Method for manufacturing high-dispersion ultrafine molybdenum-based powder
A powder and molybdenum-based technology, which is applied in the field of low-cost preparation of highly dispersed ultrafine molybdenum-based powders, can solve the problems of high difficulty of highly dispersed ultrafine molybdenum-based powders, and achieve the effects of low cost, small particle size and high density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Embodiment 1: Mo-4wt.%La 2 O 3 Preparation of composite powder
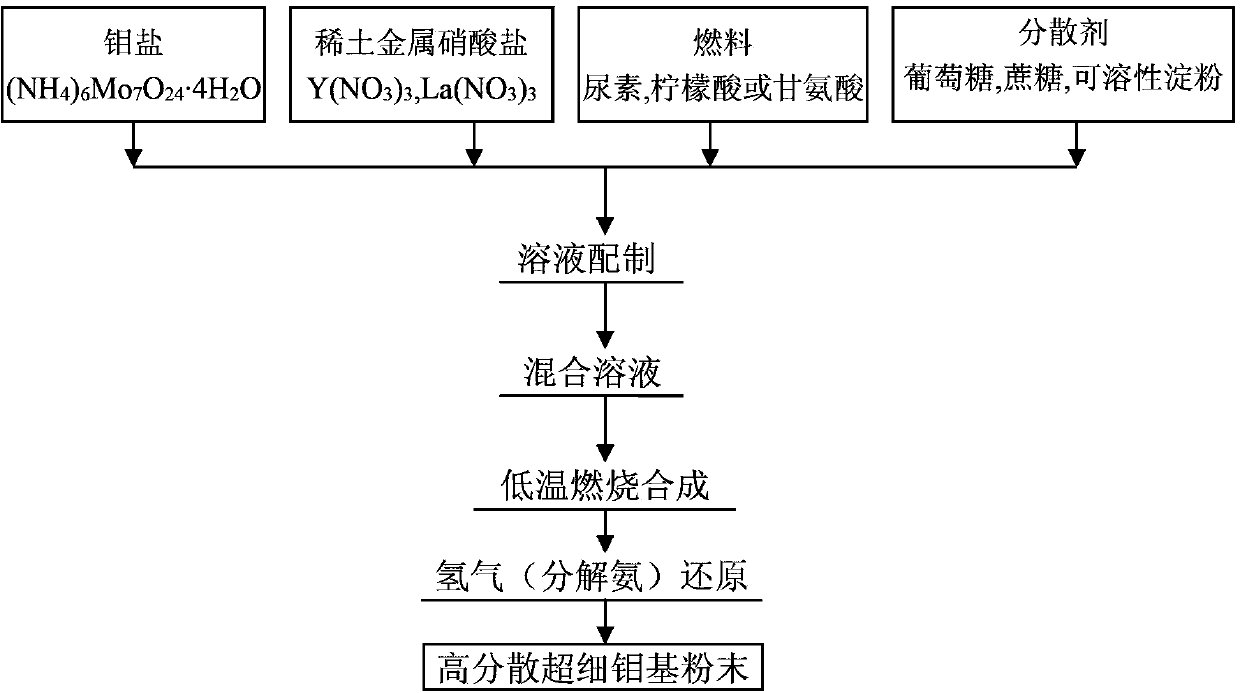
[0016] Weigh 0.024mol of (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O, 0.00412mol of La(NO 3 ) 3· 6H 2 O, 0.48mol of HNO 3 , 0.1mol of CH 4 N 2 O and 0.1 mol of C 6 h 12 o 6 ·H 2 O, dissolved in 100ml deionized water, stirred evenly in a 1000ml beaker to obtain a mixed solution. The mixed solution is heated in a temperature-controlled furnace to volatilize the aqueous solution. As the reaction proceeds, the heat released will cause pyrolysis and carbonization of the dispersant, and the target element will be converted into extremely fine nano-sized oxide particles and molybdenum oxide particles, thereby obtaining Mo-rare earth oxide composite powder particles. The calcined precursor powder is reduced in hydrogen: the reduction temperature is 450° C., and the temperature is kept for 1 hour. After reduction, Mo-4wt.%La is obtained 2 o 3 Composite powder.
Embodiment 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: Mo-25wt.%Y 2 O 3 Preparation of composite powder
[0018] Weigh 0.024mol of (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O, 0.0476mol of Y (NO 3 ) 3· 6H 2 O, 0.48mol of HNO 3 , 0.17mol of CH 4 N 2 O and 0.15mol of C 6 h 12 o 6 ·H 2 O, dissolved in 100ml deionized water, stirred evenly in a 1000ml beaker to obtain a mixed solution. The mixed solution is heated in a temperature-controlled furnace to volatilize the aqueous solution. As the reaction proceeds, the heat released will cause pyrolysis and carbonization of the dispersant, and the target element will be converted into extremely fine nano-sized oxide particles and molybdenum oxide particles, thereby obtaining Mo-rare earth oxide composite powder particles. The calcined precursor powder is reduced in an atmosphere of decomposed ammonia: the reduction temperature is 550° C., and the temperature is kept for 1.5 hours. After reduction, Mo-25wt.%Y is obtained 2 o 3 Composite powder.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: Mo-8wt.%La 2 O 3 -22wt.%Y 2 O 3 Preparation of composite powder
[0020] Weigh 0.024mol of (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O, 0.0086mol of La(NO 3 ) 3· 6H 2 O, 0.040 mol of Y (NO 3 ) 3· 6H 2 O, 0.72mol of HNO 3 , 0.12mol of CH 4 N 2 O and 0.17 mol of C 6 h 12 o 6 ·H 2 O, dissolved in 100ml deionized water, stirred evenly in a 1000ml beaker to obtain a mixed solution. The mixed solution is heated in a temperature-controlled furnace to volatilize the aqueous solution. As the reaction proceeds, the heat released will cause pyrolysis and carbonization of the dispersant, and the target element will be converted into extremely fine nano-sized oxide particles and molybdenum oxide particles, thereby obtaining Mo-rare earth oxide composite powder particles. The calcined precursor powder is reduced in an atmosphere of decomposed ammonia: the reduction temperature is 650° C., and the temperature is kept for 2 hours. After reduction, Mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com