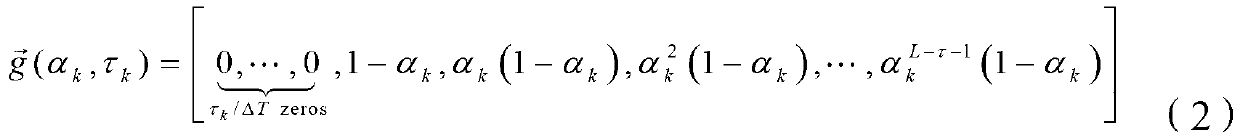Bayesian framework-based dynamic soft measurement modeling method and device
A Bayesian framework and modeling method technology, applied in the direction of instruments, adaptive control, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve problems such as feedback results that affect measurement, deterioration of control performance, and reduction of model tracking capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] In this embodiment, the dynamic soft sensor modeling method based on the Bayesian framework includes the following steps:
[0055] Step A: Establish a first-order impulse response model and a support vector machine model;
[0056] The first-order impulse response model is:
[0057] x ( t ) = x 1 ( t ) x 2 ( t ) · · · x m ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] This embodiment embodies the step A on the basis of the first embodiment;
[0070] Step A1: Construct the formula about u as described in formula (1) and formula (3) k (...,t)(k=1,...,m) and the system structure relationship of y(t);
[0071] Step A2: Get and u k (...,t)(k=1,...,m) corresponding data U k (...,t)(k=1,...,m) and with U k (..., t) (k=1,...,m) is a data sample composed of Y(t) mapped to each other, and forms an increasing time series according to the sampling time; usually when collecting the U k (…,t)(k=1,…,m) follow Shannon’s theorem;
[0072] Step A3: Standardize the data in the data sample so that the data has zero mean and unit variance in each dimension;
[0073] Step A4: Set the initial parameter α of the first-order impulse response model and support vector machine model training k ,τ k , impulse response sequence length L, training parameters ε, C, RBF kernel parameter σ and iteration stop threshold μ:
[0074] Step A5: Put the U in the dat...
Embodiment 3
[0077] This embodiment further details step A on the basis of embodiment two.
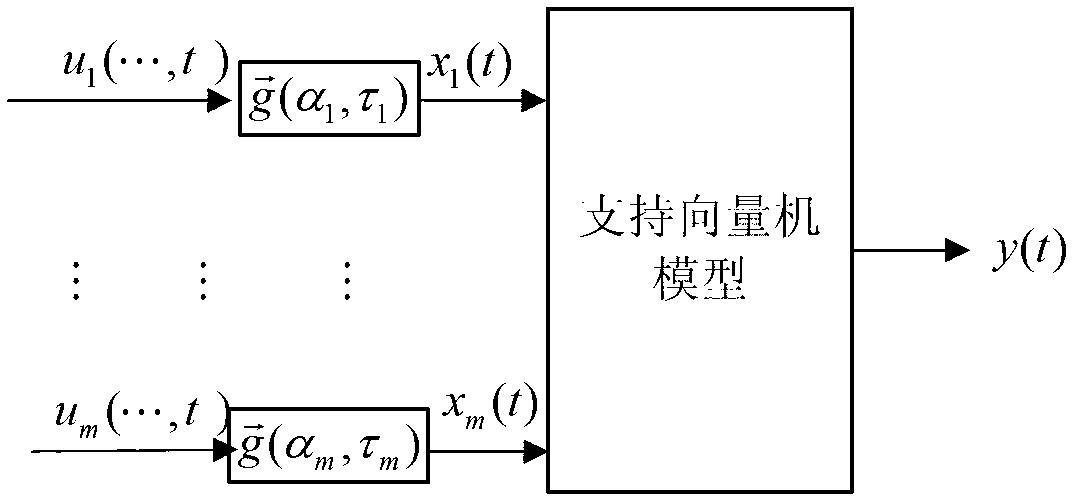
[0078] Such as figure 2 As shown, Step S1: On the basis of the analysis of the production process mechanism or actual experience, construct a systematic structural relationship between a difficult-to-measure leading variable and multiple easy-to-measure auxiliary variables, namely
[0079] u k (...,t)(k=1,...,m) and y(t) are the system structure relationship; and the parameter constraint range of the system is given.
[0080] The system structure relationship is: the system output y(t) represents the unpredictable leading variable, and the system input u k (…,t)(k=1,…,m) represent relevant and easily measurable auxiliary variables. The system is composed of a dynamic link and a nonlinear static link in series, and the dynamic link is expressed in the form of a first-order impulse response model:
[0081] Among them, m is the dimension of the input variable and also the dimension of the state v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com