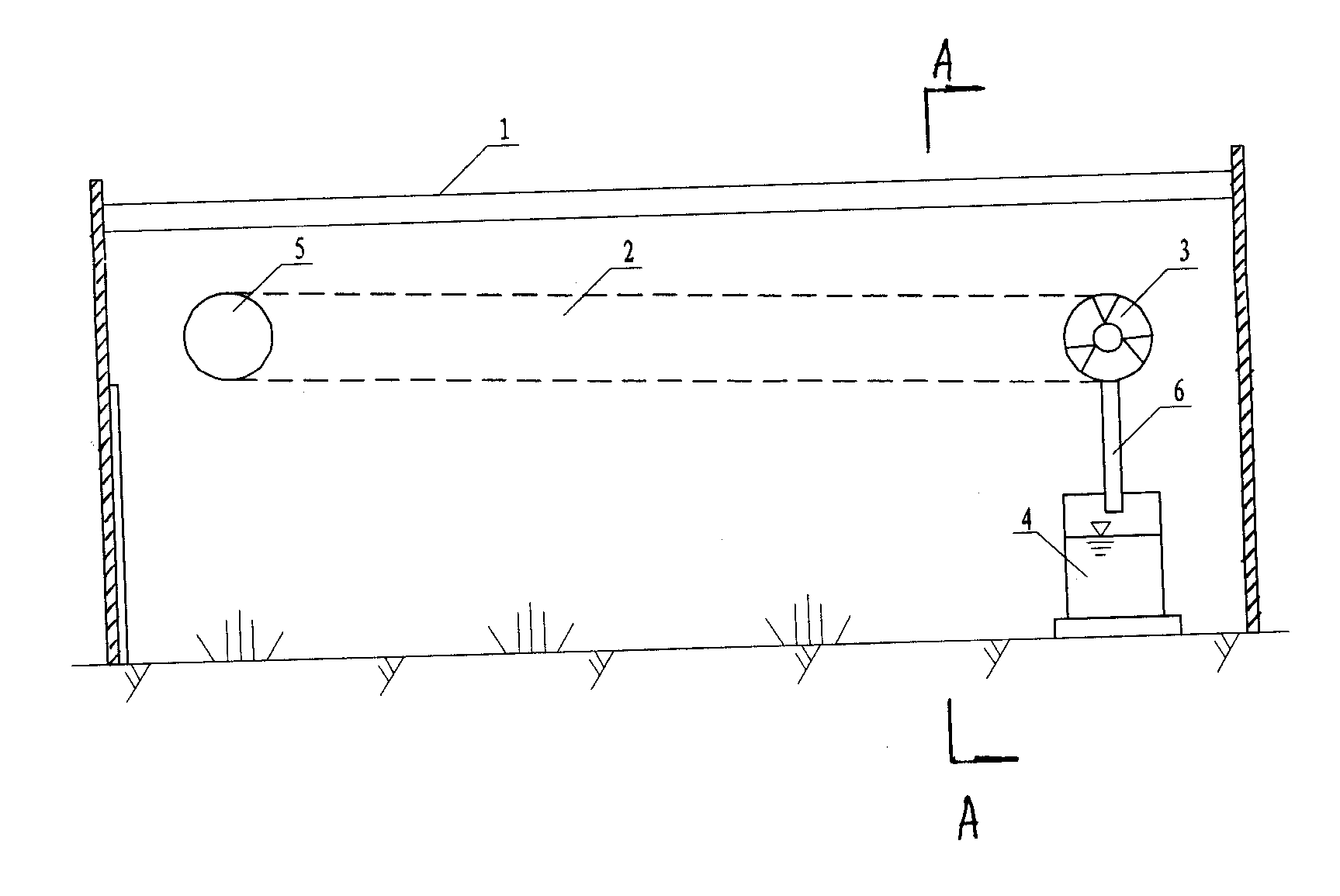
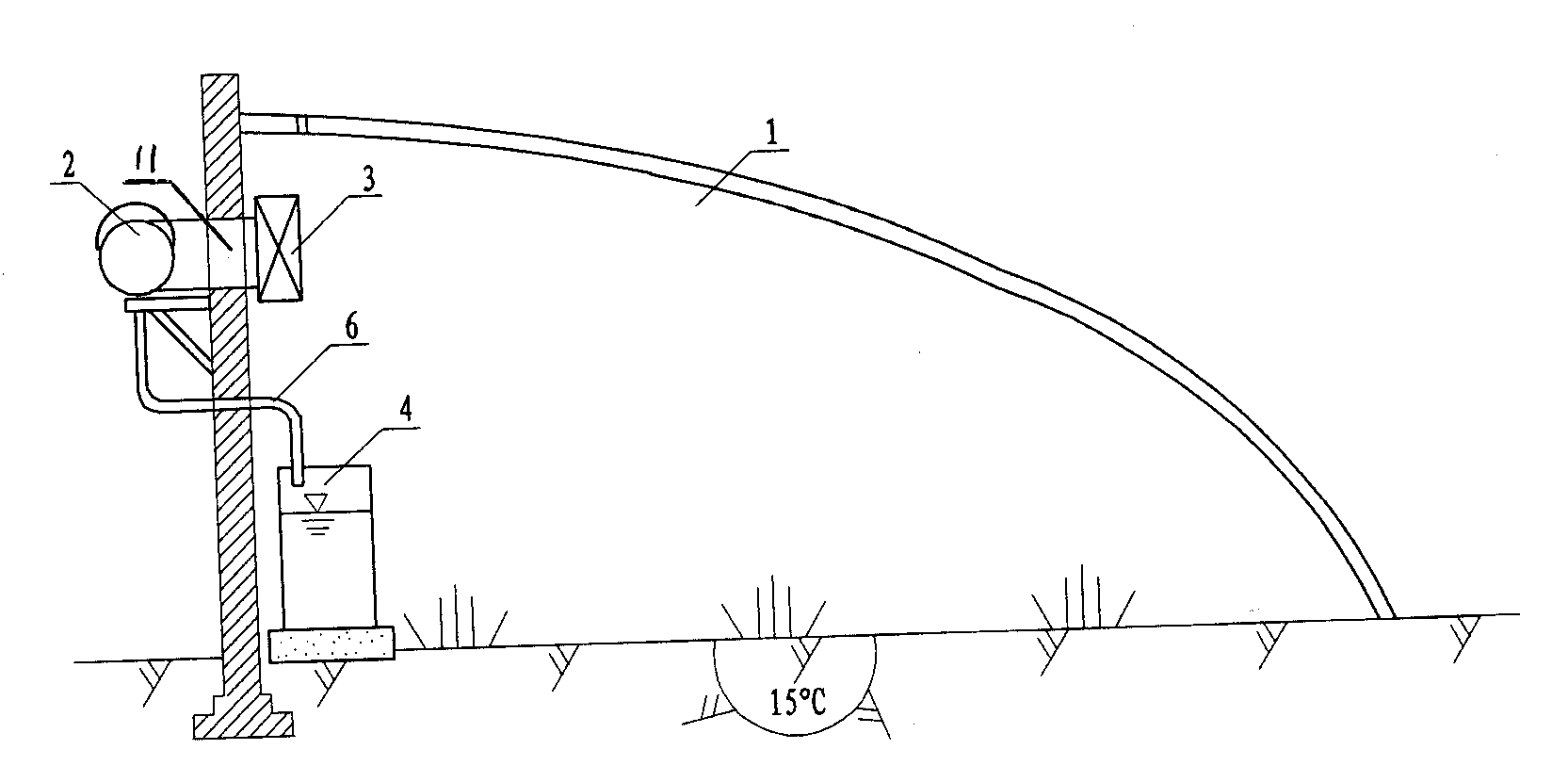
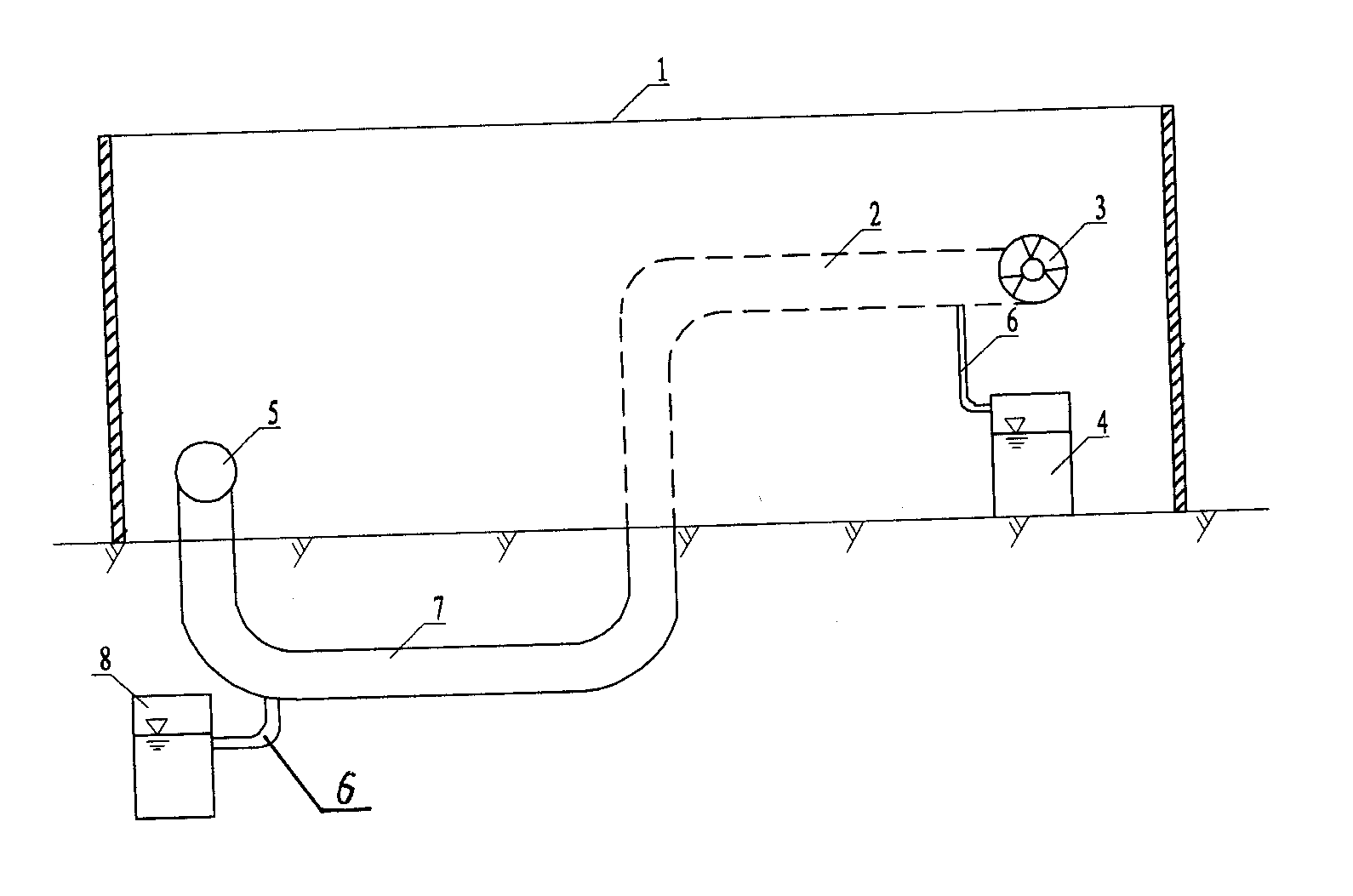
[0002] As a modern agricultural facility, greenhouses are increasingly appearing in people's lives, especially the development of greenhouse vegetables and greenhouse melons and fruits, which has greatly enriched people's lives and played a role in improving and improving people's lives. The effect is becoming more and more important, and there are more and more varieties of planting in greenhouses.
Greenhouse seedlings, peppers, greenhouse tomatoes, grapes, strawberries, greenhouse watermelons, etc., involve almost all vegetables and melon and fruit varieties. The growth of greenhouses Large-scale development has become a development trend of modern
agriculture.
Greenhouse vegetables in Turpan, Xinjiang first started in 2002. Because it is adjacent to Urumqi City, vegetable sales have a certain
consumer market, coupled with the inherent advantages of sufficient sunshine in the area, short Within a few years, the number of vegetable greenhouses in Turpan has grown to more than 40,000, and it has gradually become the source of vegetable supply for Urumqi and surrounding cities. The temperature,
humidity and light conditions in the greenhouse are directly related to the growth and development of crops. Reasonably adjust the temperature,
humidity and light conditions in the greenhouse to form a small environment in the greenhouse that is conducive to the growth and development of vegetables. , high-quality, high-efficiency important link, greenhouse temperature and humidity control is extremely critical, the existing humidity control method is mainly through indoor and outdoor ventilation to reduce humidity, a little
carelessness may cause the humidity in the greenhouse to be high, As a result, the
slow growth of crops is caused, and the spread of diseases and
insect pests is induced, which is not conducive to the growth and development of vegetables. The contradictory relationship is very unfavorable for the growth and development of crops in the shed.
Water resources in
arid areas are very precious. Water is the most fundamental
constraint factor for the development of
agriculture. The water needed by the crops in the greenhouse is completely guaranteed by artificial irrigation measures. Therefore ,
water saving has generally been paid attention to by people, and more advanced sprinkler irrigation and
drip irrigation have been gradually adopted for irrigation, and some greenhouses have also adopted more advanced irrigation methods. However, the existing efficient water-saving irrigation methods can only reduce very limited seepage Leakage loss, the
evaporation in the field of the greenhouse and the
transpiration of the crops still need to be discharged outside the greenhouse through ventilation. Ventilation and dehumidification not only make the
water vapor in the greenhouse ineffectively discharged into the outside, but also consume manpower and increase labor intensity, which is different from the existing vegetable field. Compared with orchards, the greenhouse is a relatively closed production facility. It is possible to directly condense and recycle the
water vapor in the greenhouse through the existing condensation technology, so as to achieve dehumidification in the greenhouse and reuse
water resources, but the cost is very expensive. The reason is that the
latent heat of
vaporization of
water vapor is large. Using the most advanced
refrigeration machinery with an energy efficiency ratio of 5 times, condensing 1 cubic meter of water also needs to consume about 133.3kW·h of
electricity. Therefore, using a relatively closed greenhouse characteristics, the method of directly condensing water vapor in the air and recycling
water resources is almost impossible to apply to production practice
The
water consumption of temperature-controlled greenhouses in
arid areas is relatively large. According to the actual measurement data of vegetable greenhouses in Turpan, the annual
water consumption is as high as 450-600 cubic meters per mu. About 25% of this water seeps into the ground, and the remaining 75% comes from the ground. The
crop transpiration and land
evaporation in the greenhouse enter the air in the greenhouse. The temperature-controlled greenhouse is a relatively airtight production facility. The average daily water vapor volume of a greenhouse with an area of one mu is as high as 1.2 to 1.6 cubic meters.
Evaporation and
transpiration of crops increase the humidity of the air. If there is no ventilation, the
relative humidity of the air in the shed can reach more than 90%, or even 100%, and the transpiration of
plant leaves will be inhibited, which is not conducive to the growth and development of plants. It also causes germs to multiply, and diseases are popular, which affects the quality and yield of crops. Therefore, adjusting the humidity in the shed is an important measure to prevent and
control diseases and promote the growth and development of crops. Ventilate in time to
discharge the water vapor in the greenhouse to the outside of the greenhouse, but this method will affect the temperature in the greenhouse, which is not conducive to the growth of crops. The water vapor in the greenhouse can be directly recycled and reused through the existing condensation technology to control the humidity in the greenhouse , is technically possible, but very expensive
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More