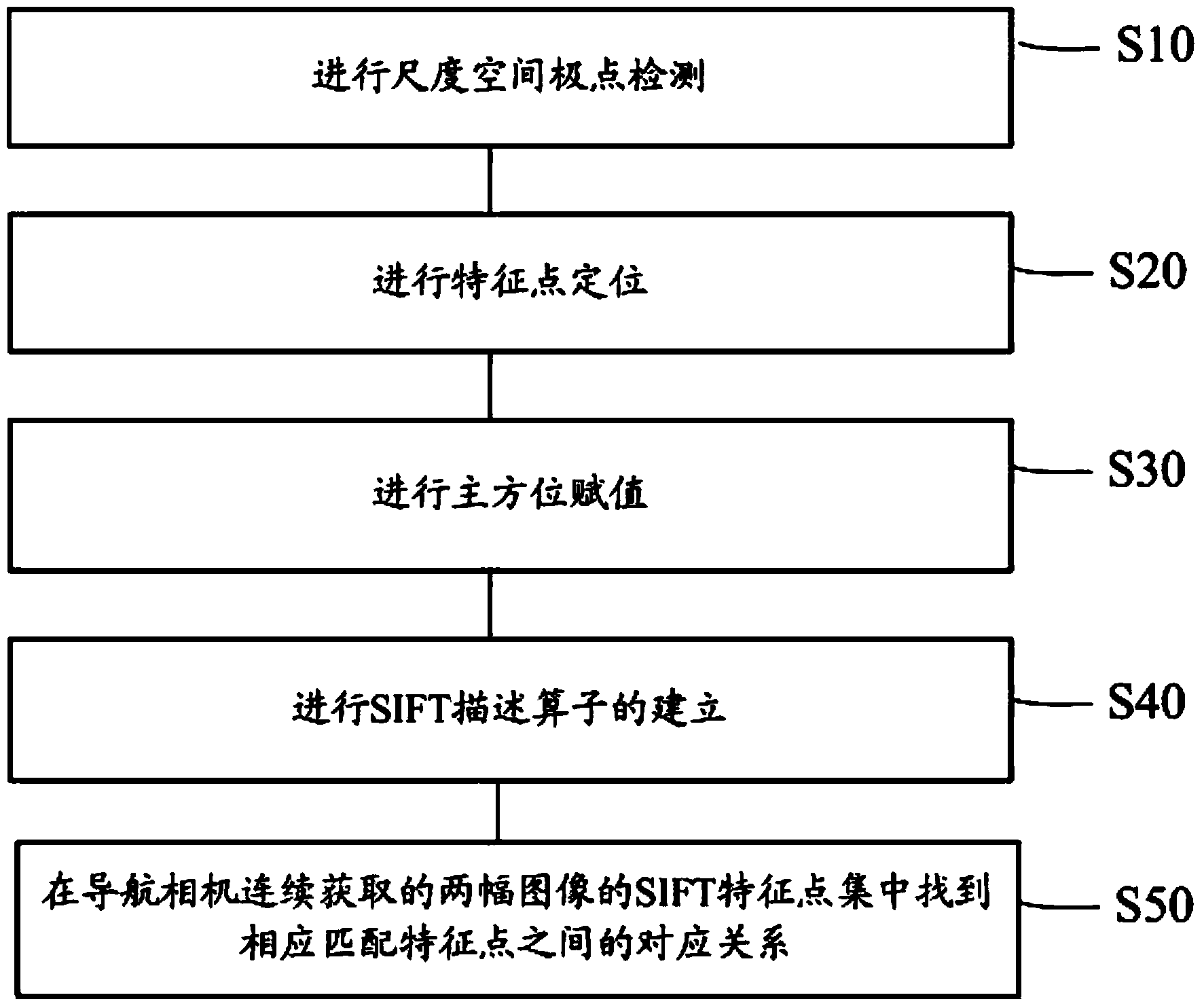
[0030] In order to make the content of the present invention clearer and easier to understand, the content of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
[0031] The present invention overcomes the deficiencies of the above-mentioned methods in the prior art, uses the SIFT algorithm to realize feature extraction and tracking of natural landmarks, determines the position of the robot according to the position information of natural landmarks in the image sequence, and adopts dynamic extended Kalman filtering and inertial navigation system parameters In order to realize the correction of the error of the inertial navigation system by visual navigation information, obtain accurate navigation coordinates, and at the same time, achieve the characteristics of miniaturization and low cost, so as to improve the practicability in small and medium-sized robots.
[0032] Specific embodiments of the present in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com