Tree root allocation and message processing method and routing network bridge
A routing and tree root technology, which is applied in the field of communication and can solve problems such as message discarding, tree allocation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
application example 1
[0113] Application example 1: Point-to-point LAG application scenario
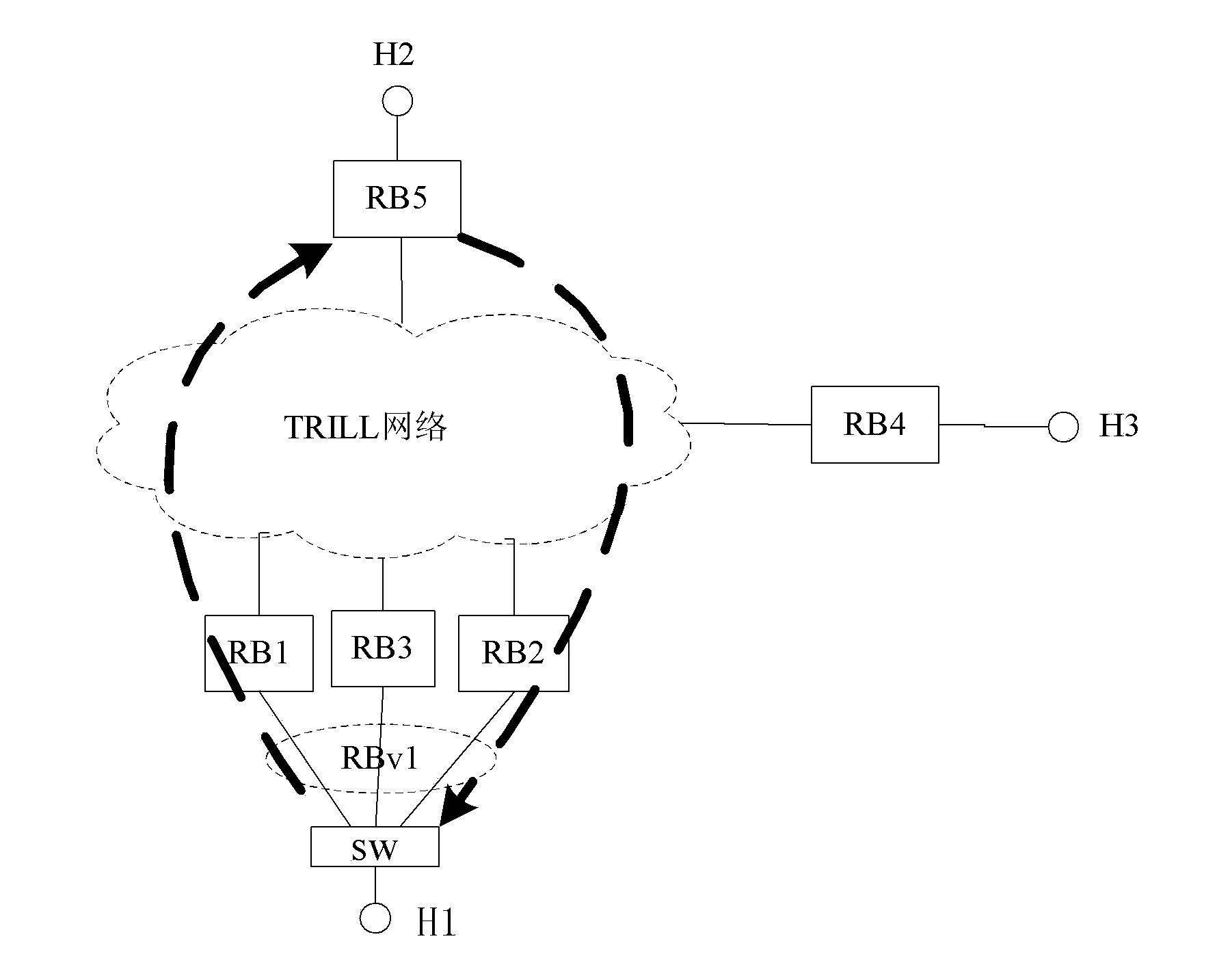
[0114] In the personal draft draft-tissa-trill-cmt-00 of the TRILL working group, an Affinity TLV is proposed, which is used to notify which trees are used by group members when using RBv encapsulation. However, the document adopts a scheme for tree allocation: perform a modulo operation on the sorting number of the tree root and the sorting number of the group members, that is, if there are n trees, the sorting is 1-n, and there are j group members in the group, The tree number assigned to the i-th group member is i, i+j, i+2j...i+xj in n trees, where i+xj<n<i+(x+1)j. This allocation method has nothing to do with the physical location of the specific node and the tree root node. Assume that the tree root allocated to member RB1 is RBi and the tree root allocated to member RB2 is RBj in this way, and RB1 is far from When RBj is close and RB2 is close to RBi, the intermediate link bandwidth will be wasted....
application example 2
[0121] Application example 2: LAN application scenario
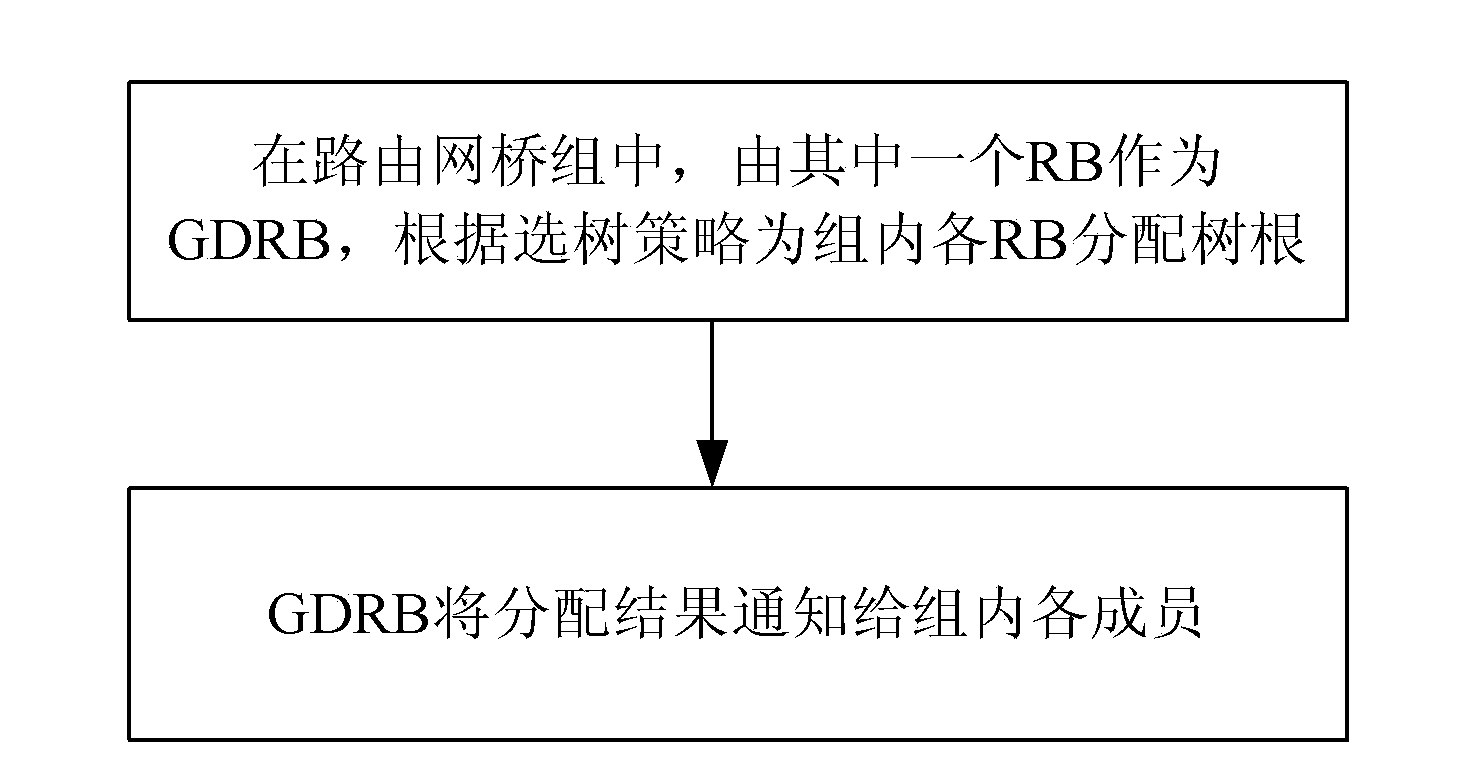
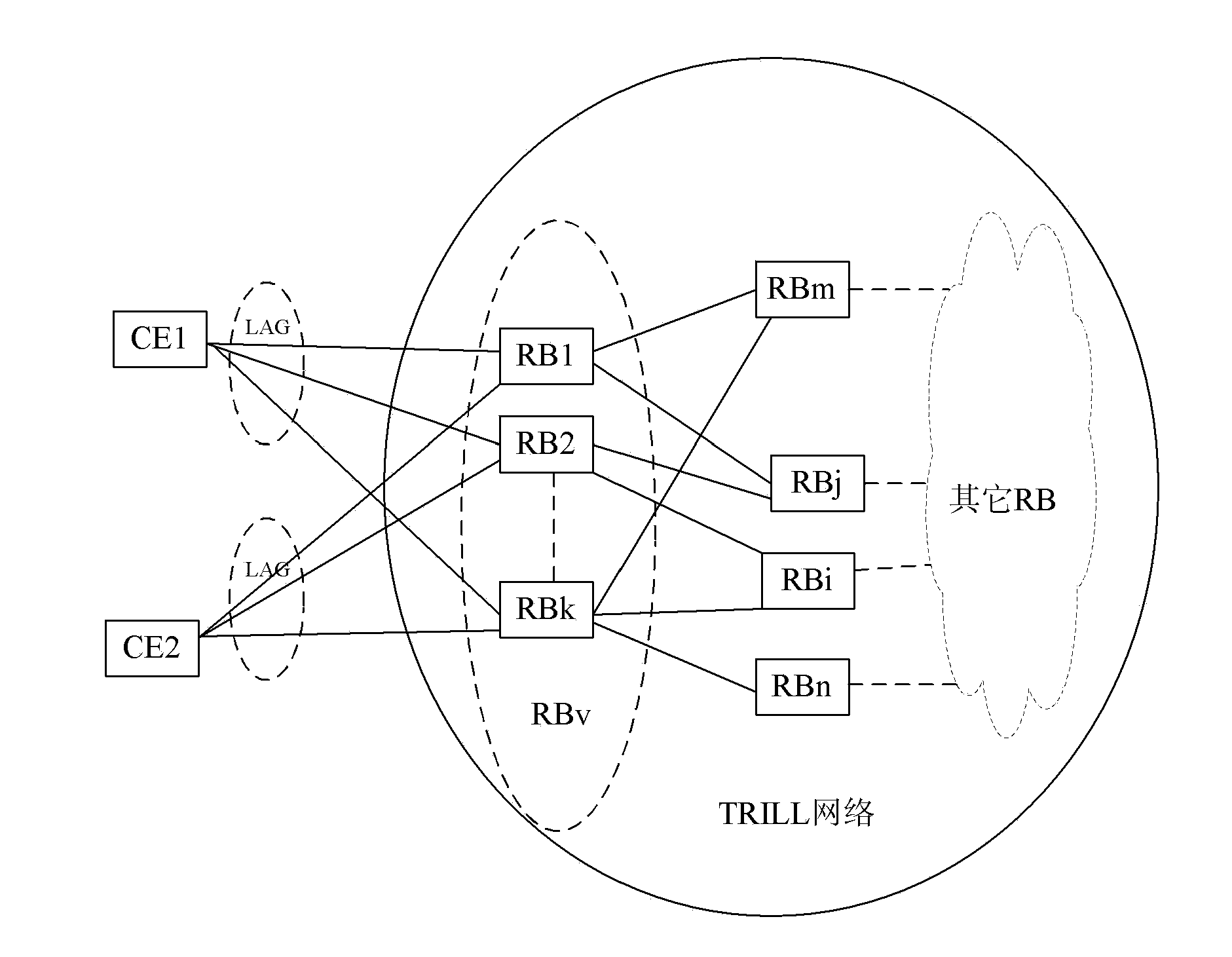
[0122] Such as Figure 6 As shown, RB1~RBk are in a routing bridge group, and the nickname of the routing bridge group is RBv, if the root priorities of RB1~RBk are sorted from high to low (it can also be sorted according to other principles, such as when the tree root When the root priorities are the same, they can be sorted by system id. If the system ids are the same, they can be sorted by nickname size) are RB1 to RBk. Suppose RB1 to RBk is configured or elected as RB2 as GDRB. According to the method described in Application Example 1, RB2 performs tree selection calculation, and publishes the tree distribution results to other group members.
[0123] The notification information containing the allocation result can be carried in the HELLO message on the LAN. The message structure is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, in this way, other nodes do not need to perceive the existence of the message, and the group members...
application example 3
[0124] Application example 3: Designation, election and failure handling of GDRB
[0125] The designation, election and invalidation processing of the GDRB in the above application example 1 and application example 2 can be specifically as follows:
[0126] When there is a designated GDRB in the group, GDRB can automatically set its own election priority to the highest according to the automatic election rules, and at the same time send out a message identifying itself as a GDRB (transmitted through the intra-portal link in the group) ), other group members stop the election after receiving the GDRB identification message sent by other members, and wait for the GDRB to release the allocation result. When other group members know that the GDRB is invalid (such as DBR downtime), if other nodes in the group are configured with GDRB, the node will set its own election priority to the highest and send a GDRB identification message, which is determined by Nodes in this group will k...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com