Method and device for resource distribution
A resource allocation and resource technology, applied in the field of resource allocation of wireless resources, can solve the problems of large amount of SDU data, easy damage to SDU integrity, affecting the overall performance of LTE, etc., to protect integrity, reduce overhead and be retransmitted possibility, the effect of reducing overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] refer to figure 1 , shows a flowchart of steps of a resource allocation method according to Embodiment 1 of the present application.
[0030] The resource allocation method in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0031] Step S102: After obtaining the uplink grant, determine whether the variable Bj of each RB is greater than 0.
[0032] Bj is used to identify the length of radio resources that need to be allocated to the RB. Bj is the product of the RB's PBR (Prioritised Bit Rate, guaranteed rate) and TTI (Transmission Time Interval, transmission time interval) when the RB is not authorized, indicating the data length that needs to be allocated to the RB in the first round during the current scheduling. Bj will gradually grow over time. After allocating resources for RB, Bj will be updated, and the resource value allocated for this RB will be subtracted from the original Bj, and Bj can be a negative value.
[0033] Step S104: For each RB with Bj greater th...
Embodiment 2
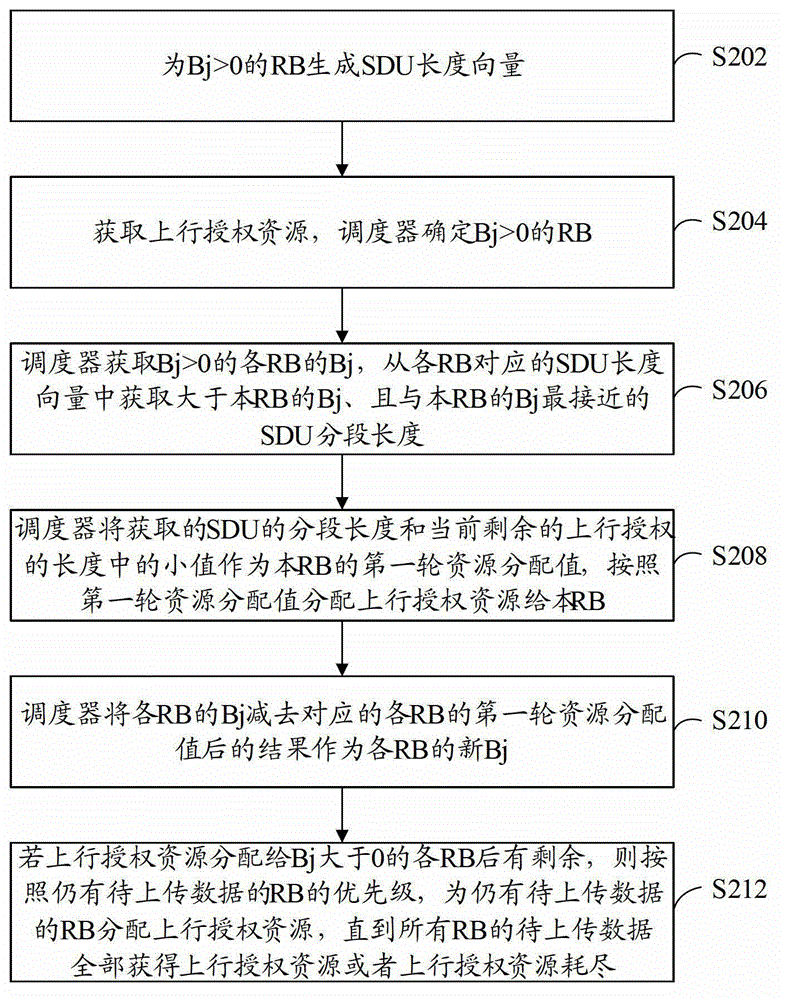
[0041] refer to figure 2 , shows a flowchart of steps of a resource allocation method according to Embodiment 2 of the present application.
[0042] The resource allocation scheme in this embodiment is based on the basic framework of two rounds of scheduling. The first round of scheduling is aimed at the PBR result Bj. For RBs with Bj>0, the ULgrant resources are allocated according to the priority order of the RBs according to the Bj result and the SDU length vector. For each RB; the specific scheduling scheme can refer to the above figure 1 Description of the examples shown. If each channel is satisfied before the ULgrant resources are exhausted, the second round of scheduling can be entered; the second round of scheduling will allocate the remaining ULgrant resources to the RBs that still have data to be sent in order according to the priority order of the RBs .
[0043] The resource allocation method in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0044] Step S202:...
Embodiment 3
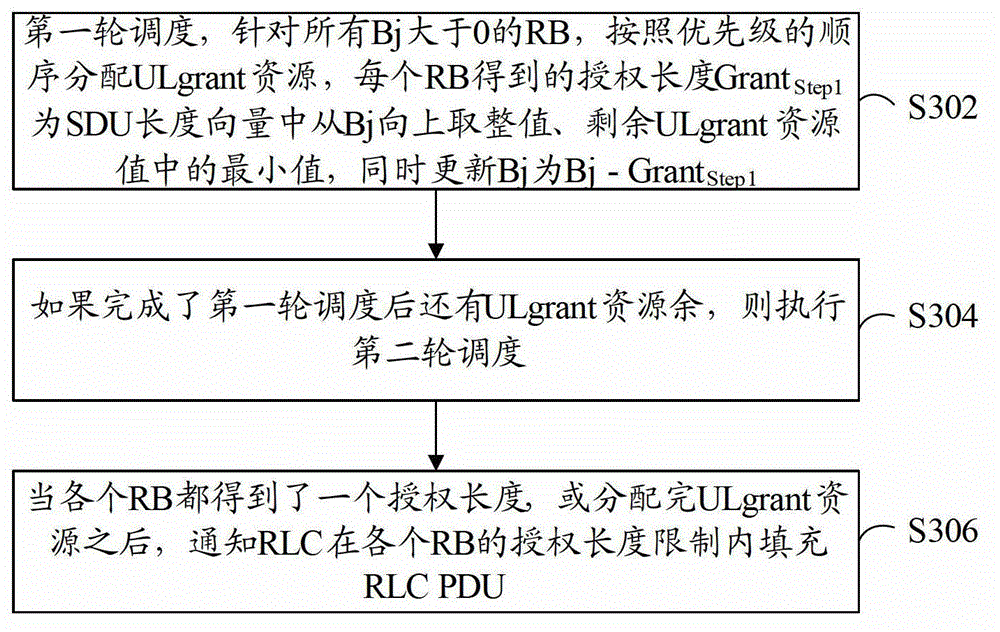
[0066] refer to image 3 , shows a flowchart of steps of a resource allocation method according to Embodiment 3 of the present application.
[0067] This embodiment still uses the basic framework based on two-round scheduling, and introduces the resource allocation method of this embodiment from the level of two-round scheduling. It should be explained first that whether two-round scheduling is required can be determined in the following way:
[0068] Th Step 1 = ∑ n = 0 N - 1 min ( L Total 1 ( n ) , Bj ( n ) ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com