A Method for Measuring Wavefront Phase Radius of Partially Coherent Gaussian Beams
A Gaussian beam, wavefront phase technology, applied in measurement devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as dependence, high measurement costs, and expensive measurement equipment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
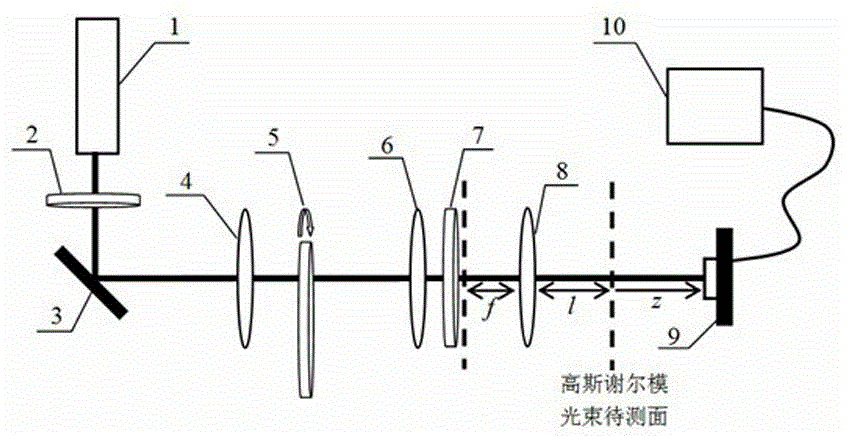
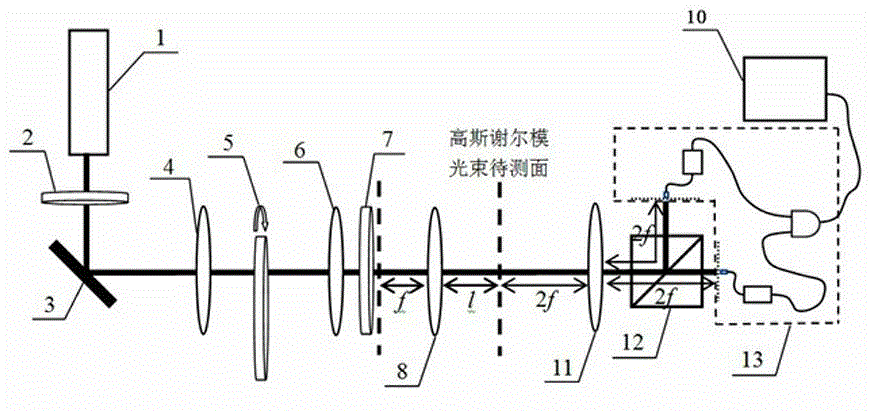
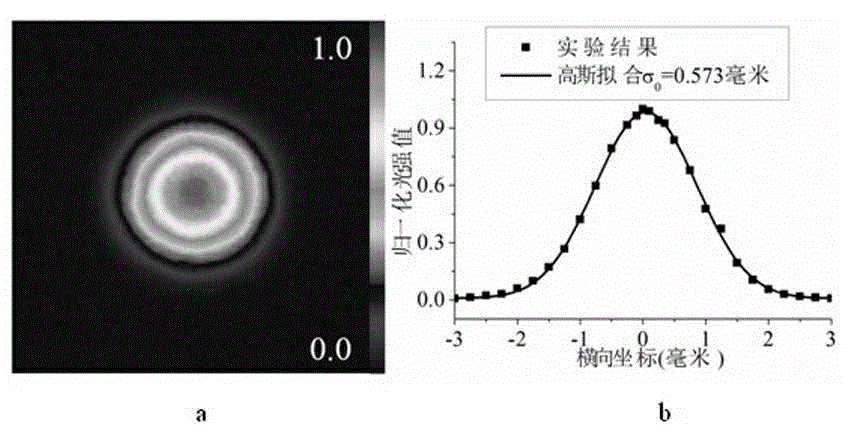
[0063] See attached figure 1 , which is a structural schematic diagram of a partially coherent Gaussian beam waist width measuring device provided in this embodiment; laser 1 generates a randomly polarized beam, passes through a linear polarizer 2 to generate a linearly polarized laser beam, and passes through a mirror 3 and the thin lens 4 are focused on the ground glass plate 5 to generate a partially coherent linearly polarized beam with Gaussian statistical correlation; the generated partially coherent beam passes through the collimating lens 6 and the Gaussian amplitude filter 7 to obtain a collimated part A coherent Gaussian beam with a wavefront radius of curvature that is approximately infinite. The generated partially coherent Gaussian Shell mode beam is focused by a focusing lens 8 with a focal length of 25 cm. The gathered partially coherent Gaussian beam has a spherical wavefront phase, and the radius of the spherical wavefront phase is the parameter to be measure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com