An Efficient Multi-Writer Model Public Audit Method for Cloud Data Security
A multi-write, auditing technology, applied in the field of cloud computing security, can solve the problems of unfaithful cloud server providers, complex key management problems, indistinguishability, etc., to achieve privacy protection for multiple writers, and to achieve multiple writes the effect of reducing the burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
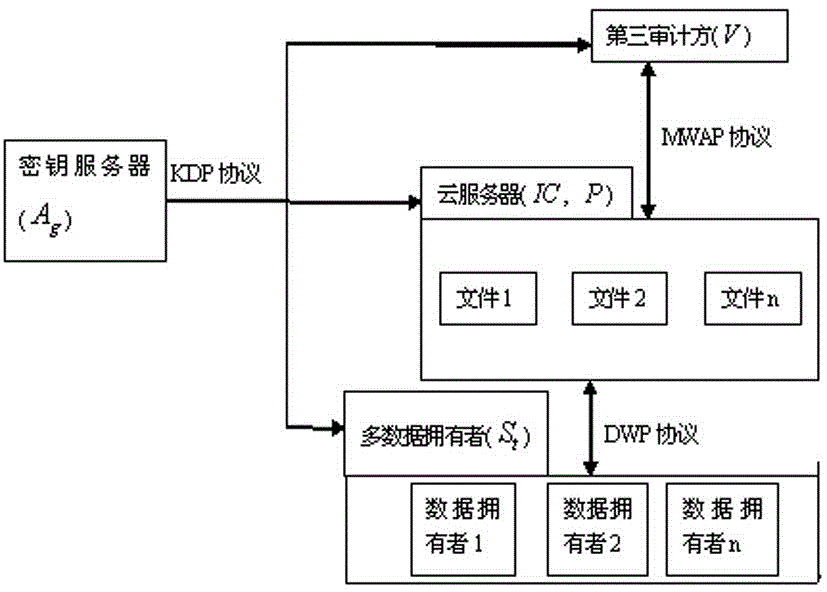
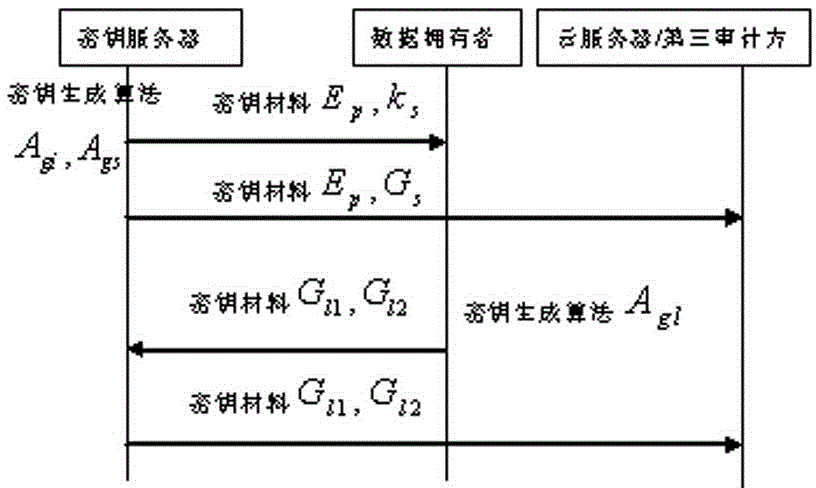
[0048] In this embodiment, the KDP protocol is designed and completed. The purpose of this protocol is to complete the generation and distribution of a series of keys. Including but not limited to the following steps (expressed in a table):
[0049]
[0050] The KDP protocol is as follows image 3 shown.
[0051] The steps in Embodiment 1 are described as follows:
[0052] (1) Step 100: The key server creates a base point as , the order is elliptic curve . The parameters of the elliptic curve are known to the third auditor TPA, the cloud server CS and all data owners DO.
[0053] (2) Step 102: The key server randomly generates a key , Denote the residual class ring modulo n and assign it to DOs on the secure channel between the key server and DOs. therefore, is the shared key of DOs. The key server then utilizes the key base point corresponding key , and put Announced to the cloud server CS, the third auditor TPA and all DOs.
[0054] (3) Step 104...
Embodiment 2
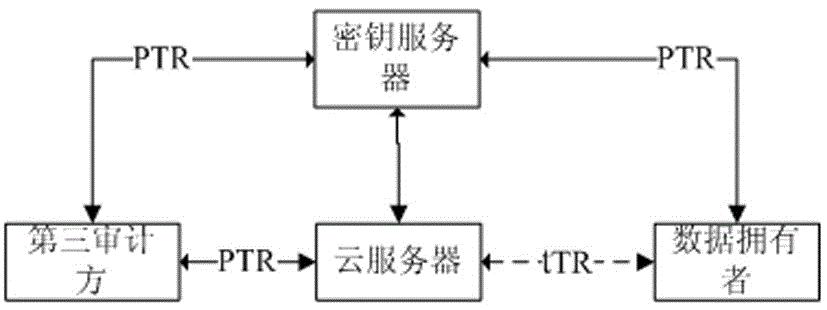
[0056] This embodiment defines the DWP protocol. The purpose of this protocol is to realize that the data owner DO signs the data and correctly stores the data and its corresponding signature in the cloud server CS. Including but not limited to the following steps (expressed in a table):
[0057] steps
content
106
do use Algorithm to get and send it to CS.
108
take over When, CS utilizes Algorithm verification , and send a reply message to DO.
[0058] The DWP protocol is as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0059] The steps and the protocol flowchart in Embodiment 2 are described as follows:
[0060] (1) Step 106: When DO to sign documents (E.g ) blocks in , Represents a collection of files, Represents a collection of data blocks, the data owner DO uses the signature algorithm and combines the function (This function can realize the string file and blocks converted to a point on the elliptic curve) to cal...
Embodiment 3
[0063] This embodiment defines the MWAP protocol. The purpose of this agreement is: to complete the third auditor TPA's audit of the data written by DOs stored in the cloud server CS. Including but not limited to the following steps (expressed in a table):
[0064] steps
content
110
TPA to be audited by When writing data in DOs, she selects a set of , and put sent to CS.
112
receiving When, CS utilizes Algorithm to get and send it to TPA.
114
receiving When, TPA utilizes Algorithms audit data in CS.
[0065] The protocol flow of this embodiment is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0066] The steps in Embodiment 3 and the protocol flow chart are described as follows:
[0067] (1) Step 110: When the third auditor TPA wants to audit the When writing data in DOs, she uses a suitable algorithm to select a set of flag data corresponding to the document to be verified , and put Send to the cloud server CS...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com