Mortierella alpina mutant strain capable of producing high-yield arachidonic acid, and fermentation method and application thereof
A technology of Mortierella alpina and mutant strains, which is applied in the field of microbial technology, can solve problems such as genotoxicity and chronic toxicity, and achieve the effects of easy extraction, good growth characteristics, and increased oxygen-dissolving area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] 60 Coγ-irradiation mutagenesis
[0087] In this experiment, the ARA-producing strain Mortierella alpina200012201-12 (M12 for short, the same below) isolated and screened from Mortierella alpina was used as the starting strain. 60 A high-yield mutant strain of Mortierella alpina was obtained by Co-γ-ray irradiation mutagenesis breeding method. The specific method is as follows:
[0088] First, because the strain seldom produced conidia, the cells that grew well on the plate were selected for mutagenesis. The starting strain M12 was activated, that is, the M12 strain stored on the slant of the test tube in the refrigerator was transferred to the plate medium and cultured at 26°C for 5 days to activate. Then, according to the previous preprocessing experiments, it was found that when 60 When the irradiation dose of Co-γ ray was less than 1kGy, the mutagenic effect was not obvious, the characters of the original strain did not change basically, and the probability of po...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Mutation breeding
[0096] 60 After the Co-γ-ray mutagenesis is over, wrap the plate with black cloth and put it back into the sterile room, separate it in the sterile operating table, pick the irradiated mycelium with an inoculation loop and insert it on the primary screening plate medium, Each mutagenized strain was connected to 5 primary screening plates. And because the plate after mutagenesis is still likely to continue to grow and survive, we numbered it and put it in a constant temperature incubator together with the primary screening plate for cultivation. Taking M12-1-1 as an example, put it in the incubator for cultivation The plate numbers are M12-1-1, M12-1-1-1, M12-1-1-2, M12-1-1-3, M12-1-1-4 and M12-1-1-5 , and so on for the numbers of other primary screening plates. Since there are 24 plates taken for irradiation, there are 144 plates cultured in the incubator. After cultivating for a period of time, first calculate the lethality of strains under diff...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Scanning electron microscope observation of mutant strains
[0107] The Mortierella alpina mutant strains were made into 6 samples respectively cultured for 2-7 days, and at least 5 spray-coated slices were made for each sample, and observed by S-3000N and JSM-6390 scanning electron microscopes (SEM) and take photos.
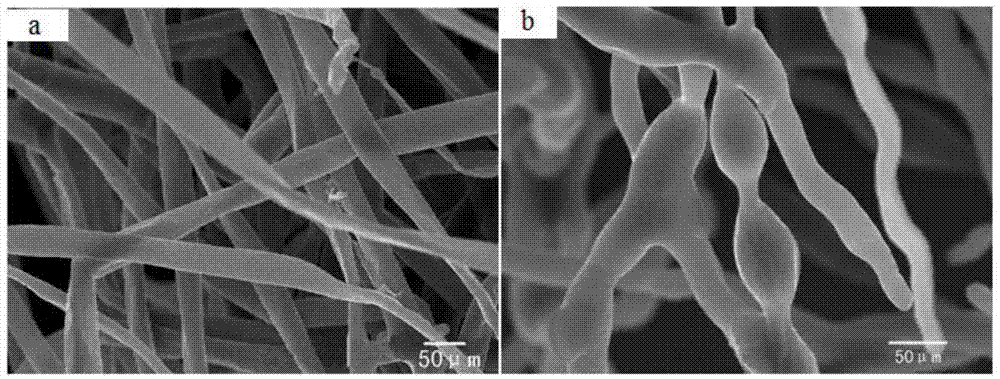
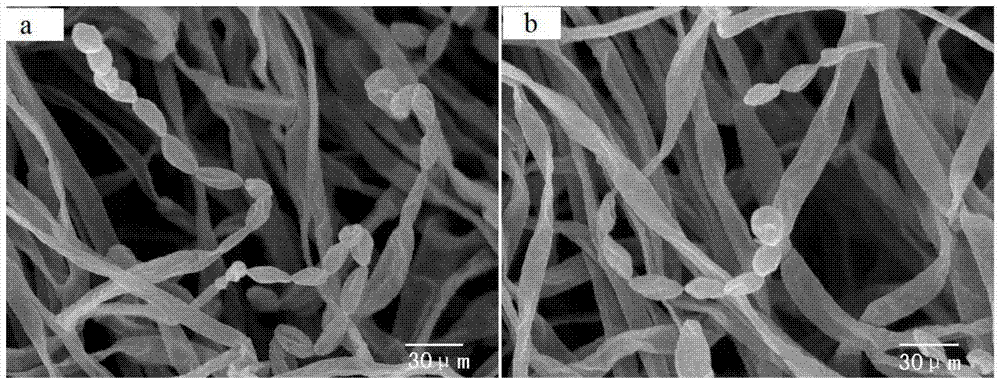
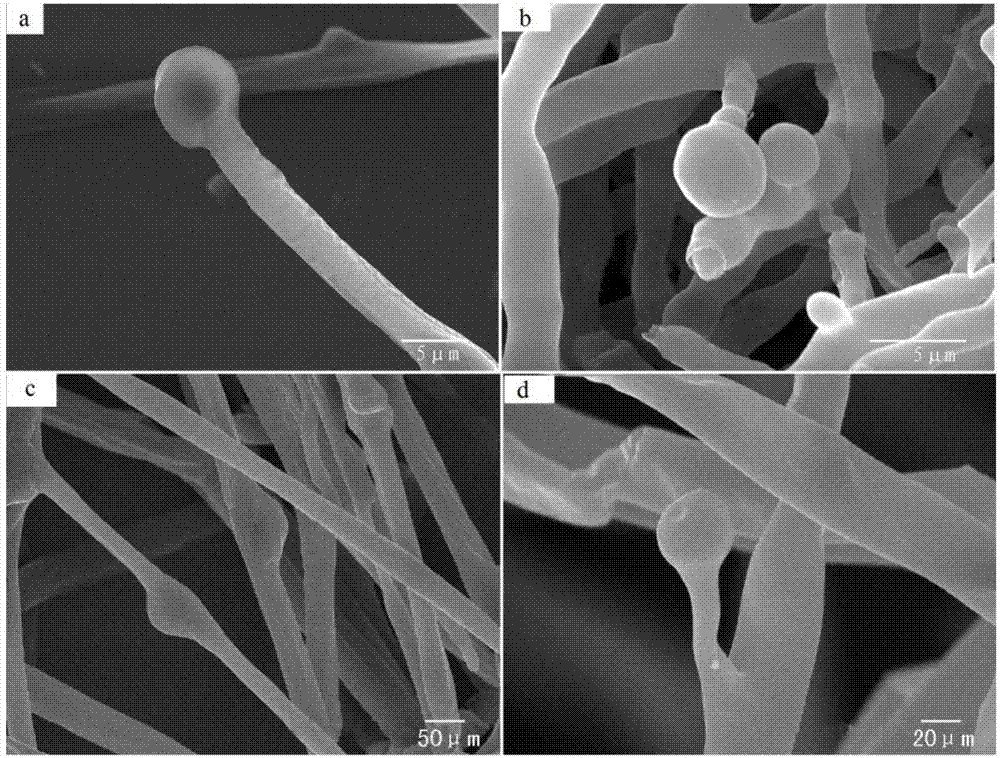
[0108] The mycelium of Mortierella alpina mutant strain is tubular, colorless and transparent, with well-developed mycelia and dense growth, thicker than that of the wild-type strain (the diameter of the wild-type mycelium is 10-20 μm). After 7 days of cultivation, the mycelium diameter up to 30-40μm, and the hyphae are in the shape of lotus root joints ( figure 1 ). The asexual reproduction of wild-type Mortierella alpina relies on asexual spores, and its asexual spores are divided into conidia, stalks, etc. The adult spores of the conidia, stalks, etc. are separated and matured, even under an optical microscope. Many spherical and elliptical conidia ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pov | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com