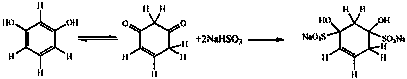Regeneration plant tanning agent and preparation method thereof
A vegetable tanning agent and vegetable tanning technology, applied in the field of regenerated vegetable tanning agent and its preparation, can solve the problems of unstable quality of finished leather and inability to completely solve the problem of effective component utilization of vegetable tanning waste liquid, achieve low price, reduce production The effects of pollution in leather production and simple process operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) Sulfonation treatment
[0035] Add 350 parts of Vitex bark extract vegetable tanning waste liquid into the reactor, add 2.8 parts of sodium sulfite and 1.2 parts of sodium bisulfite, then raise the temperature of the reactor to 75°C, stir thoroughly for 3.5 hours, and the sulfonation treatment is completed , the pH of the system at this moment is 5.5;
[0036] (2) Cross-linking treatment
[0037] Reduce the temperature of the reactor containing waste vegetable tanning liquid obtained in step (1) to 35°C, then add 7.5 parts of concentrated sulfuric acid to the reactor to lower the pH of the system to 3.1, add 1.4 parts of formaldehyde, and then adjust the temperature of the reactor to 30°C, stirred and reacted for 0.5 hours, and added 0.10 part of sodium sulfosuccinate to obtain a regenerated vegetable tanning agent.
Embodiment 2
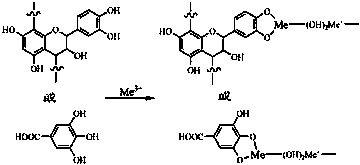
[0039] (1) Sulfonation treatment
[0040] Add 200 parts of eucalyptus extract vegetable tanning waste liquid into the reactor, add 4.1 parts of sodium sulfite and 3.4 parts of sodium bisulfite, then raise the temperature of the reactor to 85°C, stir thoroughly for 9.5 hours, and the sulfonation treatment is completed. Now the pH of the system is 7.2;
[0041] (2) Cross-linking treatment
[0042] Reduce the temperature of the reactor containing waste vegetable tanning liquid obtained in step (1) to 35°C, then add 4.2 parts of concentrated sulfuric acid to the reactor to lower the pH of the system to 4.2, add 4.0 parts of glutaraldehyde, and then turn the reactor The temperature was adjusted to 40° C., stirred and reacted for 3.5 hours, and 0.02 part of alkylphenol ether sodium sulfosuccinate was added to obtain a regenerated vegetable tanning agent.
Embodiment 3
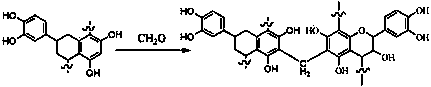
[0044] (1) Sulfonation treatment
[0045] Add 600 parts of larch extract vegetable tanning waste liquid into the reactor, add 3.6 parts of sodium sulfite and 7.8 parts of sodium bisulfite, then raise the temperature of the reactor to 75°C, stir thoroughly for 8.0 hours, and the sulfonation treatment is completed. Now the pH of the system is 6.2;
[0046] (2) Cross-linking treatment
[0047] Reduce the temperature of the reactor containing waste vegetable tanning liquid obtained in step (1) to 25°C, then add 6.2 parts of concentrated sulfuric acid to the reactor to lower the pH of the system to 3.6, add 1.9 parts of modified glutaraldehyde, and then The temperature of the reactor was adjusted to 35° C., stirred and reacted for 0.5 hour, and 0.08 part of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether was added to obtain a regenerated vegetable tanning agent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com