An integrated artificial cervical intervertebral disc prosthesis with high mobility
A cervical intervertebral disc and mobility technology, applied in prosthesis, medical science, spinal implants, etc., can solve problems such as large difference in mobility, failure of prosthesis replacement, and prone to complications, so as to improve health, Increased mobility, a noticeable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
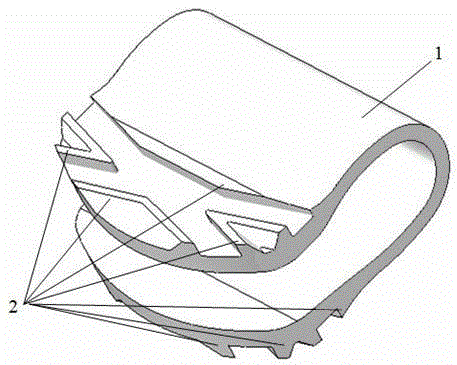
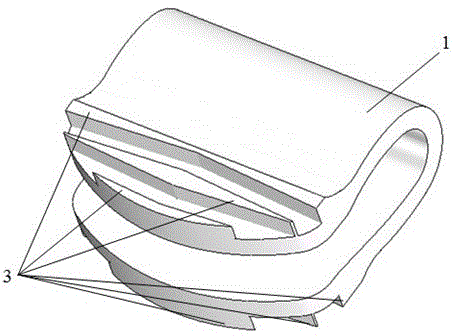
[0026]Example 1: Establishing a finite element model of the C5-C6 segment of the cervical spine with an integrated artificial cervical intervertebral disc. The body (1) in the finite element model is an Ω-shaped non-contact elastic structure with integrated upper and lower end plates. The outer surfaces of the upper and lower end plates of the body (1) are respectively symmetrically equipped with herringbone bidirectional anti-retraction teeth (2). The thickness of the rear end bending section of (1) is 0.8mm, and the material of the body (1) is respectively selected from near-β-type Ti13Nb13Zr titanium alloy, Ti6Al4V titanium alloy or pure titanium, among which: the elastic modulus of near-β-type Ti13Nb13Zr titanium alloy is 60GPa; The elastic modulus of titanium material is 114GPa; the elastic modulus of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy is 110GPa.
[0027] The simulation analysis was carried out under the forward bending load, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0028] Table 1 Si...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Establishing a finite element model of the C5-C6 segment cervical vertebra of the integrated artificial cervical intervertebral disc. The body (1) in the finite element model is an Ω-shaped non-contact elastic structure with integrated upper and lower end plates. The outer surfaces of the upper and lower end plates of the body (1) are respectively symmetrically equipped with herringbone bidirectional back and forth teeth. The body (1) The thickness of the rear end bending section is 0.8mm, and the body (1) is made of β-type titanium alloy Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr, whose strength, fatigue life, wear resistance and mechanical properties are close to TC4 titanium alloy, but the elastic modulus The amount of 70GPa is much lower than that of TC4 titanium alloy. The simulation analysis was carried out under the loads of flexion, extension and lateral flexion, and the results obtained were compared with the finite element segmental simulation results of prostheses made of...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: Select an integrated Ω-shaped non-contact elastic artificial cervical intervertebral disc with the following specifications: the length of the lower end plate of the body (1) is 14 mm, the width is 16 mm, and the distance between the upper and lower end plates is 3.3 mm; the rear end of the body (1) The overall height is 6.0mm; the maximum height of the herringbone two-way stop and fall tooth (2) is selected as 0.8mm.
[0037] The finite element models of the C5-C6 segments of the cervical spine of the integrated Ω-shaped non-contact elastic artificial cervical intervertebral disc with thicknesses of 0.5mm, 0.6mm, 0.8mm and 0.9mm implanted in the body (1) were respectively established. (1) The materials are all made of biomedical β-type titanium alloy Ti13Nb13Zr. Using the finite element simulation analysis method, the simulation analysis is carried out under three loads of forward flexion, backward extension and lateral flexion, and the maximum Von Mises stre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com