A composite layer slow-release chemical fertilizer and its preparation method
A compound layer and chemical fertilizer technology, applied in fertilization devices, fertilizer mixtures, applications, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, unfavorable for large-scale promotion and application, difficulty in controlling the slow release rate, and expensive coating materials, so as to facilitate the promotion of industrialization The effect of short application and process cycle and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
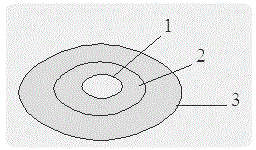
[0031] like figure 1 As shown, a compound layer slow-release chemical fertilizer is coated with a first coating layer and a second coating layer in sequence on the dry original fertilizer 1 particle surface, and the first coating layer is a sub-hydrophobic modified layer 2 , the second coating layer is a hydrophobic modification layer 3 .
[0032] Preparation:
[0033] The first step: drying chemical fertilizer: put a certain quality of urea in an oven, and dry it at 80°C for 3 hours to obtain the inner layer;
[0034] The second step: preparation of oxidized molasses starch ester (SME glue): add 100 parts by mass of corn starch and beet oxidized molasses (the mass ratio of starch to oxidized molasses is 1:1) mixture into the reactor, at 30 °C, the frequency 60MH Z Next, ultrasonic vibration for 30min. Obtain a brown viscous liquid, filter out the solid acid catalyst to obtain SME glue, cool it for later use;
[0035] The third step: making sub-hydrophobic modified layer...
Embodiment 2
[0038] like figure 1 As shown, a compound layer slow-release chemical fertilizer is coated with a first coating layer and a second coating layer in sequence on the dry original fertilizer 1 particle surface, and the first coating layer is a sub-hydrophobic modified layer 2 , the second coating layer is a hydrophobic modification layer 3 .
[0039] Preparation:
[0040] The first step: dry chemical fertilizer: put a certain quality of ammonium bicarbonate in an oven, and dry it at 80°C for 3 hours to get the inner layer;
[0041] Step 2: Preparation of oxidized molasses starch ester (SME glue): add 100 mass parts of corn starch and beet oxidized molasses (the mass ratio of starch to oxidized molasses is 1:1) mixture into the reaction kettle, at 30 ° C, the frequency 80MH Z Next, ultrasonic vibration for 20min. Obtain a brown viscous liquid, filter out the solid acid catalyst to obtain SME glue, cool it for later use;
[0042] The third step: making the sub-hydrophobic mod...
Embodiment 3
[0045] like figure 1 As shown, a compound layer slow-release chemical fertilizer is coated with a first coating layer and a second coating layer in sequence on the dry original fertilizer 1 particle surface, and the first coating layer is a sub-hydrophobic modified layer 2 , the second coating layer is a hydrophobic modification layer 3 .
[0046] Preparation:
[0047] The first step: make dry chemical fertilizer: put a certain quality of potassium sulfate in an oven, and dry it at 150°C for 1 hour. get the inner layer;
[0048] The second step: making oxidized molasses starch ester (SME glue): add 100 parts by mass of corn starch and sugarcane oxidized molasses (the mass ratio of starch to oxidized molasses is 1:1) mixture into the reaction kettle, at 30 ° C, the frequency 40MH Z Next, ultrasonic vibration for 60min. Obtain a brown viscous liquid, filter out the solid acid catalyst to obtain SME glue, cool it for later use;
[0049] The third step: making the sub-hydro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com