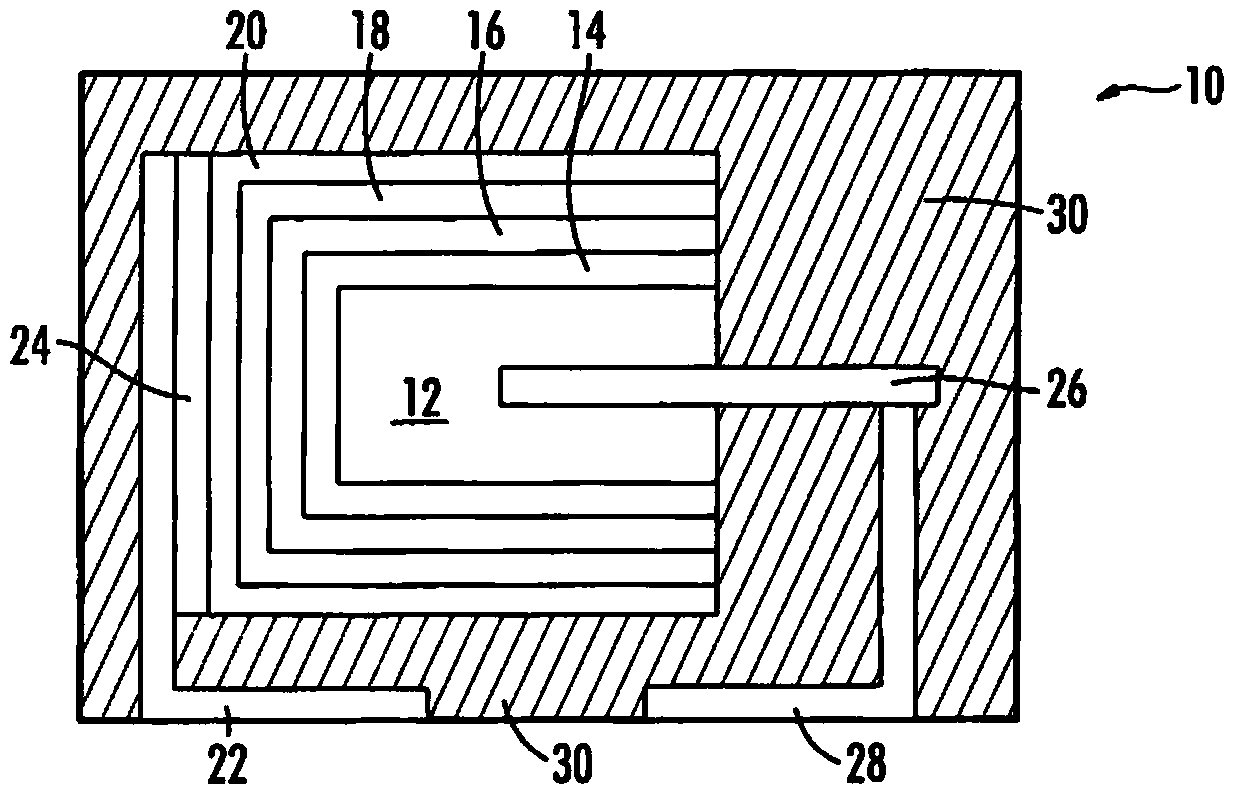
Conductive polymer dispersions for solid electrolytic capacitors
A conductive polymer, conductive polymer layer technology, applied in the field of improved cathodes, the manufacture of inherently conductive polymer dispersions, and improved capacitors, which can solve problems such as high leakage, low operating voltage, exposure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] A part was prepared in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1 except that a hydrophilic polymer polyethylene oxide (marked as HL) was used to prepare a conductive polymer dispersion. A conventional graphite coating is applied followed by a silver layer. The parts were assembled and the ESR measured before and after surface mounting. The relationship between the moisture content and the leakage current was measured, and it is described in Table 2.
Embodiment 2
[0092] A part was prepared in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1 except that an oligomer having hydroxyl and carboxyl groups (marked as HP) available for crosslinking was used to prepare a conductive polymer dispersion. A conventional graphite coating is applied followed by a silver layer. The parts were assembled and the ESR measured before and after surface mounting. The relationship between the moisture content and the leakage current was measured, and it is described in Table 2.
[0093] Table 2
[0094]
Embodiment 3
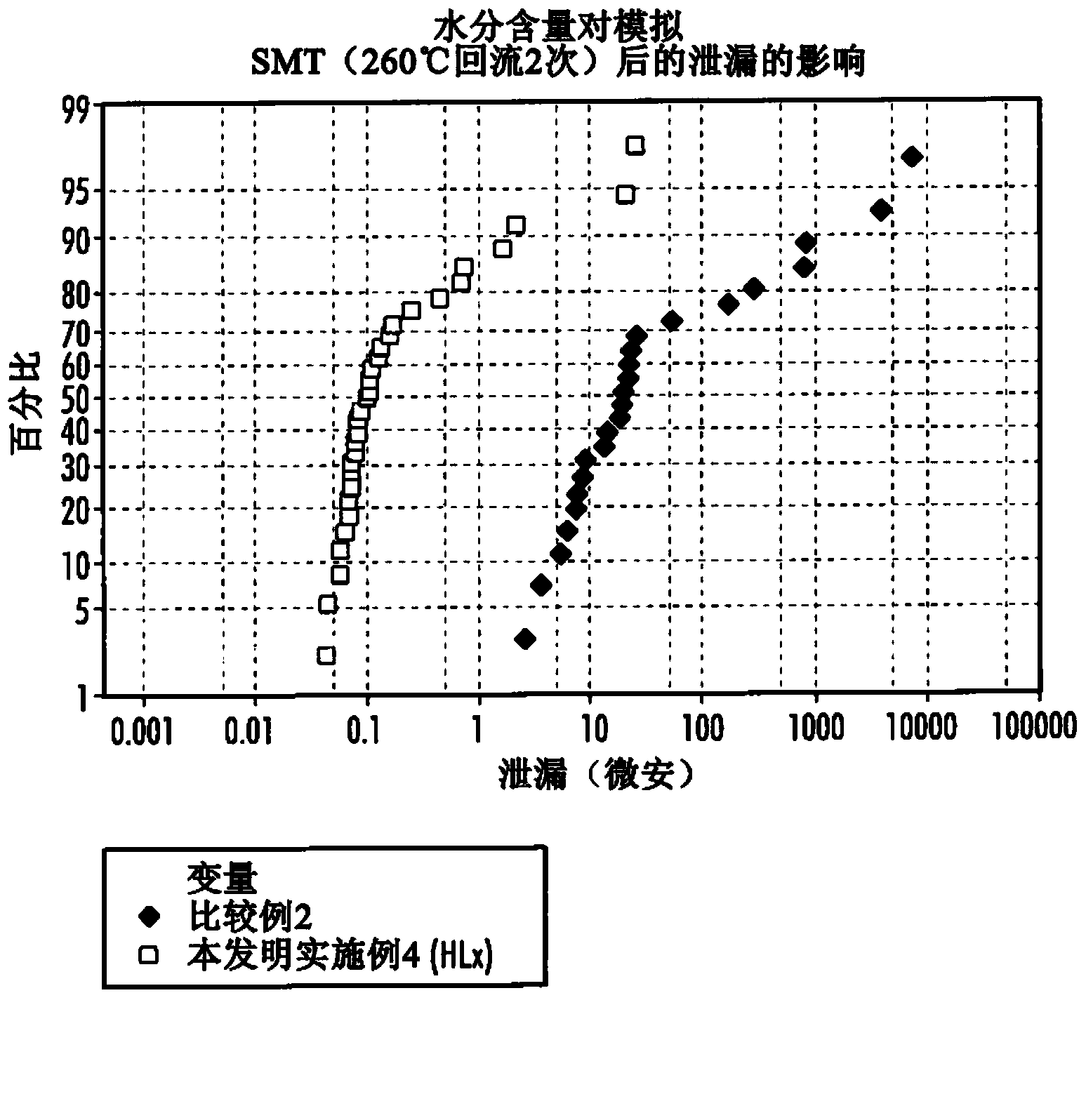
[0096]A part was prepared in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1, except that a conductive polymer dispersion was prepared using a polymer mixture containing polyethylene oxide, polyvinyl alcohol, and hydroxyethyl cellulose (marked for HLx). A conventional graphite coating is applied followed by a silver layer. The parts were assembled and the ESR measured before and after surface mounting. The moisture content measured by the Karl Fischer method was 24% by weight, while that of Comparative Example 2 was 18% by weight. After a post-simulation SMT (two cycles) at 260 °C, the effect of moisture content on leakage is in image 3 displayed in .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| critical surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com