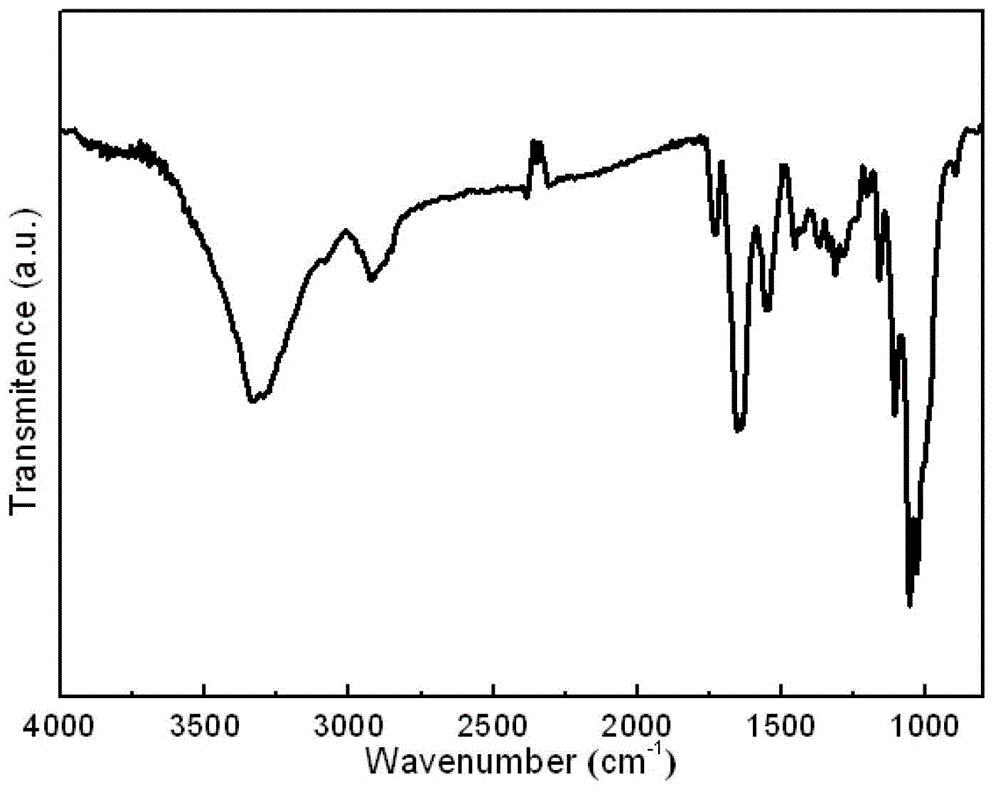
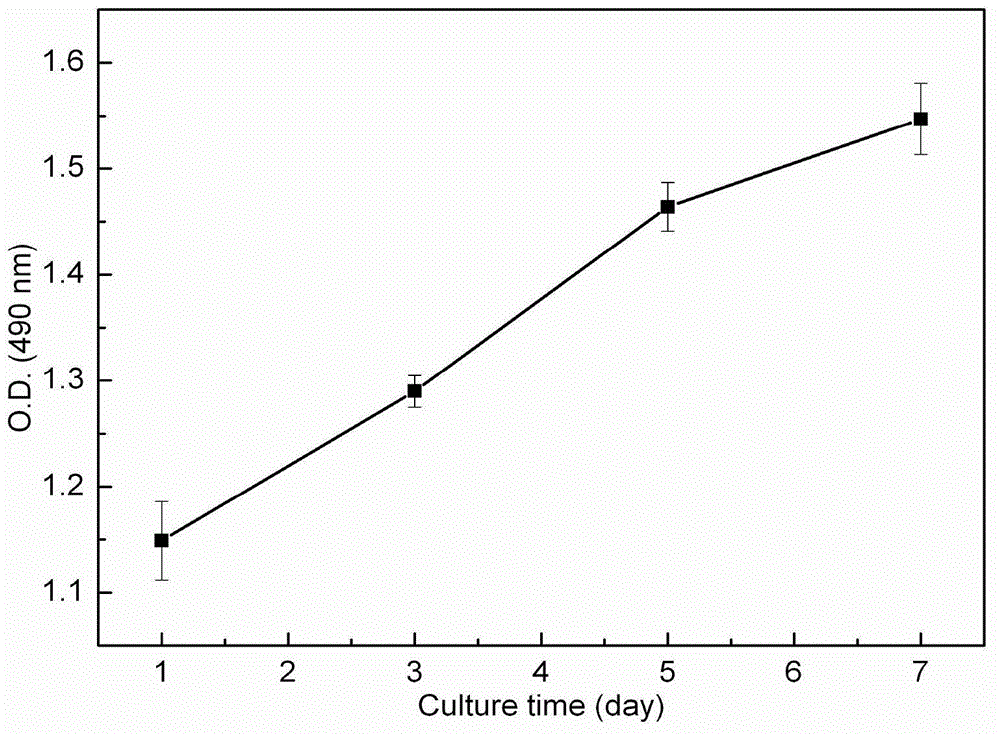
Bacterial cellulose/collagen composite material having biocompatibility and preparation method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and biocompatibility, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems that the biological activity cannot meet the wide application in the medical field, and achieve the effect of retaining the advantages of structure and performance, easy access to raw materials, and uniform synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
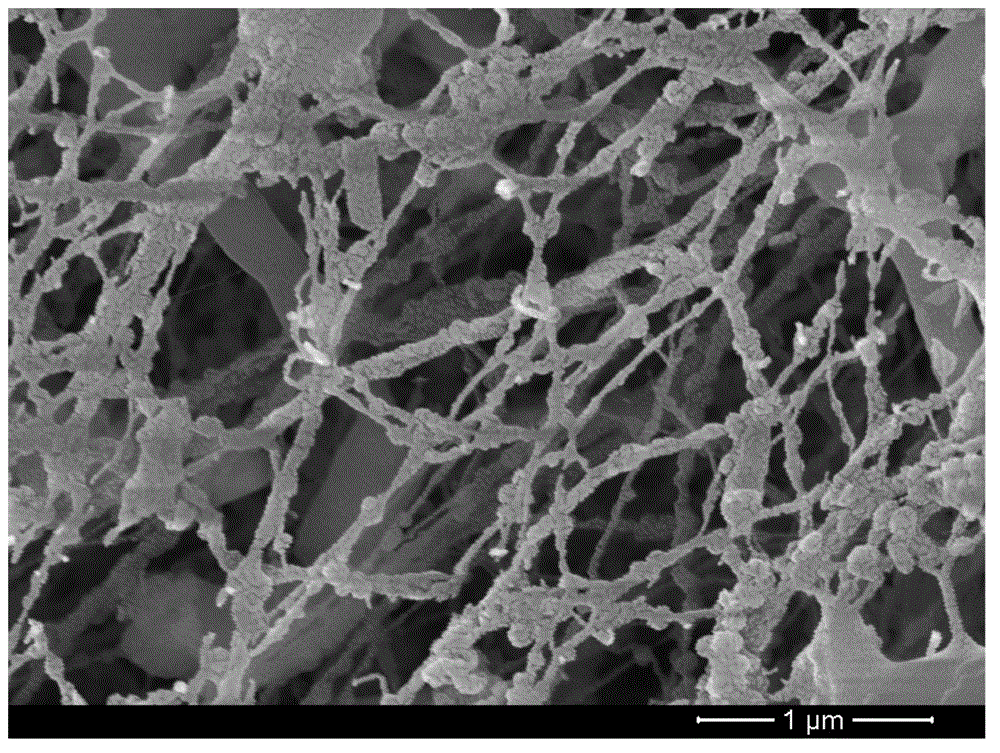
[0023] The bacterial cellulose secreting strain of the present invention is Acetobacter xylinum (Ax). Ax is Gram-negative, 0.6-0.8 μm wide, 1.0-4.0 μm long, light brown, round, exists in single, paired or chain form, opaque, with protruding colonies, rough surface, and is aerobic. It has been used as a model microorganism for basic and applied research on bacterial cellulose.
[0024] 1. Preparation of bacterial cellulose
[0025] Glucose 5.0% (w / v) (or mannitol 10% (w / v)), soybean peptone 0.9% (w / v), Na2HPO4·12H2O0.8% (w / v) and citric acid 0.5% (w / v) / v) Add to the beaker in sequence, adjust the pH value to the range of 5.5-7.0 with acetic acid, take out after high temperature sterilization at 115° C. for half an hour, and use it as a growth medium for Acetobacter xylinum.
[0026] Acetobacter xylinum strains were inoculated into the above-mentioned liquid medium, shaken sufficiently to make the bacterial liquid uniform, and cultured at a constant temperature of 28° C. for ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] 1. Preparation of bacterial cellulose
[0032] Glucose 5.0% (w / v) (or mannitol 10% (w / v)), soybean peptone 0.9% (w / v), Na2HPO4·12H2O0.8% (w / v) and citric acid 0.5% (w / v) / v) Add to the beaker in sequence, adjust the pH value to the range of 5.5-7.0 with acetic acid, take out after high temperature sterilization at 115° C. for half an hour, and use it as a growth medium for Acetobacter xylinum.
[0033] Acetobacter xylinum strains were inoculated into the above-mentioned liquid medium, shaken sufficiently to make the bacterial liquid uniform, and cultured at a constant temperature of 28° C. for 3 days to obtain bacterial cellulose. Alternately wash and boil with 1% sodium hydroxide solution and deionized water until milky white, and finally wash with deionized water until neutral. The bacterial cellulose obtained at this time is wet state bacterial cellulose.
[0034] 2. Preparation of bacterial cellulose / collagen composites
[0035] 100 ml of 1 g / L collagen (sigma, US...
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1. Preparation of bacterial cellulose
[0038] Glucose 5.0% (w / v) (or mannitol 10% (w / v)), soybean peptone 0.9% (w / v), Na2HPO4·12H2O0.8% (w / v) and citric acid 0.5% (w / v) / v) Add to the beaker in sequence, adjust the pH value to the range of 5.5-7.0 with acetic acid, take out after high temperature sterilization at 115° C. for half an hour, and use it as a growth medium for Acetobacter xylinum.
[0039]Acetobacter xylinum strains were inoculated into the above-mentioned liquid medium, shaken sufficiently to make the bacterial liquid uniform, and cultured at a constant temperature of 28° C. for 3 days to obtain bacterial cellulose. Alternately wash and boil with 1% sodium hydroxide solution and deionized water until milky white, and finally wash with deionized water until neutral. The bacterial cellulose obtained at this time is wet state bacterial cellulose.
[0040] 2. Preparation of bacterial cellulose / collagen composites
[0041] 100 ml of 3.5 g / L collagen (sigma, U...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com