Method for removing water in acrylic acid aqueous solution
An acrylic acid and aqueous solution technology, applied in the separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of low dehydration rate, high recovery cost, easy polymerization of acrylic acid, etc., and achieve high dehydration rate, efficient water removal, heating The effect of low cooling energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
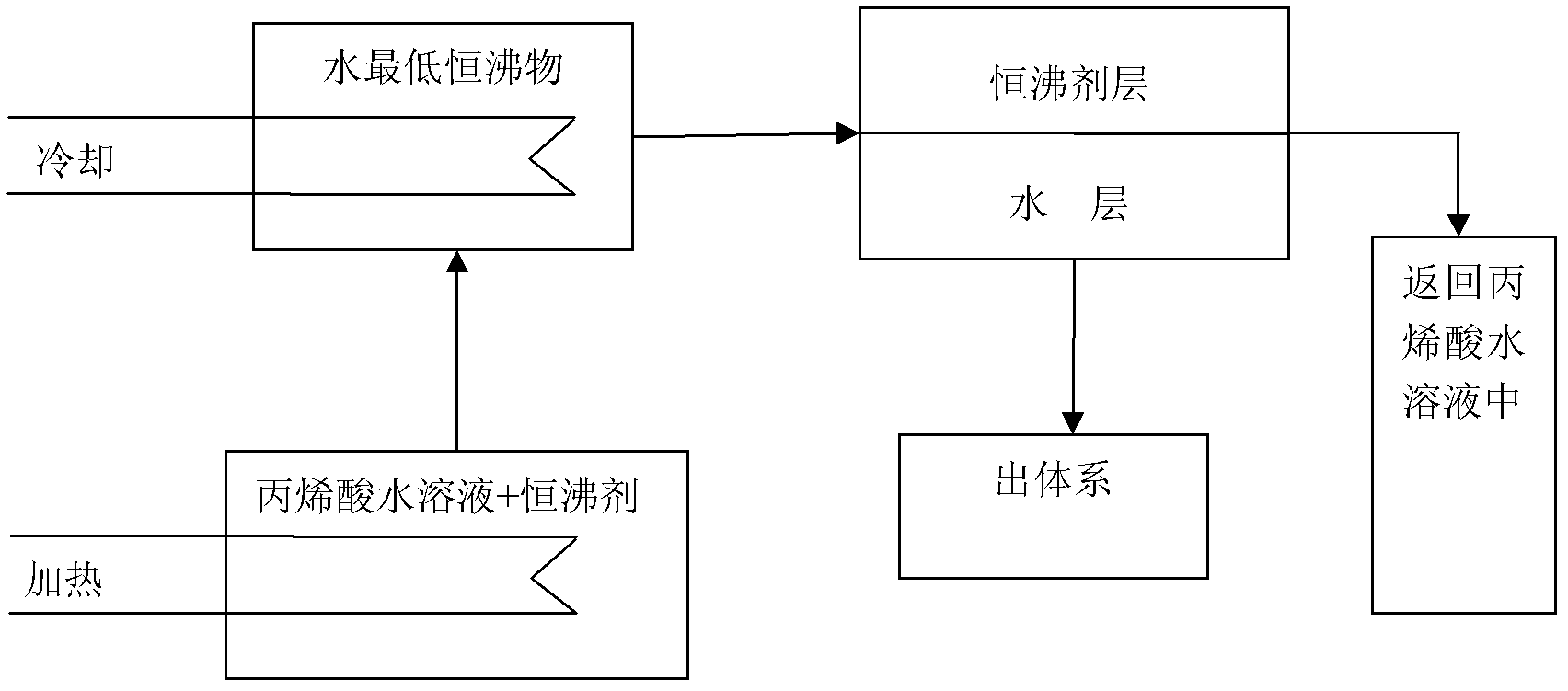
[0019] An aqueous solution of acrylic acid containing about 56.88 molar percent acrylic acid, 41.91 molar percent water and 1.21 molar percent acetic acid. A single m-xylene is used as the constant boiling agent, and the mass of the constant boiling agent is 20 times the total mass of the water. Under the vacuum degree of 0.085MPa, the system is heated and evaporated by steam heating. When the temperature of the tower kettle reaches 55°C, The minimum azeotrope of m-xylene and water comes out of the system, which can reduce the moisture content in the acrylic acid aqueous solution to below 0.1%. The minimum azeotrope vapor between m-xylene and water is cooled by water to form a liquid phase, and the temperature at the top of the tower reaches 53°C, which is the constant boiling point under this pressure. The effluent from the condensing cooler enters the stratifier, and the condensate is divided into two layers. , water is in the lower layer, m-xylene is in the upper layer, the...
Embodiment 2
[0021] An aqueous solution of acrylic acid containing about 56.88 molar percent acrylic acid, 41.91 molar percent water and 1.21 molar percent acetic acid. A single m-xylene is used as the constant boiling agent, and the ratio of the mass of constant boiling agent to the total mass of water is 1:1. Under the vacuum degree of 0.085MPa, the system is heated and evaporated by steam heating, and the temperature in the tower kettle reaches 55 At ℃, the minimum azeotrope of m-xylene and water evaporates from the system, which can reduce the water content in the acrylic acid aqueous solution to below 0.1%. The lowest azeotrope vapor between m-xylene and water is cooled by water to form a liquid phase, and the temperature at the top of the tower reaches 53°C, which is the azeotropic point under this pressure. The effluent from the condensing cooler enters the stratifier, and the condensate is divided into two layers , water is in the lower layer, m-xylene is in the upper layer, the wa...
Embodiment 3
[0023] An aqueous solution of acrylic acid containing about 56.88 molar percent acrylic acid, 41.91 molar percent water and 1.21 molar percent acetic acid. A single m-xylene is used as the constant boiling agent, and the ratio of the mass of the constant boiling agent to the total water is 1:20. Under the vacuum degree of 0.085MPa, the system is heated and evaporated by steam heating, and the temperature in the tower kettle reaches 55°C When the minimum azeotrope of m-xylene and water comes out of the system, the moisture content in the acrylic acid aqueous solution can be reduced to below 0.1%. The lowest azeotrope vapor of m-xylene and water is cooled by water to form a liquid phase, which is divided into two layers, water is in the lower layer, m-xylene is in the upper layer, the water in the lower layer is extracted, and the upper layer m-xylene is returned to the original acrylic acid aqueous solution. Continue to use steam heating to evaporate the lowest azeotrope, and f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com