Dunaliellaviridis myo-Inositol-1-phosphatesynthase gene, and protein coded thereby and application thereof
A technology of phosphate synthase and salina inositol, which is used in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment one: DvMIPS Cloning and analysis of the full-length coding region
[0023] Salina ( D. viridis ) to analyze the EST sequences (expressed sequence tags) of the cDNA library induced by different concentrations of salt, focusing on the sequences whose expression is obviously induced by salt. Through sequence alignment, a Salina salina inositol phosphate synthase gene was isolated from the EST sequence numbered contig 187, named DvMIPS . DvMIPS The open reading frame (ORF) of the gene is 1548 bp, and the full length of the cDNA is 2194 bp, which contains the specific tailing signal TGTAA and poly(A) structure of the green algae gene.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment two: DvMIPS Encoded protein structure, homology analysis
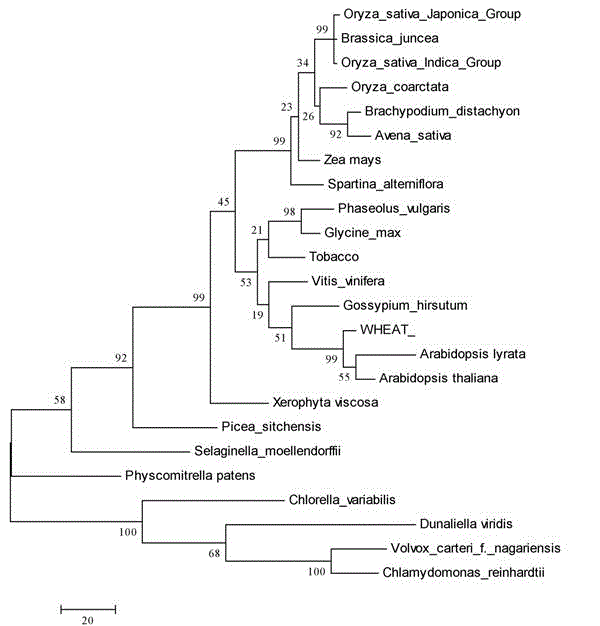
[0025] The analysis results of Vector NTI software showed that the gene encoded a protein with 516 amino acids, the molecular weight of the protein was 56.9 kDa, and the isoelectric point was 5.38. DvMIPS It has high homology with the MIPS gene of other species, and the protein encoded by this gene also has inos-1-P-synth domain and NAD-binding-5 domain. DvMIPS contains in the homologous segment the GWGGNNG amino acid motif conserved among all species of inositol-1-phosphate synthases and is NAD + the binding active site. The highly conserved NGSPQNTFVPGL motif, SYNHLGNNDG motif and LWTANTERY motif in eukaryotic inositol-1-phosphate synthase were also found in the sequence of DvMIPS, suggesting that the protein is highly conserved in species evolution. figure 1 for the present invention DvMIPS The evolution analysis diagram of the protein encoded by the gene shows that the encoded protein be...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Embodiment three: DvMIPS Location prediction and prokaryotic expression analysis of encoded protein
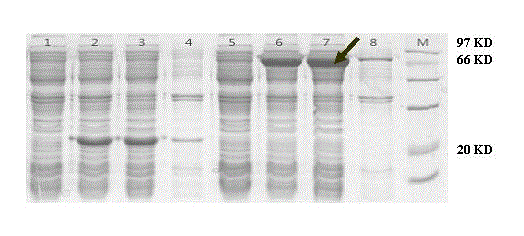
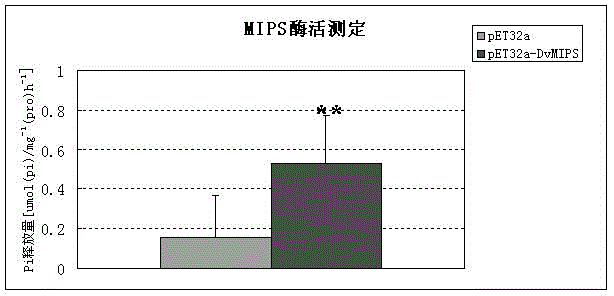
[0027] DvMIPS was localized in the cytoplasm as predicted by WoLFPSORT software. By the method of PCR, in DvMIPS Add restriction endonuclease sites to both ends of the ORF of the gene EcoR I and xho I, after the sequence of the connected T vector is correct, EcoR I and xho I double-enzyme-digested target fragments were connected to the same double-enzyme-digested prokaryotic expression vector pET32a to obtain recombinant plasmid pET32a- DvMIPS. The recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli expression strain BL21, induced with 1 mM IPTG at 16 °C for 8 h, and an appropriate volume of PBS buffer was added to sonicate the cells. The supernatant obtained by centrifugation is the crude protein extract. figure 2 SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis image of DvMIPS protein fused with His tag.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com