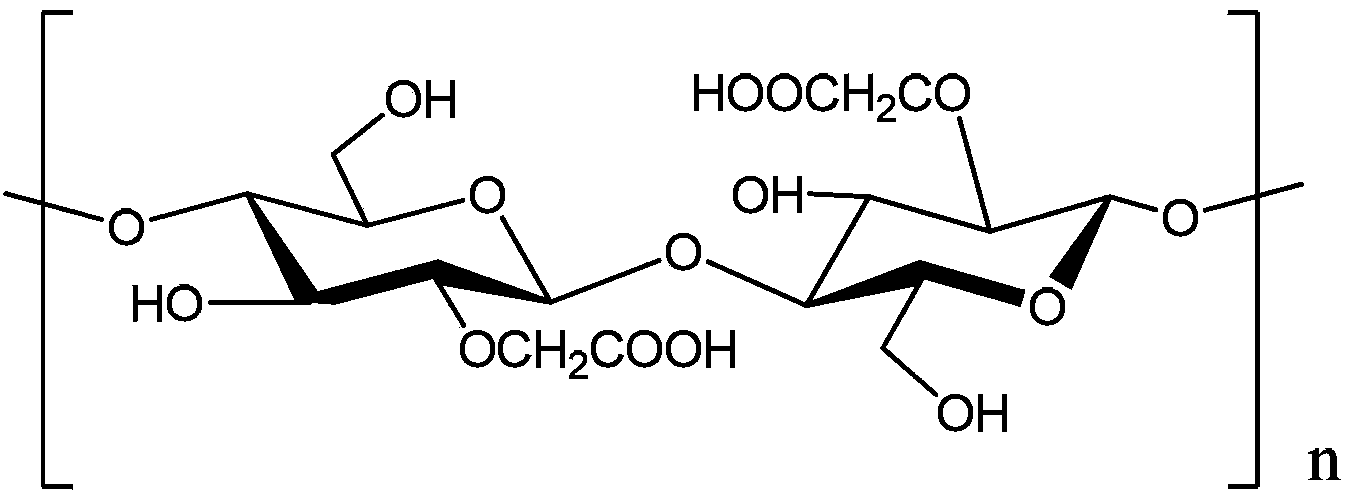
Method for preparing porous compound type high permeability absorption hemostasis coating with modified nano-crystalline cellulose
A technology of nanocellulose and hemostatic dressing, applied in the field of biomedical materials or medical composite materials, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory and poor wound healing promotion effect, bacterial cellulose has no antibacterial and hemostatic properties, etc., and achieve excellent water absorption and water retention. Performance, Proliferation Promotion, Excellent Biocompatibility and Cell Affinity Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Step 1: Take the bacterial cellulose membrane 10×20 cm prepared by Acetobacter xylinum and wash it with deionized water several times to remove the culture medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane. Then soak the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, ultrasonically treat it in a cell pulverizer for 15 minutes, and then put it in a water bath at 90°C for 60 minutes to remove the bacteria and residual medium left in the nanofiber network. Run up and milky white translucent. Then rinse with deionized water several times, and measure the pH value with an acidity meter, which is about 7.0 to 8.0, to obtain a purified bacterial cellulose membrane for removing endotoxin;
[0039] Step 2. Soak the bacterial cellulose membrane pretreated in step 1 in 0.01mol / L NaOH solution, place it under a high-speed disperser and disperse it into fine fibers of 800nm to 400μm, so that the fibers are semi-coagulated in the aqueous solution colloidal state, and then 1000r / min low-sp...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Step 1: Take the bacterial cellulose membrane 10×20 cm prepared by Acetobacter xylinum and wash it with deionized water several times to remove the culture medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane. Then soak the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, ultrasonically treat it in a cell pulverizer for 20 minutes, and then bathe in water at 100°C for 60 minutes to remove the bacteria and residual medium left in the nanofiber network. Run up and milky white translucent. Then rinse with deionized water several times, and measure the pH value with an acidity meter, which is about 7.0 to 8.0, to obtain a purified bacterial cellulose membrane for removing endotoxin;
[0051] Step 2. Soak the bacterial cellulose membrane pretreated in step 1 in 0.05mol / L NaOH solution, place it in a high-speed disperser and disperse it into fine fibers of 800nm to 400μm, so that the fibers are semi-coagulated in the aqueous solution Colloidal state, and then 1200r / min low-speed centri...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Step 1: Take the bacterial cellulose membrane 10×20 cm prepared by Acetobacter xylinum and wash it with deionized water several times to remove the culture medium and impurities on the surface of the membrane. Then soak the membrane in 0.1mol / L NaOH solution, ultrasonically treat it in a cell pulverizer for 18 minutes, and then bathe in water at 90°C for 60 minutes to remove the bacteria and residual medium left in the nanofiber network. Run up and milky white translucent. Then rinse with deionized water several times, and measure the pH value with an acidity meter, which is about 7.0 to 8.0, to obtain a purified bacterial cellulose membrane for removing endotoxin;
[0063] Step 2. Soak the pretreated bacterial cellulose membrane in step 1 in 0.02mol / L NaOH solution, and place it under a high-speed disperser to disperse into fine fibers of 800nm to 400μm, so that the fibers are semi-coagulated in the aqueous solution. Colloidal state, and then 900r / min low-speed cent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com