Paddy rice leaf color control gene OscpSRP54 and protein encoded by same
A protein and gene technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of leaf color genes to be identified
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Isolation and genetic analysis of mutants
[0028] Through the screening of the rice (IR64) mutant library induced by EMS, a rice leaf color mutant HM14 was isolated and obtained. figure 1 shown). The mutant HM14 was crossed with Moroberekan to obtain F1. The F1 plants had normal leaf color phenotypes. The segregation ratio of the wild-type and mutant phenotypes in the F2 generation was consistent with the segregation ratio of the Mendelian single recessive mutation, indicating that the mutant HM14 The light green leaf phenotype is controlled by a single recessive gene.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Fine Mapping of Mutant Genes
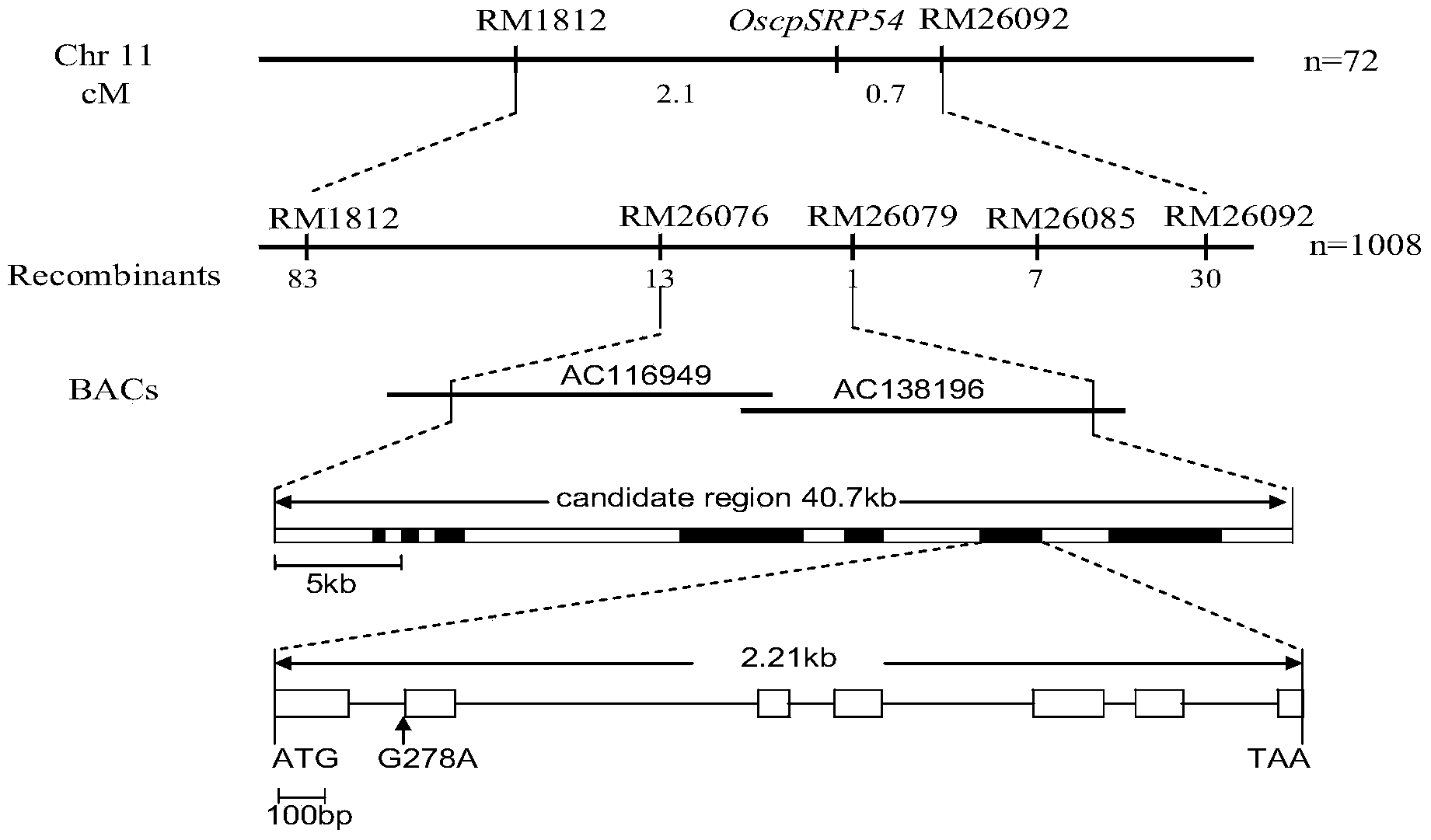
[0030] According to the published molecular genetic maps of japonica and indica rice, SSR primers approximately uniformly distributed on each chromosome were selected for polymorphism detection and preliminary location analysis, and the mutant phenotype was found in the F2 population obtained by crossing mutant HM14 with Moroberekan A total of 1008 F2 individuals with mutant phenotype were identified, and 72 of them were used as the initial mapping population. The preliminary mapping results showed that the mutant gene was located between RM1812 and RM26092 on the short arm of chromosome 11.
[0031] The primers RM26076, RM26079 and RM26085, which were polymorphic between the parents between RM1812 and RM26092, were screened, and these 5 pairs of primers were used to analyze the mutant individuals in 1008 F2 populations, and the obtained information was used to construct a physical map. Finally, the mutated gene was finely ma...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Gene prediction and sequence comparison analysis
[0033] According to the results of fine mapping, 8 predicted genes in this interval were analyzed, and a gene cpSRP54 encoding chloroplast signal recognition granule protein was found. Sequencing found that the last base in the first intron of the gene in the mutant HM14 was mutated, which may affect the normal splicing, so the gene was designated as a candidate gene and named OscpSRP54.
[0034] Utilizing RT-PCR technology, using primer pair SEQ ID No.3 (TCGCTCATCGGCAATGGA) and SEQ ID No.4 (TTCCACGGCATTCTTGGTTATT) to amplify cDNA, compare the fragment size of OscpSRP54 gene in wild type and mutant HM14, the experiment confirmed that the base The base mutation caused the retention of the first intron in the mutant, and its amplified fragment was 119bp larger than the normally spliced wild type (such as Figure 5 shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com