Method for preparing rare-earth modified zinc-iron composite oxide catalyst and application of catalyst in reaction of preparing butadiene from butene
A composite oxide and catalyst technology, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as low yield and impact on butadiene yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0041] Reactivity of Rare Earth-Free Zn-Fe Catalysts
[0042] 7.44g zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O) was dissolved in 15mL deionized water, and the corresponding molar amount of ferric nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O) dissolved in 20mL deionized water, at the same time. Mix the two solutions to obtain a zinc-iron mixed solution. Mix 50mL of ammonia solution with a mass fraction of 17% and 300mL of deionized water to prepare a pH=12 alkaline precipitant.
[0043] Use a peristaltic pump to slowly drop the zinc-iron mixed solution into the ammonia precipitation agent for co-precipitation. The dropwise addition time is 2 hours, and the magnetic stirring is maintained during the dropwise addition process and the constant temperature water bath is 30°C. After the co-precipitation is completed, continue to keep the constant temperature water bath for aging for 6 hours. After the supernatant was poured out, it was washed repeatedly with deionized water u...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0048] Preparation of rare earth-modified zinc-iron composite oxide catalysts: Specifically, in order to prepare rare earth-modified zinc-iron composite oxide catalysts composed of three metal components with different contents of rare earth, zinc and iron, rare earth: zinc: iron The molar ratio was set at 0.01˜1:0.5˜2:1˜8, thereby preparing fourteen kinds of catalysts. 10.8g lanthanum nitrate hexahydrate (La(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) or cerium nitrate (Ce(NO 3 ) 3 ) was dissolved in 50 mL of deionized water, and stirred to dissolve. Zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O) and ferric nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O) were dissolved in 50mL distilled water, stirred to dissolve. Then the rare earth solution, zinc solution and iron solution are mixed and stirred thoroughly. In addition, 100 mL of ammonia solution with pH=14 was prepared with ammonia solution with a mass fraction of 17%. In a water bath at a constant temperature of 90° C. under magnetic stirring...
Embodiment 1
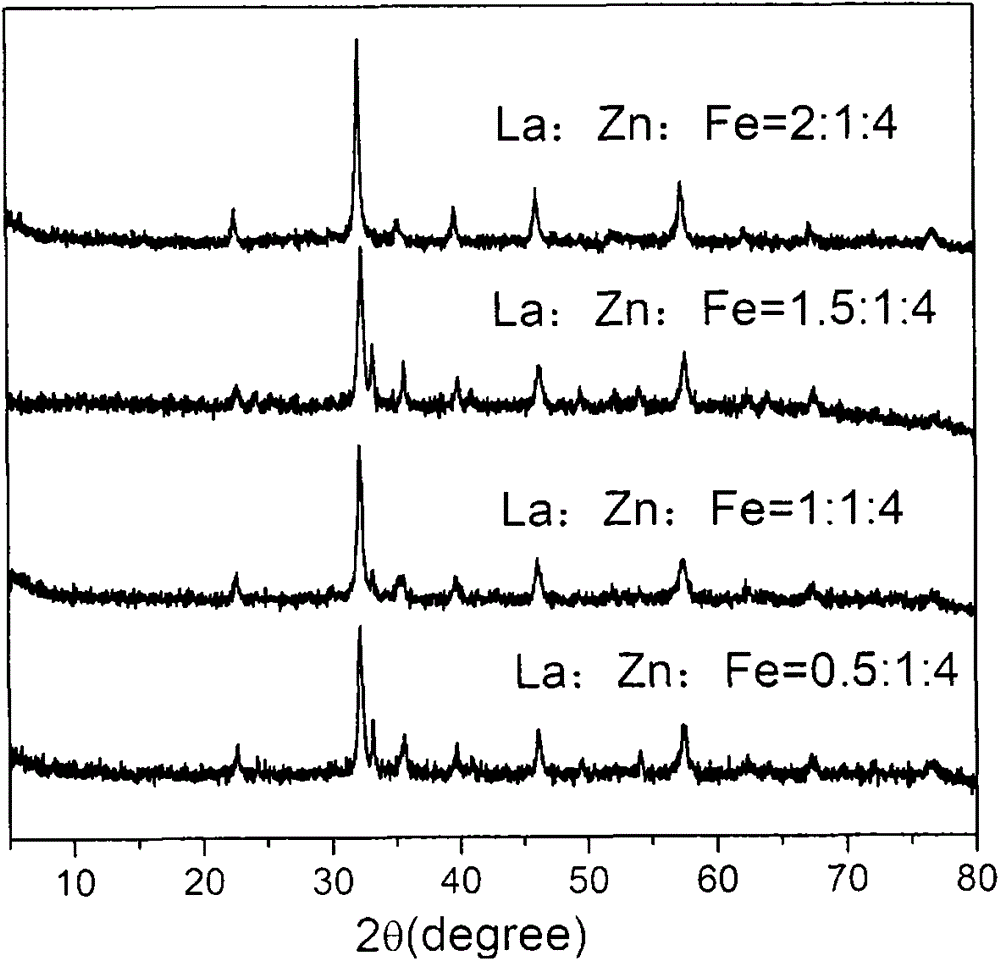
[0055] Oxidative dehydrogenation of butene on the zinc-iron oxide catalyst: The zinc-iron composite oxide catalyst produced in Preparation Example 1 was used to carry out the oxidative dehydrogenation of butene under the following conditions. The XRD diffraction pattern shows that the catalyst is ZnFe-containing 2 o 4 and α-Fe 2 o 3 zinc-iron composite oxides (participated in figure 1 ). At 380°C, the molar ratio of butene:air:steam is 1:0.4:8, and the gas hourly space velocity is 300h -1 The activity of the catalyst is shown in the table below
[0056] Table 3 Zinc-iron oxide catalyst activity varies with the iron ratio in the catalyst
[0057]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com