Band-gap reference voltage circuit
A reference voltage and circuit technology, applied in the field of bandgap reference voltage circuits, can solve the problems of unusable and high power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
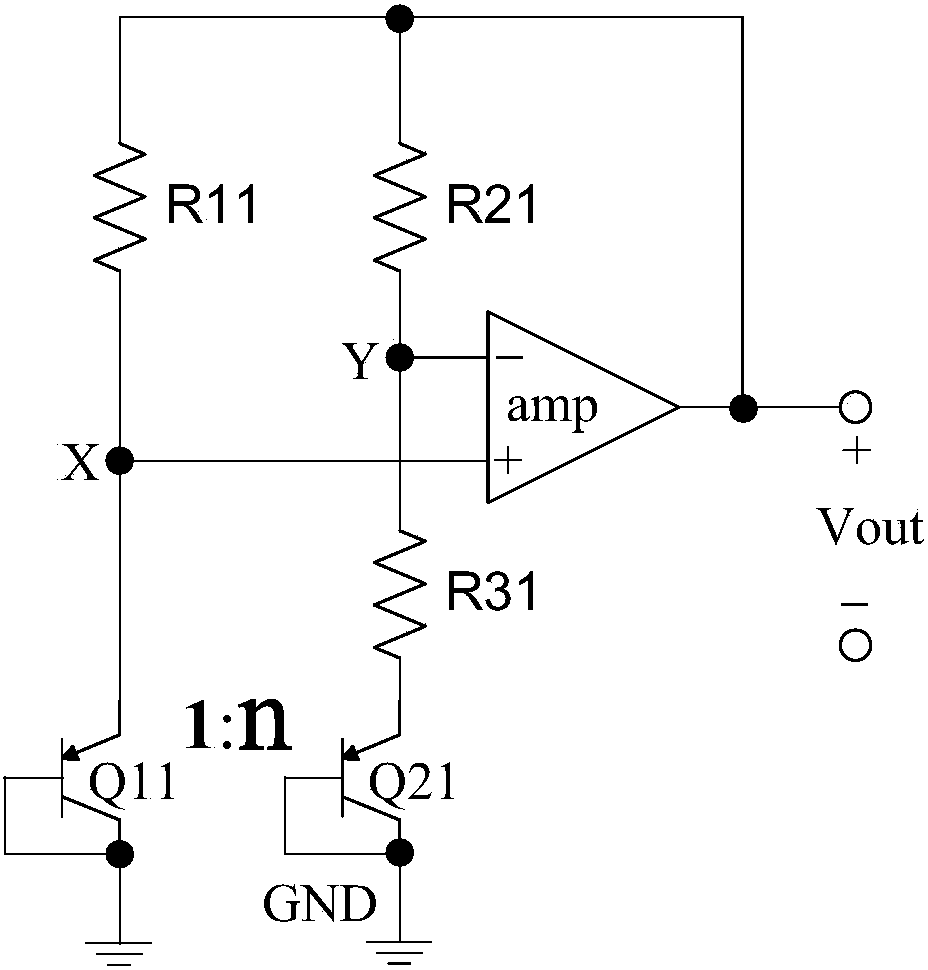
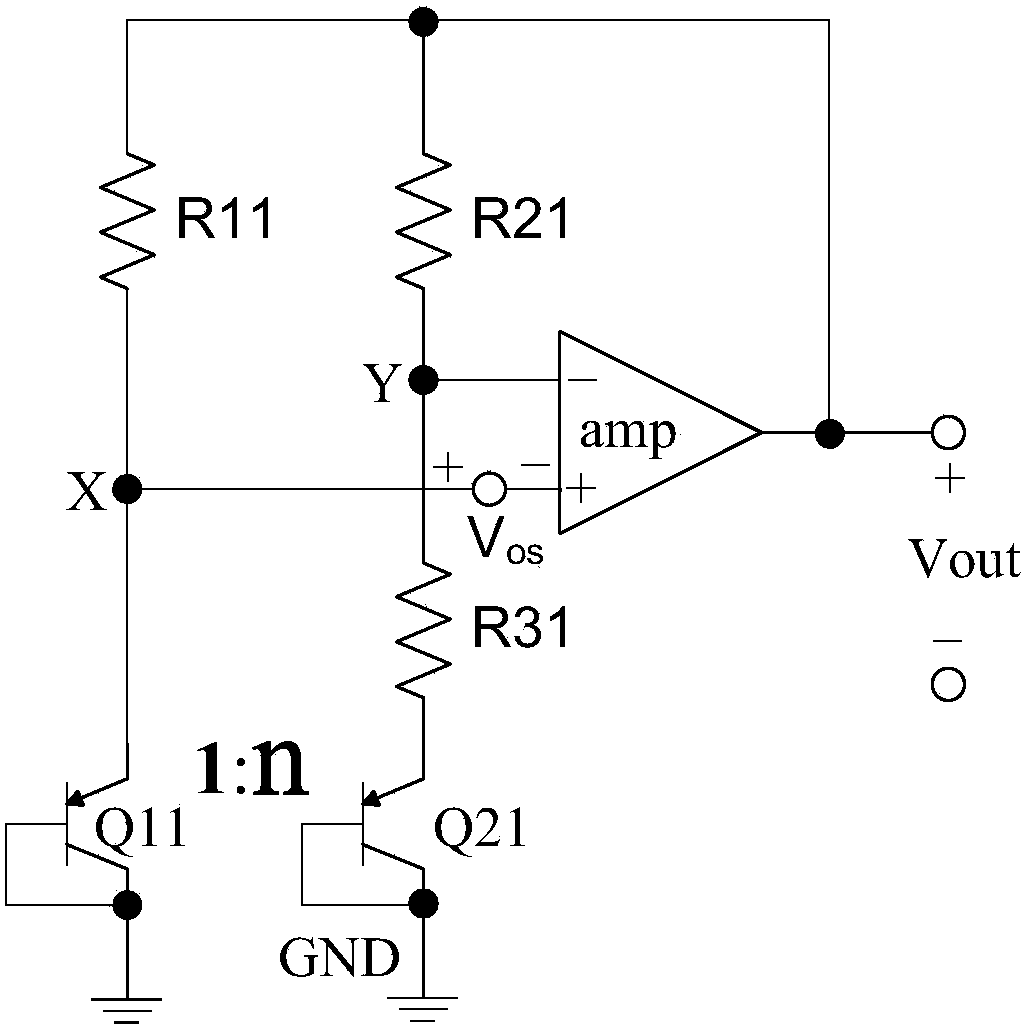
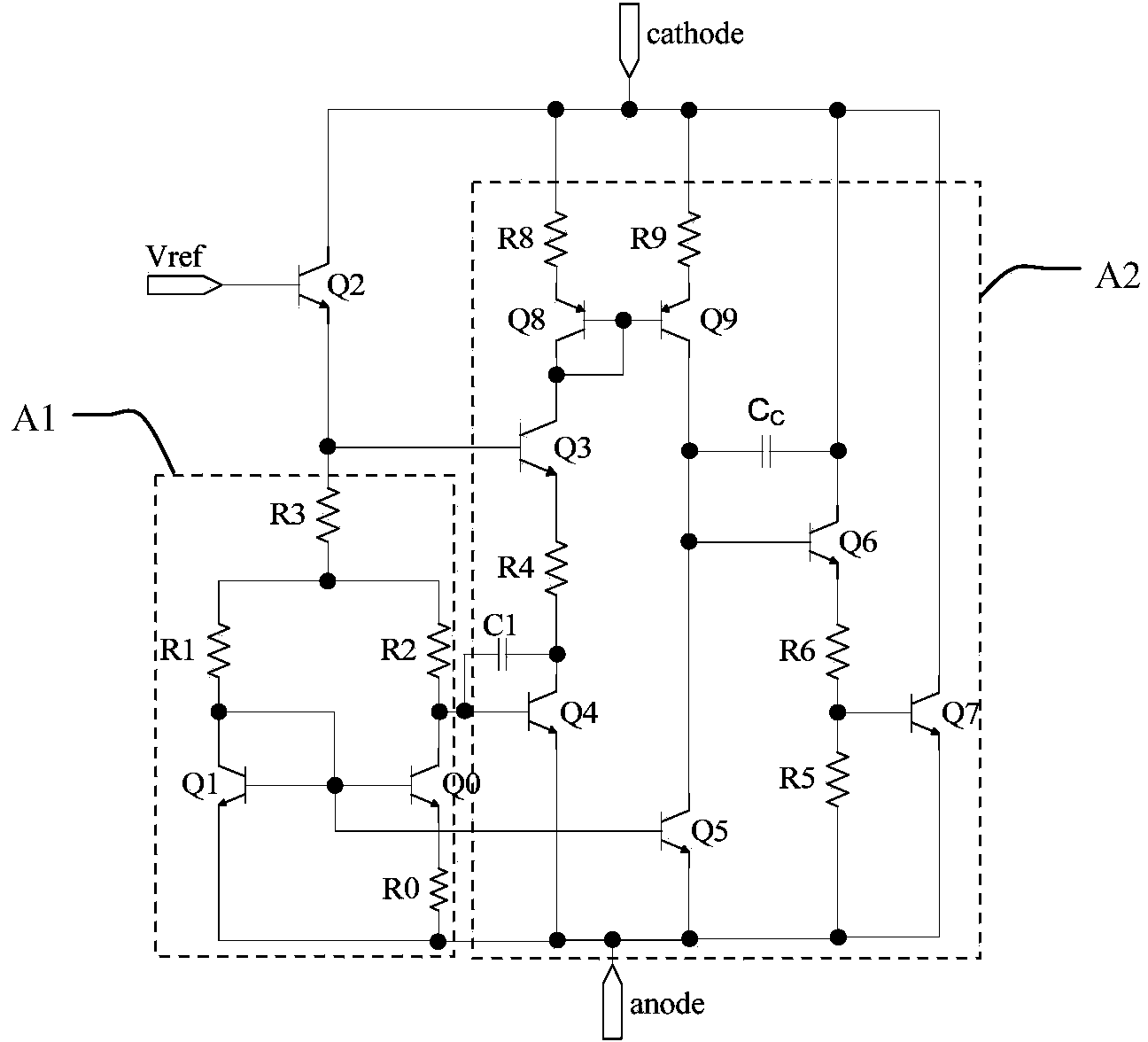
[0058] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the bandgap reference voltage circuit of the first embodiment includes a micro-current source unit A1, a third transistor Q2, a differential amplifier unit A2 and a current source Iref, and is provided with a reference voltage output terminal Vref and an external voltage The power supply terminal VCC of the source.
[0059] The micro current source unit A1 is composed of first and second transistors Q0 and Q1 and first to fourth resistors R0 to R3, one end of the fourth resistor R3 is connected to the second transistor Q1 through the second resistor R1. collector, the other is connected to the collector of the first triode Q0 through the third resistor R2, the connection points of the second, third and fourth resistors R1~R3 form a node ③, the collector and base of the second transistor Q1 pole is connected to the base of the first triode Q0 to form node ①, the emitter of the second triode Q1 is connected to the reference ground terminal G...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the bandgap reference voltage circuit of the second embodiment is basically the same as that of the first embodiment, and their difference is that the bandgap reference voltage circuit of the second embodiment also includes a first voltage dividing resistor R7 and a second voltage dividing resistor R8 , and there is also a reference voltage high-voltage output terminal Vref_H; the first voltage dividing resistor R7 is connected between the reference voltage output terminal Vref and the reference ground terminal GND, and the connection point between the collector of the third triode Q2 and the output terminal of the differential amplifier unit A2 form node It is connected to the reference voltage output terminal Vref through the second voltage dividing resistor R8, and the connection point between the collector of the third transistor Q2 and the output terminal of the differential amplifier unit A2 serves as the reference voltage high voltage ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the bandgap reference voltage circuit of the third embodiment is basically the same as that of the second embodiment, and their difference is that the power supply terminal of the differential amplifier unit A2 is the source of the first and second P-channel MOS transistors MP1 and MP2 The connection point is not connected to the power supply terminal VCC, but to the reference voltage high-voltage output terminal Vref_H, which is the node Because if the reference voltage output by the reference voltage high-voltage output terminal Vref_H is large enough, the first and second P-channel MOS transistors MP1 and MP2 can work in the saturation region, that is, there is sufficient voltage margin. The advantage of this connection is that the power supply rejection ratio of the differential amplifier unit A2 is increased, so that the power supply noise of the output bandgap voltage is small. Because the compensation capacitor Cc is relatively large...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com