Microdochium bolleyi F10 strain microbial inoculum as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of bacterial strains and bacterial agents, which is applied in the field of plant diseases in Ming Dynasty, can solve the problems of high toxicity, no resistance to nematodes, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of labor saving, strong parasitic effect, and simple application methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
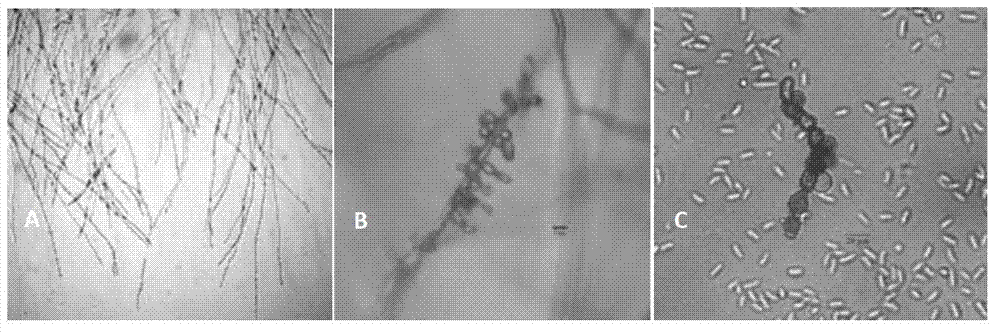
[0041] Embodiment 1: Isolation and identification of bacterial strain
[0042] 1. Isolation location and isolation method of the strain:
[0043] The diseased soil where wheat cyst nematode occurred was collected from Niushou Town, Xiangfan City, Hubei Province, and the nematode cysts in the soil were separated by floating. Put a sterilized circular qualitative filter paper + cellophane on the bottom of a petri dish with a diameter of 90 cm, sterilize the surface of the cysts in 70% (volume ratio) ethanol for 2 min, soak in sterile water for 2 min, and place on the filter paper to keep it moist at 25 °C Culture 5d. The fungal hyphae grown from the cysts were purified and cultured on a PDA plate, and the strain was transferred to a PDA slant, and stored in a 4°C refrigerator for later use. The strain was sent to the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) located in Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei Province for preservation on May 7, 2012, and its preservation number i...
Embodiment 2
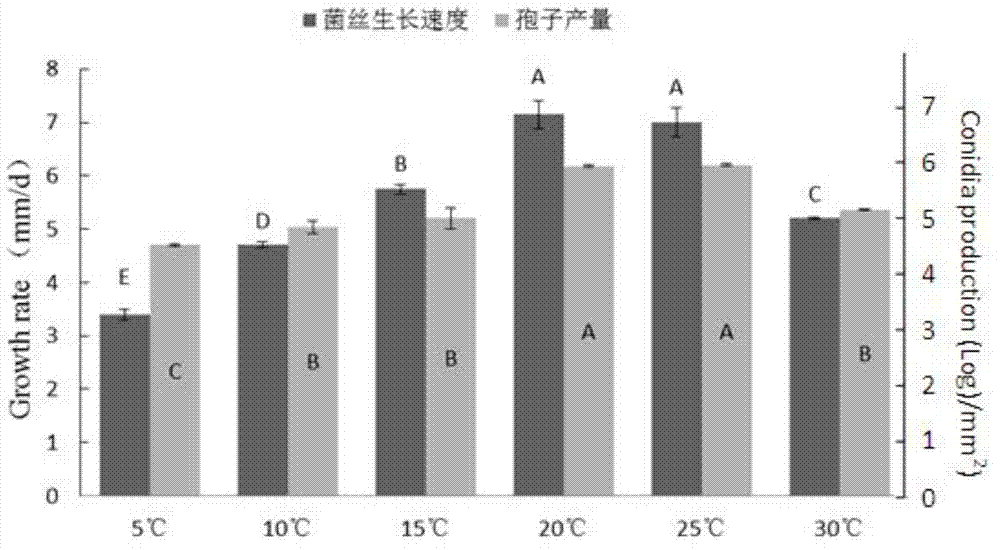
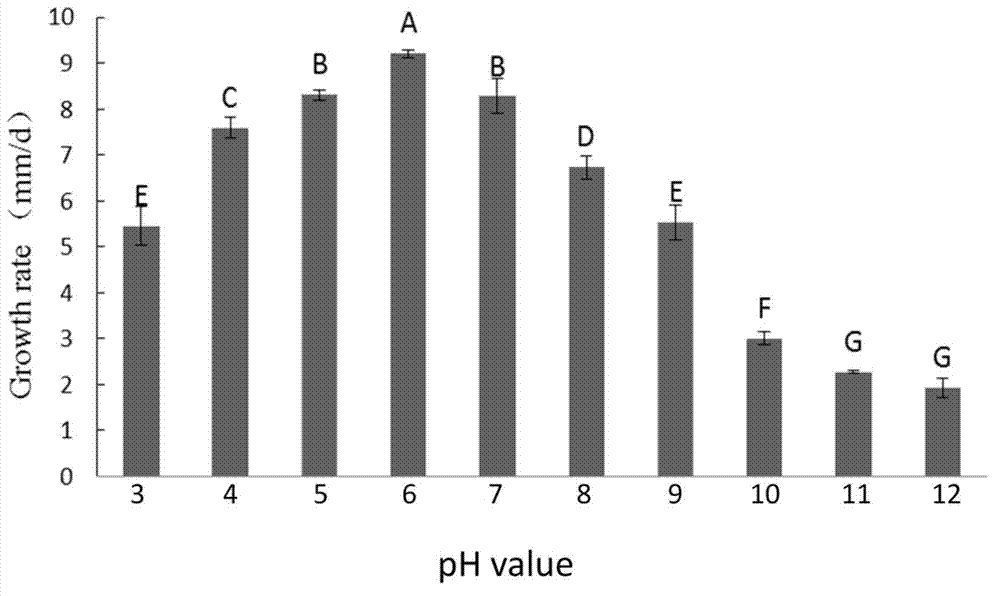
[0053] Embodiment 2: Research on the biological characteristics of bacterial strain F10 of the present invention
[0054] 1. The influence of temperature on the growth and sporulation of F10 strain:
[0055] Inoculate F10 on PDA medium, culture at 25°C for 1 day, use a hole puncher (5mm in diameter) to punch out mycelium from the edge of the colony, and transfer it to a Petri dish (90mm in diameter) containing 20ml of PDA In the center, place them at 5°C, 10°C, 15°C, 20°C, 25°C and 30°C for culture respectively, use the cross method, measure the diameter of the colony every 12h, and take out the bacteria with a puncher with a diameter of 6mm in 5 days The silk block was ground, and the yield of conidia per unit area was counted, and 3 replicates were set for each treatment. see results figure 2 , indicating that the F10 strain grows the fastest and produces the largest amount of sporulation under the condition of 20°C-25°C, which is a suitable temperature for growth and spo...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: the parasitic effect of bacterial strain F10 of the present invention on wheat cyst nematode cyst
[0067] The soil without cysts was taken and sterilized by dry heat at 160°C for 2 hours. Put the sterilized soil into plastic cups, 200g per cup, insert 100 cysts of wheat cyst nematodes, and pour the F10 strain spore liquid every 15 days (concentration is 1.3×10 7 ), watering 10ml each time, using sterile water as the blank control, repeated three times, and cultured in the culture room at 20°C in the dark. After 45 days, the cysts were separated from the soil again, the number of cysts was recorded, and the cyst reduction rate was calculated. . Cyst reduction rate = number of control cysts - number of treated cysts / control cysts × 100%. The number of three repeated cysts decreased by 39, 49, and 55, respectively, and that of the control decreased by 5, 4, and 6. The results showed that in sterilized soil, strain F10 could make the cyst reduction rate of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com