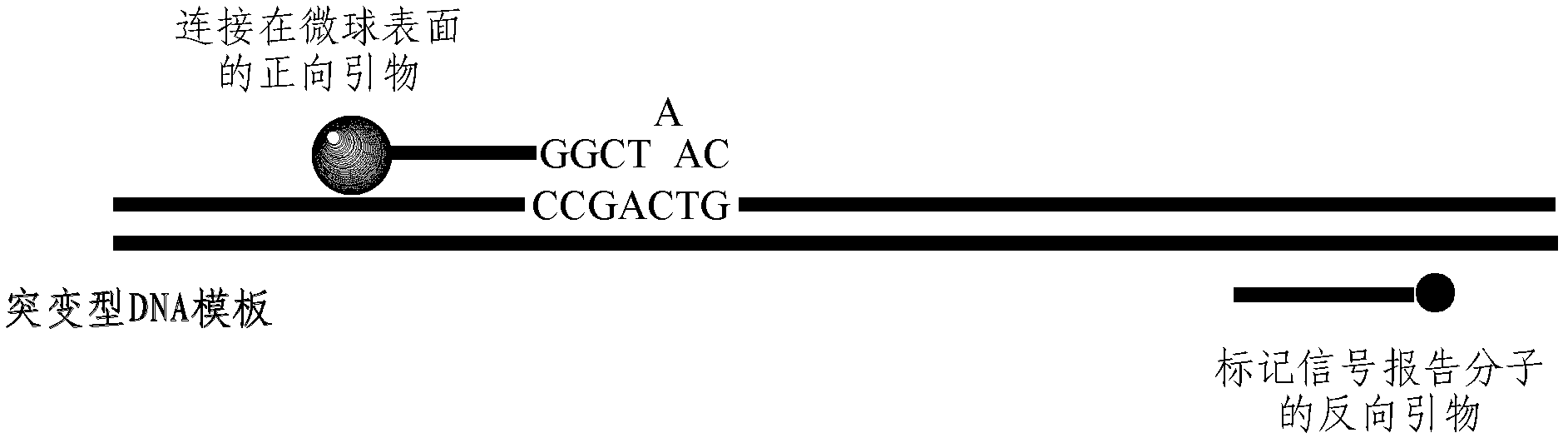Liquid chip for detecting gene point mutation and method
A liquid phase chip, point mutation technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity of gene point mutation detection, wild-type gene interference, etc. Accurate and reliable results, enhanced signal-to-noise ratio, and improved sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Detection of samples by the liquid phase chip of the present invention
[0047] 1. A pair of specially designed specific primers
[0048] A pair of specific primers were designed for the common mutation site Y220C of the P53 gene, the structure of which is as follows:
[0049]
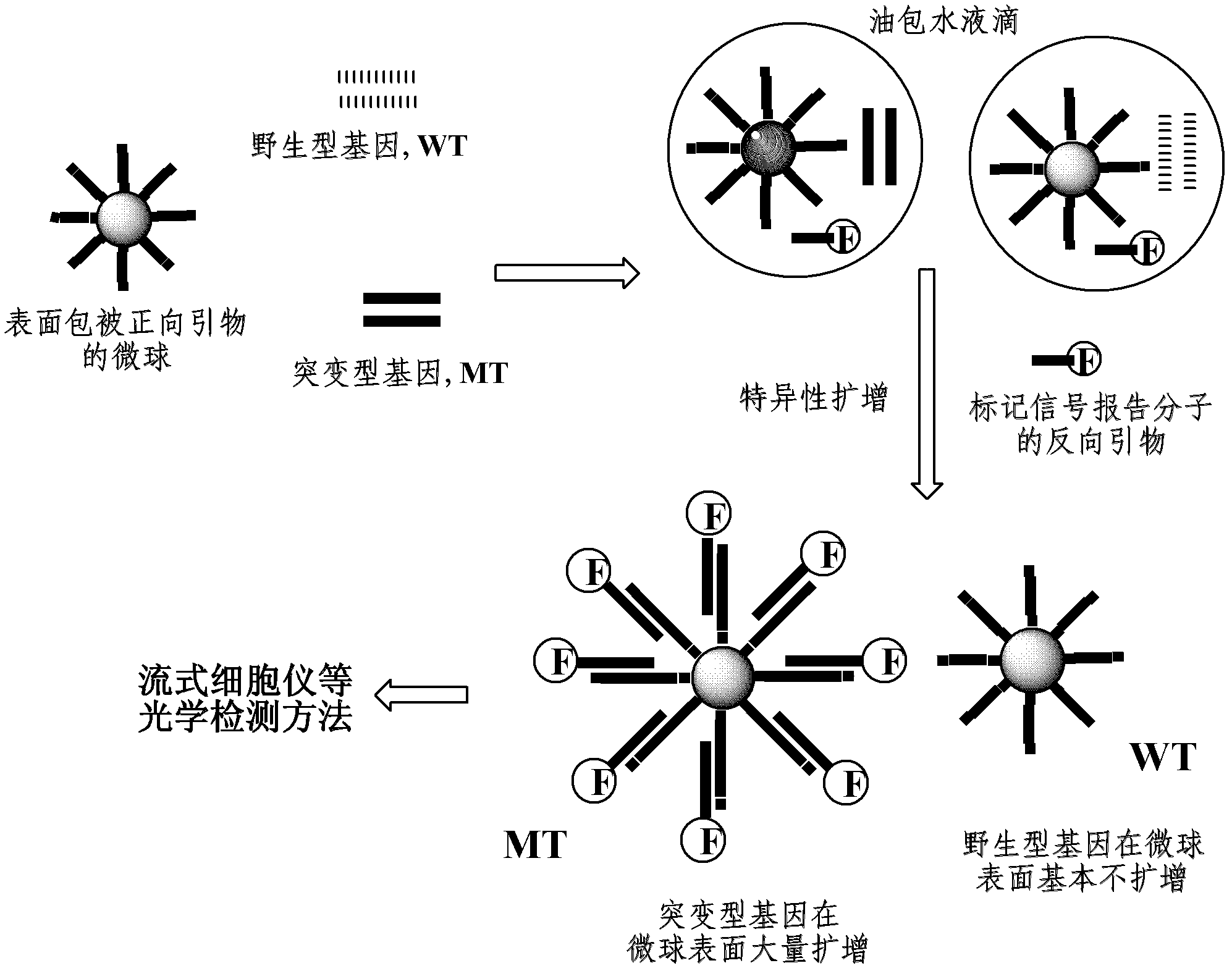
[0050] The forward primer is coated on the surface of the microsphere, and the first base C at the 3' end is complementary to the base of the mutation site of the gene to be detected, and is not complementary to the wild-type gene; the third base A at the 3' end is An artificially introduced base that is not complementary to the mutant and wild-type genes; the 10 base A at the 5' end is the connecting arm between the primer sequence and the microsphere. The 5' end of the reverse primer was modified with biotin as a signal reporter molecule.
[0051] 2. Amplification of mutant genes in water-in-oil emulsion
[0052] (1) The volume of the aqueous phase is 72 μl, and the amplification...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2 Detection of samples by the liquid phase chip of the present invention
[0069] 1. A pair of specially designed specific primers
[0070] A pair of specific primers were designed for the common mutation site Y220C of the P53 gene, the structure of which is as follows:
[0071]
[0072] The forward primer is coated on the surface of the microsphere, and the first base C at the 3' end is complementary to the base of the mutation site of the gene to be detected, and is not complementary to the wild-type gene; the third base A at the 3' end is An artificially introduced base that is not complementary to the mutant and wild-type genes; the 6 carbon atoms (C6) at the 5' end are the connecting arms between the primer sequence and the microsphere. The 5' end of the reverse primer was modified with CY5 fluorescein as a signal reporter.
[0073] 2. Amplification of mutant genes in water-in-oil emulsion
[0074] (1) The volume of the aqueous phase is 100 μl, and th...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Embodiment 3 Comparison experiment between the present invention and allele-specific primer extension method
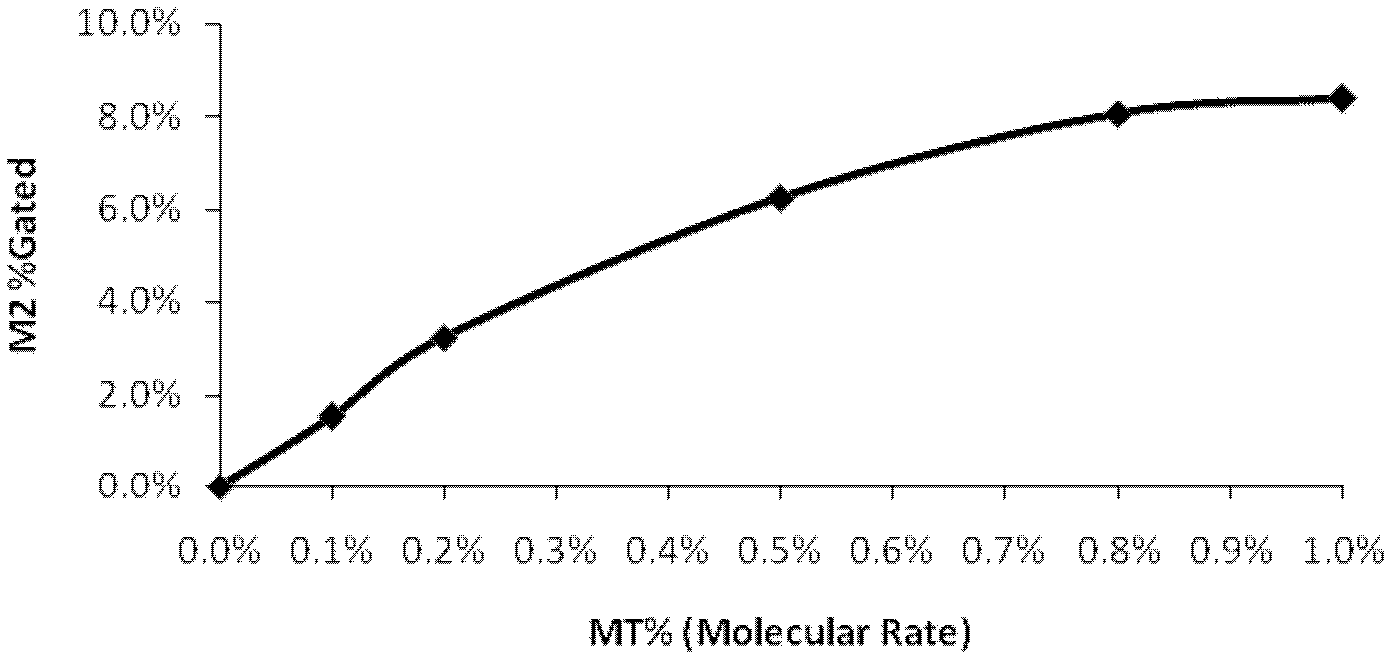
[0089] Allele-specific primer extension (Allele specific primer extension, ASPE) is a common method for detecting gene point mutations. For the primer, the base that is different from the normal allele is arranged at the 3' end of the primer, so that the primer is completely paired with the mutant gene, and an extension reaction occurs after the primer binds to the mutant gene template; while the 3' end of the primer The terminal base is a mismatch with the wild-type gene, and no extension reaction occurs after combining with the wild-type gene template, and whether the sample contains a mutant gene can be detected by detecting the extension product.
[0090] This embodiment compares the sensitivity of the present invention and the ASPE method in detecting gene point mutations. In order to facilitate visual comparison with the detection results of the present ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com