Preparation method of HEPES (hydroxyethylpiperazine ethane sulfonic acid) molecule guided porous zinc oxide microspheres
A technology of porous zinc oxide and microspheres, applied in the direction of zinc oxide/zinc hydroxide, etc., can solve the problems of increasing process complexity and environmental pollution, and achieve the effects of low price, good repeatability and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 A preparation method for porous zinc oxide microspheres, comprising the steps of:
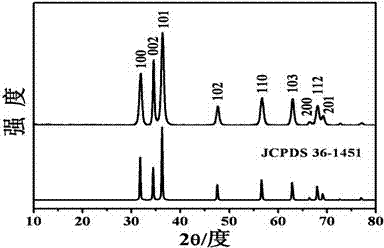
[0024] Dissolve 2 mmol of zinc acetate in 30 mL of triethylene glycol (TEG), sonicate for 10 min to completely disperse the zinc acetate, then add 5 mmol of hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) and place the reaction mixture in the liner 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene stainless steel autoclave, at 150 o C under reaction for 6 hours; after centrifugal washing to remove residual solvent and HEPES, the product was placed at 60 o C and dried for 24 hours, after cooling, porous zinc oxide microspheres with high specific surface area can be obtained. The specific surface area of this sample is 51.9 m 2 / g, the average pore diameter is 30 nm.
[0025] figure 1 It is the diffraction pattern of the sample of Example 1 obtained by Bruker axs D8 type X-ray diffraction analyzer (XRD). It can be seen from the spectrum that the diffraction peaks of the spectrum corresp...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 A preparation method for porous zinc oxide microspheres, comprising the steps of:
[0030] Dissolve 4 mmol of zinc acetate in 50 mL of diethylene glycol (DEG), sonicate for 10 min to completely dissolve the zinc acetate, then add 8 mmol of hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) and place the reaction mixture in the liner 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene stainless steel autoclave, at 150 o Reaction at C temperature for 15 hours; after centrifugal washing to remove residual solvent and HEPES, the product was placed at 60 o C and dried for 24 hours, after cooling, porous zinc oxide microspheres with high specific surface area can be obtained. The specific surface area of this sample is 63.1 m 2 / g, with an average pore size of 5 nm.
[0031] Figure 5 It is a topography diagram of the sample of Example 2 observed by a Hitachi S4800 scanning electron microscope (SEM). It can be seen from the figure that the synthesized zinc oxide is spherical wi...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 A preparation method for porous zinc oxide microspheres, comprising the steps of:
[0033] Dissolve 3 mmol of zinc acetate in 40 mL of dimethylformamide (DMF), sonicate for 10 min to completely dissolve the zinc acetate, then add 6 mmol of hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), and place the reaction mixture in In a stainless steel autoclave lined with 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene, at 150 o Reaction at C temperature for 12 hours; after centrifugal washing to remove residual solvent and HEPES, the product was placed at 60 o C and dried for 24 hours, after cooling, porous zinc oxide microspheres with high specific surface area can be obtained. The specific surface area of this sample is 56.9 m 2 / g, the average pore diameter is 32 nm.
[0034] Image 6 It is a topography diagram of the sample of Example 3 observed by a Hitachi S4800 scanning electron microscope (SEM). It can be seen from the figure that the synthesized zinc oxide is spheri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com