Preparation method of modified zero-valence nano-iron suitable for underground water treatment
A zero-valent nano-iron and groundwater pollution technology, applied in the field of nano-materials, can solve the problems of unsuitable zero-valent nano-iron, high price, and large dosage, and achieve the effect of saving input, cheap price, and low dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
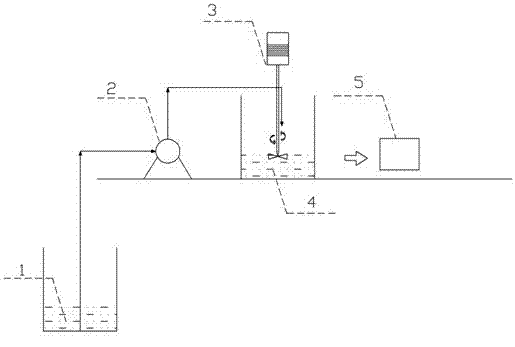
[0027] with FeCl 3 .6H 2 O and deionized water to prepare FeCl with a concentration of 0.045 mol / L 3 solution, stirred at 600 rpm for 20 min; then with NaBH 4 Prepare the same FeCl with deionized water 3 An equal volume of NaBH with a concentration of 0.25 mo / L 4 solution, pump FeCl at a rate of 40 mL / min with a constant flow pump 3 solution; after adding NaBH 4 At the same time as the solution, use an electric stirrer to stir the mixed solution at a speed of 600 rpm; 4 The solution is all pumped into FeCl 3 After solution, continue stirring for 15 min to make NaBH 4 with FeCl 3 The mixed reaction is complete; let it stand for 20 minutes, and use double-layer medium-speed filter paper to vacuum filter to obtain zero-valent nano-iron with a moisture content of 73.28%. Nitrogen, store below 5 ℃ for future use. Its processes and equipment such as figure 1 Shown, among them, 1 is NaBH 4 Solution, 2 is peristaltic pump, 3 is mixer, 4 is FeCl 3 solution, 5 is a vacuum f...
Embodiment 2
[0032] with FeCl 3 .6H 2 O and deionized water to prepare FeCl with a concentration of 0.045 mol / L 3 solution, stirred at 700 rpm for 10 min; then with NaBH 4 Prepare the same FeCl with deionized water 3 An equal volume of NaBH with a concentration of 0.25 mo / L 4 solution, pump FeCl at a rate of 60 mL / min with a constant flow pump 3 solution; after adding NaBH 4 At the same time as the solution, use an electric stirrer to stir the mixed solution at a speed of 700 rpm; 4 The solution is all pumped into FeCl 3 After solution, continue stirring for 15 min to make NaBH 4 with FeCl 3The mixed reaction is complete; let it stand for 15 minutes, and use double-layer medium-speed filter paper to vacuum filter to obtain zero-valent nano-iron with a moisture content of 65.43%. Nitrogen, store below 5 ℃ for future use. Its technique and equipment are with embodiment 1.
[0033] Then, sodium polystyrene sulfonate and the above-prepared zero-valent nano-iron were dissolved in deo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com