Method for cleaning compact core-soluble slat
A technology of core and dissolved salt, which is applied in the field of cleaning soluble salt of dense core, can solve the problems of low experimental efficiency, complex equipment, high equipment requirements, etc., and achieve the effect of high cleaning efficiency, convenient operation, safe and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
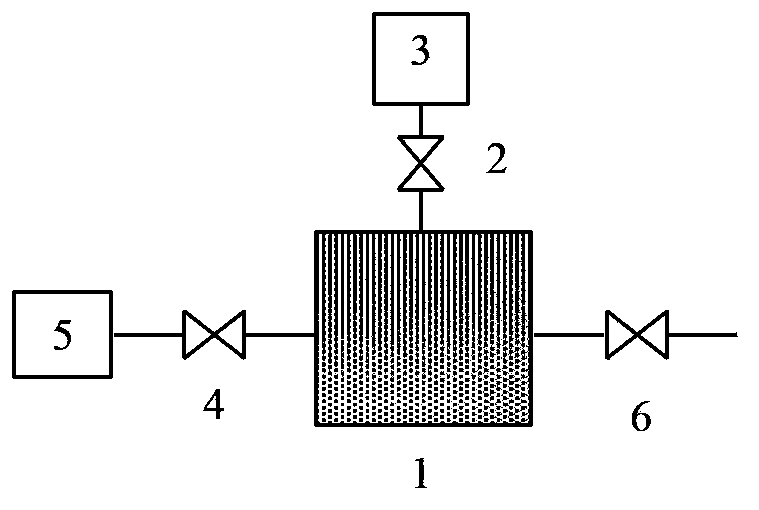
[0025] Further illustrate the present invention below by accompanying drawing.
[0026] A method for cleaning soluble salts of tight rock cores, comprising the following steps in turn (see figure 1 ):
[0027] ① Prepare the experimental core, anhydrous methanol (or other solvents that can dissolve salts) and silver nitrate solution;
[0028] ② Put the dried core into the high-pressure container 1, heat it to 60°C, open the valve 2, close the valve 4 and the valve 6, turn on the vacuum pump 3 to vacuumize until the vacuum degree reaches above 0.098MPa, and continue to vacuumize for 2 to 4 hours Finally, close the valve 2 and close the vacuum pump 3;
[0029] ③Use a syringe to fill the pipeline between valve 6 and the outside world with anhydrous methanol, connect this pipeline into a container with sufficient anhydrous methanol, open valve 6, and fill the high-pressure vessel 1 with anhydrous methanol under vacuum conditions. Water methanol, close valve 6;
[0030] ④ Draw a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com