Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing heat-stability recombinant trypsin, and its application
A trypsin and thermal stability technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of long fermentation period of Streptomyces, difficult fermentation control, low yield, etc., and achieve the effects of easy industrial application, simple extraction process and high product purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Amplification of the trypsin gene with improved thermostability
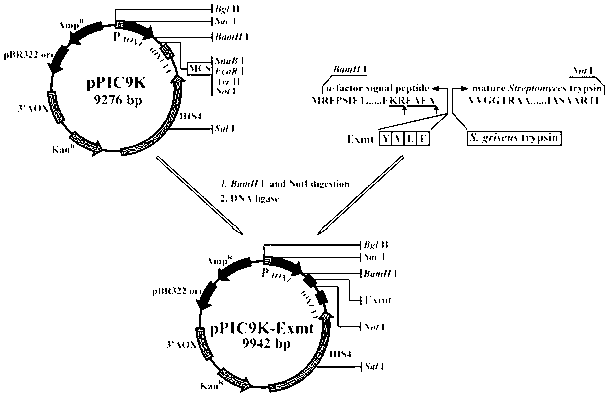
[0029] The gene of thermostable tyrpsin (thermostable tyrpsin) is derived from the coding sequence of the tryptase gene in Streptomyces griseu (GenBank Accession No. M64471), in which the 639th to 1307th positions are encoded SprT gene. After analyzing the codon bias of the gene, the leading short peptide YVEF was fused at its 5′ end, and the α-factor signal peptide from P. pastoris was fused again on the fusion fragment to obtain the gene Exmt, and in the final BamHI and Not I restriction sites are added to the 5' and 3' ends of the fragment respectively, and the nucleotide sequence of the Exmt gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: Construction of recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-Exmt
[0031] The in vitro amplified fragment of the Exmt gene and the expression vector pPIC9K were subjected to double digestion with BamH I and EcoR I, respectively, and ligated with T4 ligase after recovery. The ligation reaction system is (10 μL): target gene fragment 2 μL, carrier DNA 2 μL, 10×T4 ligase Buffer 1 μL, T4 DNA ligase 1 μL, ddH 2 04 μL.
[0032] The ligation product was transformed into competent Escherichia coli JM109 for transformation. The conversion method is as follows:
[0033] (1) Under sterile conditions, take 200 μL of competent cells and place them in a sterile microcentrifuge tube;
[0034] (2) Add 1-2 μL of recombinant plasmid to each tube, rotate gently to mix the contents, and place on ice for 30 minutes;
[0035] (3) Heat shock at 42°C for 90sec (accurate), do not shake the centrifuge tube;
[0036] (4) Quickly transfer the centrifuge tube to an ice bath to cool the cells for ...
Embodiment 3
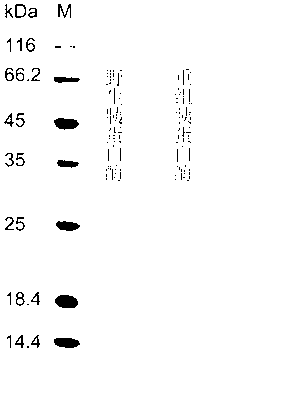
[0040] Embodiment 3: the construction of the trypsin yeast engineered bacterium that thermostability improves
[0041] The expression vector pPIC9K-Exmt was linearized by cutting with Sal I. Enzyme digestion system (50 μL system): recombinant plasmid 10 μL, Buffer 5 μL, Sal I 3 μL, ddH 2 O32 μL. Water bath at 37°C for 3 hours, purify and recover the linearized product with a PCR product purification kit, and transform Pichia pastoris GS115 by electric shock method, the specific method is as follows:
[0042] (1) Inoculate a loop of activated Pichia pastoris GS115 in 25mL YPD liquid medium, and culture overnight at 28°C to 30°C with shaking;
[0043] (2) Transfer the above culture solution into 100mL YPD (500mL Erlenmeyer flask) liquid culture medium, shake culture at 28℃~30℃, measure every 1h, and cultivate until the cell concentration OD 600 1.3~1.5;
[0044] (3) Cool in ice water for more than 10 minutes;
[0045] (4) Collect the bacteria by centrifugation at 4°C and 80...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com