Device and method for recovering activity of zero-valent iron passivated in Cr pollution removal process
A zero-valent iron and active technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor operability, reduced processing capacity, and high processing costs, and achieves a high degree of automation, Easy operation and cost-saving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
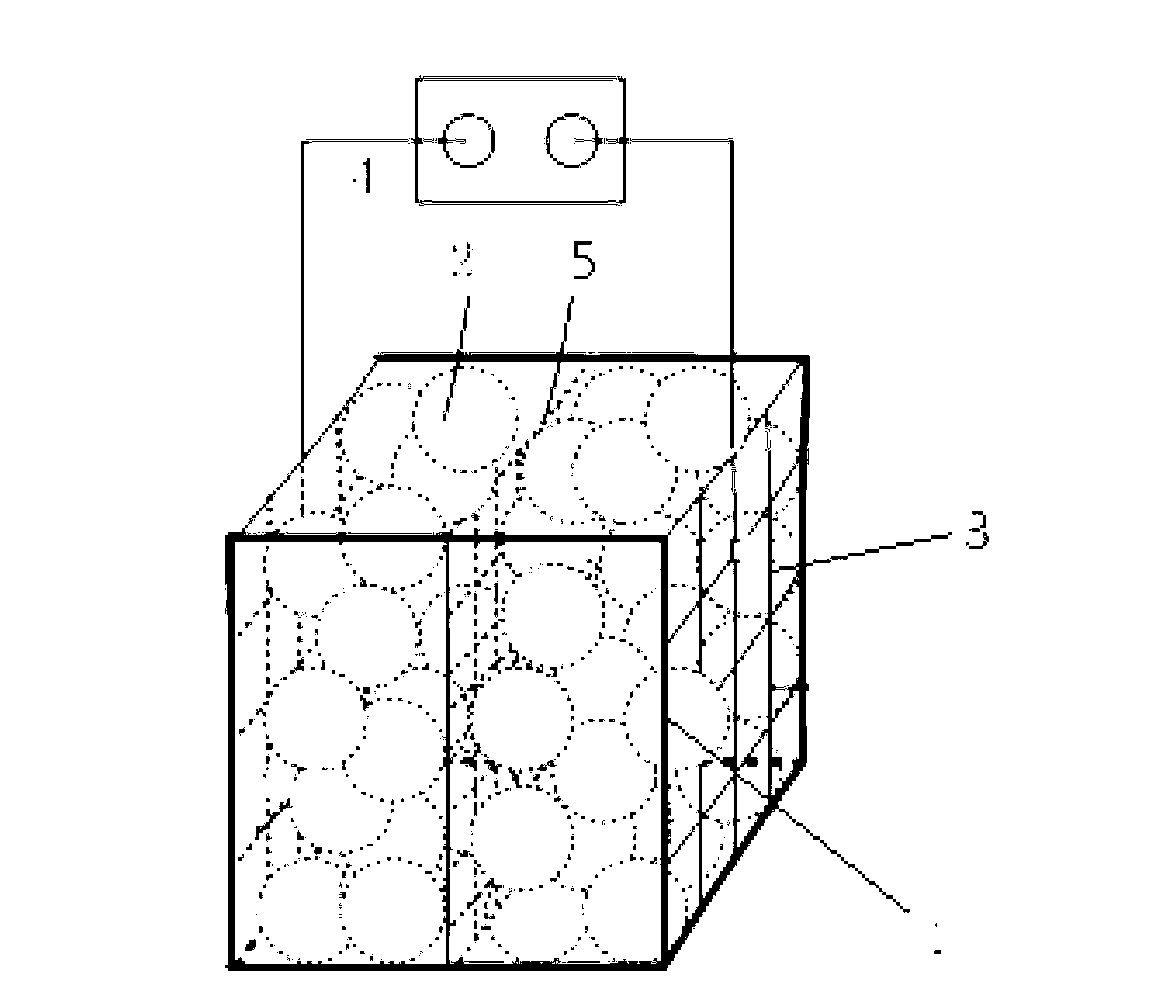
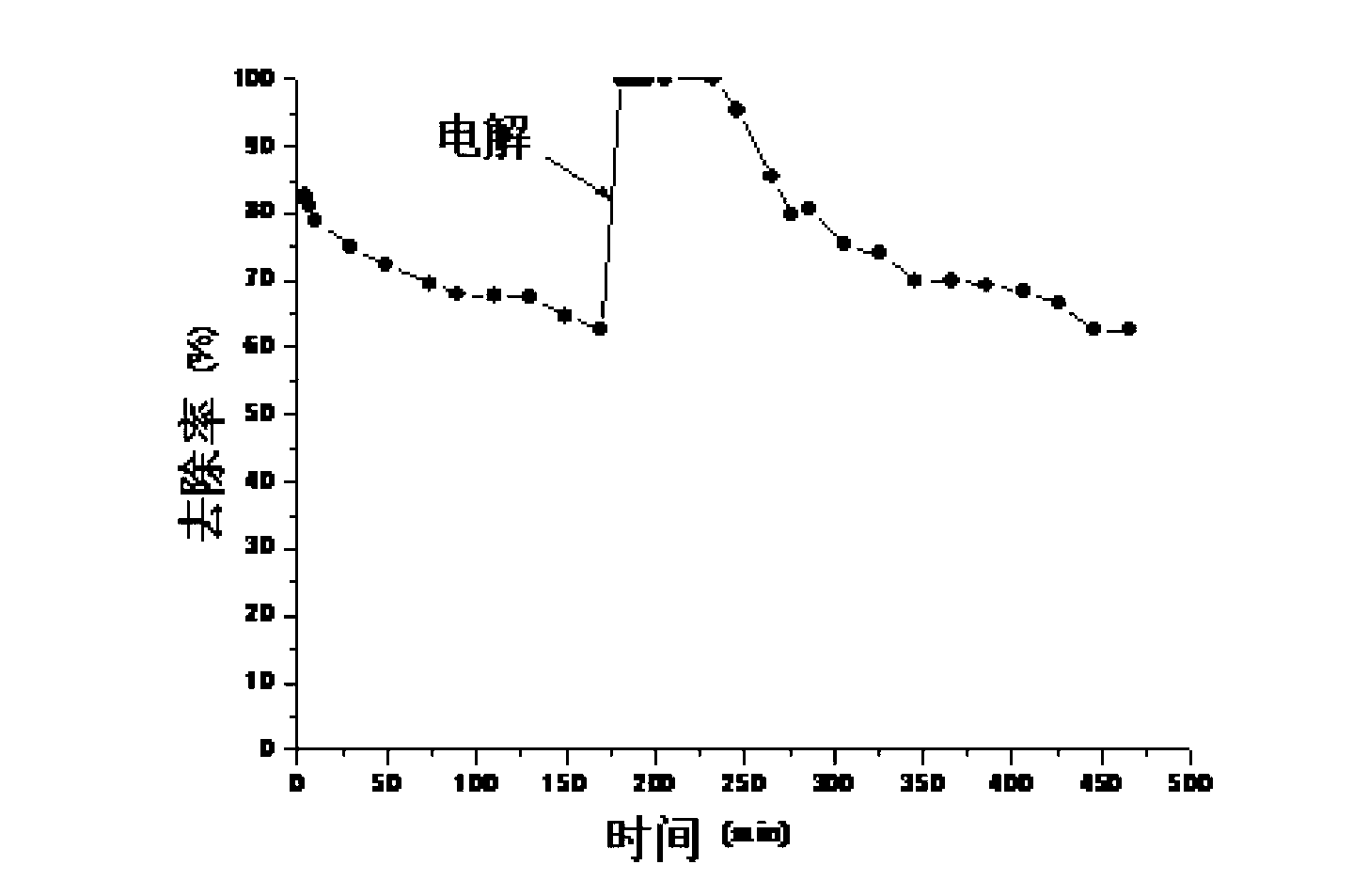
[0031] In this embodiment, the method for recovering the activity of the passivated zero-valent iron in the process of removing Cr pollution uses an organic plastic reaction tank 1 with an effective volume of 330 ml, which is filled with zero-valent iron filler 2 . Place iron mesh electrodes 3 along the sides of the tank walls parallel to the water flow direction, and place a piece of PVC mesh 5 along the center plane. The effective area of iron mesh electrodes 3 is 60cm 2 . A DC voltage regulator is used as the power supply with an effective voltage of 0-50V and an effective current of 0-5A. In the experiment, artificially synthesized Cr was used to pollute water (Cr, 25mg / L; Na 2 SO 4 ; 0.5g / L), the experimental water intake was carried out in an upflow manner, and the Cr-containing contaminated water flowed in from the bottom of the reaction tank 1 at a flow rate of 4mL / min, and flowed out from the top of the reaction tank 1. When the reaction time is about 170min, it ...
Embodiment 2
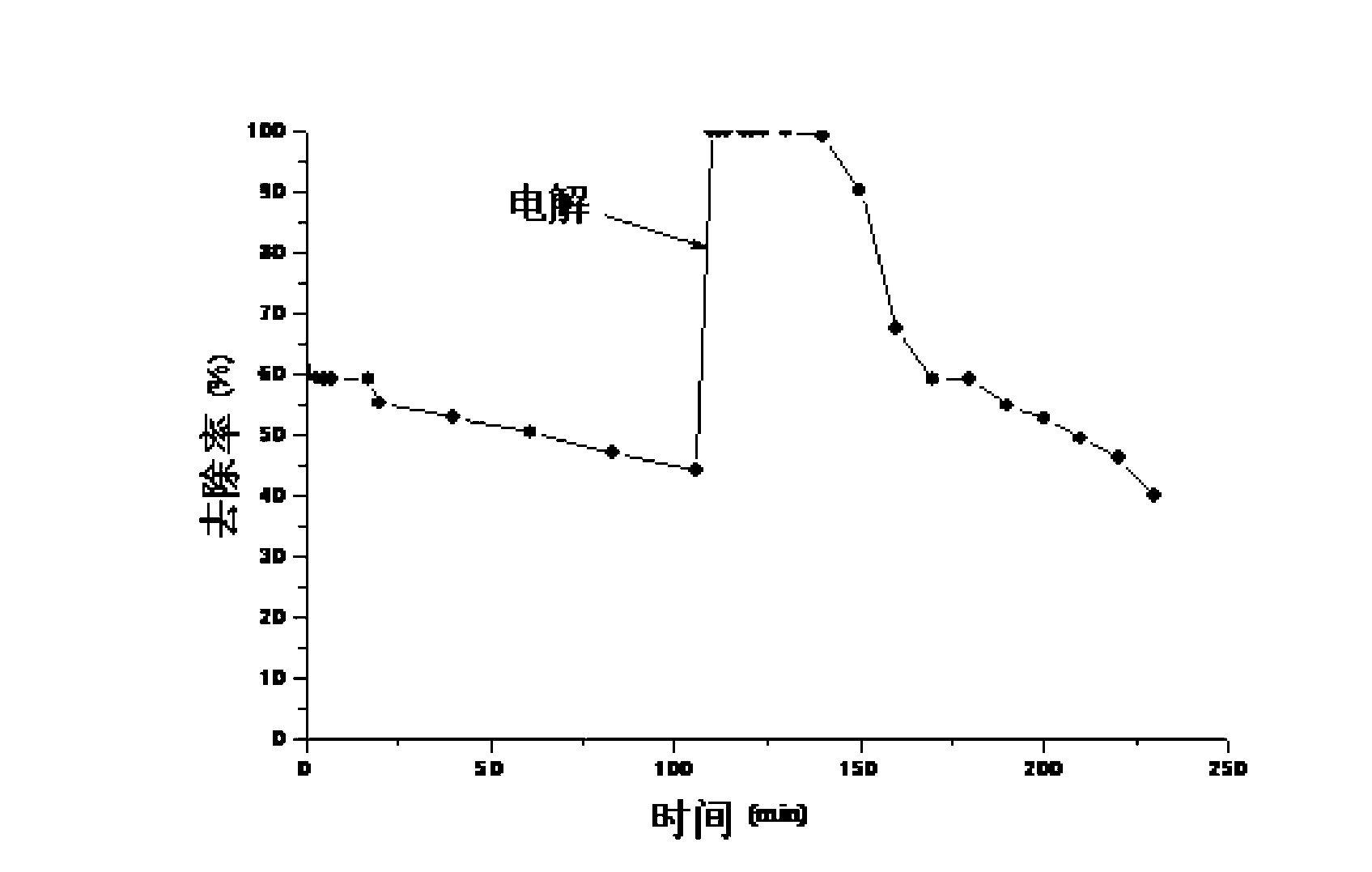
[0033] In this embodiment, the method for recovering the activity of the passivated zero-valent iron in the process of removing Cr pollution uses an organic plastic reaction tank 1 with an effective volume of 72 ml, which is filled with zero-valent iron filler 2 . Place the iron mesh electrodes 3 along the sides of the tank walls perpendicular to the water flow direction, and place a piece of PVC mesh 5 along the center surface. The effective area of the iron mesh electrodes 3 is 12cm 2 . A DC voltage regulator is used as the power supply with an effective voltage of 0-50V and an effective current of 0-5A. Other conditions are the same as example 1. With the continuous progress of the removal reaction, the removal rate of Cr(VI) decreased continuously, and when it reached 106min, the removal rate dropped to 44.21%. After energizing the iron grids at both ends with 10v for 4 minutes, turn the positive and negative poles upside down and energize for another 4 minutes. Depen...
Embodiment 3
[0035] In this embodiment, the method for recovering the activity of the passivated zero-valent iron in the Cr pollution removal process, the reaction tank 1 is the same as that of the second embodiment, and iron grid electrodes 3 are respectively placed along the sides of the tank walls parallel to the water flow direction, and a piece is placed along the center plane. PVC mesh, iron mesh electrode 3 effective area 24cm 2 . The Cr-polluted water was prepared with groundwater from Tsinghua University, and the influent flow rate was 0.8ml / min, and other conditions were the same as in Example 2. The initial removal rate of the reactor was 97.6%, and the removal rate continued to decrease as the reaction progressed. A total of 3 electrochemical depassivation operations were introduced in the experiment. After energizing at a voltage of 10v for 10 minutes, the positive and negative electrodes were reversed and then energized for 10 minutes. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com