Low-caffeine and high-GABA (Gamma Amino Acid Butyric Acid) health protection tea
A low-caffeine, health-care tea technology, applied in the direction of pre-extraction tea treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high caffeine content and poor flavor, and achieve the effects of increasing the content, reducing the odor of anaerobic treatment, and having a broad market prospect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
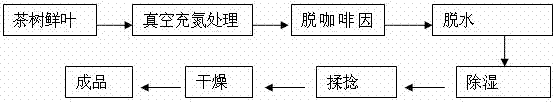
[0015] (1) Picking fresh leaves: picking fresh leaves of a tea tree with one bud and two leaves as raw materials, airing moderately to remove surface moisture, divided into A and B treatments, A is the control and directly enters step (3), and B enters step (2);
[0016] (2) Vacuum nitrogen filling treatment: Treat the fresh tea tree leaves of treatment B under vacuum nitrogen filling conditions for 3 hours respectively. Go to step (3);
[0017] (3) Gradient cooling in hot water, dipping, rinsing and decaffeination: Mix A, B, and treated tea leaves with hot water in a mass ratio of (1:15) to make the temperature of the mixed leaf water at 80°C for 150 seconds. Then quickly remove the tea leaves and soak them in a loose amount of warm water at 50°C for 15 minutes, then remove the fresh leaves and rinse them with cold water to complete the decaffeination step. Go to step (4);
[0018] (4) Dehydration and dehumidification: Fresh leaves are filtered through a vibrating tank and ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) Picking fresh leaves: picking fresh leaves of one-bud and two-leaf tea trees as raw materials, spreading them in the air to remove surface moisture, and proceeding to step (2);
[0028] (2) Vacuum nitrogen filling treatment: Treat the fresh tea tree leaves under vacuum nitrogen filling conditions for 8 hours respectively. It is divided into C and D treatments, C is the control and directly enters step (4), and D enters step (3);
[0029] (3) Gradient cooling in hot water, steeping, rinsing and decaffeination: Mix the tea leaves treated with D with hot water at a ratio of (1:15) evenly, keep the water temperature at 80°C for 300 seconds after mixing, and then quickly remove the tea leaves Immerse in loose warm water at 50°C and keep for 15 minutes, then remove the fresh leaves and rinse with cold water to complete the decaffeination step. Go to step (4);
[0030] (4) Dehydration and dehumidification: Fresh leaves are filtered through a vibrating tank and dehydrated...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Picking fresh leaves: picking fresh leaves of one-bud and two-leaf tea trees as raw materials, drying them properly to remove surface moisture, and dividing them into E and F treatments. F enters step (2);
[0040] (2) Vacuum nitrogen filling treatment: Treat the fresh leaves of the F-treated tea tree under vacuum nitrogen filling conditions for 5 hours respectively. Go to step (3);
[0041] (3) Gradient cooling in hot water, steeping, rinsing and decaffeination: Mix F-treated tea leaves with hot water in a ratio of (1:15) to keep the temperature of the leaf water at 80°C for 300 seconds, then quickly remove the tea leaves Immerse in loose warm water at 50°C and keep for 15 minutes, then remove the fresh leaves and rinse with cold water to complete the decaffeination step. Go to step (4);
[0042] (4) Dehydration and dehumidification: Fresh leaves are filtered through a vibrating tank and dehydrated by a centrifuge to remove water on the surface of the buds and l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com